Archive for the ‘Romans’ Category
Below: The picture of earth from the Moon, July 1969.

On 20 July 1969 human beings stepped onto the surface of the moon, in one giant leap for mankind.
A Giant Leap of Imagination:
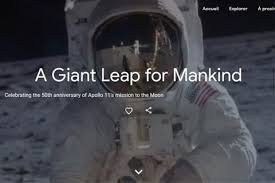 I was just twelve years old when the Apollo 11 lunar module landed on the moon. I remember the event very clearly, being allowed to stay up to watch on our small, black and white television. The whole event was in black and white for everyone on earth, as colour television transmissions did not begin until the following year when we went round to a friend’s house to watch the Football World Cup via satellite from Mexico.
I was just twelve years old when the Apollo 11 lunar module landed on the moon. I remember the event very clearly, being allowed to stay up to watch on our small, black and white television. The whole event was in black and white for everyone on earth, as colour television transmissions did not begin until the following year when we went round to a friend’s house to watch the Football World Cup via satellite from Mexico.
 Looking back over those fifty years, it’s interesting to see how much of popular culture on both sides of the Atlantic has been influenced by that event, and the subsequent two Apollo landings of the seventies. Before 1969, most classical compositions and popular song lyrics referenced the moon and the stars in the romantic terms of ‘moonlight’ and ‘Stardust’, even Sinatra’s ‘Fly me to the Moon’. These metaphors continued afterwards, but they were joined by a growing genre of songs about ‘rocketmen’ and space and time exploration which had begun in the early sixties with TV series like ‘Fireball XL-5’, ‘Dr Who’ and ‘Star Trek’.
Looking back over those fifty years, it’s interesting to see how much of popular culture on both sides of the Atlantic has been influenced by that event, and the subsequent two Apollo landings of the seventies. Before 1969, most classical compositions and popular song lyrics referenced the moon and the stars in the romantic terms of ‘moonlight’ and ‘Stardust’, even Sinatra’s ‘Fly me to the Moon’. These metaphors continued afterwards, but they were joined by a growing genre of songs about ‘rocketmen’ and space and time exploration which had begun in the early sixties with TV series like ‘Fireball XL-5’, ‘Dr Who’ and ‘Star Trek’.
Gradually, Science Fiction literature and films took us beyond cartoonish ‘superhero’ representations of space and HG Wells’ early novels until, by the time I went to University, ‘Star Wars’ had literally exploded onto the big screens and was taking us truly into a new dimension, at least in our imaginations.
The Dawning of a New Age?
The ‘Age of Aquarius’ had begun on earth as well, with rock musicals, themed albums and concerts, and ‘mushrooming’ festivals under the stars providing the soundtrack and backdrop to the broadening of minds and horizons. Those ‘in authority’ were not at all tolerant of the means used by some to help broaden these horizons and, in those days, these mass encampments were not always seen as welcome additions to the rural landscape and soundscape. Many evangelical Christians were suspicious of the ‘New Age’ mysticism embraced by the Beatles, the outrageous costumes and make-up of David Bowie and Elton John, and the heavy rock music of a series of bands who made use of provocative satanic titles and emblems, like ‘Black Sabbath’. But some, like Larry Norman and ‘The Sheep’, decided to produce their own parallel ‘Christian Rock’ culture. The first Christian ‘Arts’ Greenbelt Festival was held on a pig farm just outside the village of Charsfield near Woodbridge, Suffolk over the August 1974 bank holiday weekend.
 My Christian friends and I, having already seen the musical Lonesome Stone in Birmingham, made the trek across the country to discover more of this genre. Local fears concerning the festival in the weeks running up to it proved to be unfounded, but the festival didn’t return to the venue. We, on the other hand, were excited and enthused by what we saw and heard.
My Christian friends and I, having already seen the musical Lonesome Stone in Birmingham, made the trek across the country to discover more of this genre. Local fears concerning the festival in the weeks running up to it proved to be unfounded, but the festival didn’t return to the venue. We, on the other hand, were excited and enthused by what we saw and heard.
The ‘mantra’ we repeated when we got home to our churches was William Booth’s question, voiced by Larry, Why should the devil get all the best tunes? We wrote and performed our own rock musical, James (a dramatisation of the Book of James) touring it around the Baptist churches in west Birmingham, a different form of evangelism from that of Mary Whitehouse and her ‘Festival of Light’. One of our favourite songs was Alpha and Omega:
He’s the Alpha and Omega,
The Beginning and the End,
The first and last,
Our eternal friend.
Another of their ‘millenarian’ songs, Multitudes, also emphasised the importance of the Day of the Lord, which seemed to chime in well with the ‘nuclear age’ and the Eve of Destruction songs of Bob Dylan and Barry McGuire, among others.
Sun, Moon and Stars in their Courses Above:

But though we began to sing new songs, much of this revivalist spirit still owed its origins and source of inspiration to the 1954 North London crusade of Billy Graham, and the hymns associated with it. Great is Thy Faithfulness, written in the USA in the early 1920s, really owes its popularity in Britain to its use by the Billy Graham Crusade (pictured right).
It took some time to for it to find its way into the hymnbooks in Britain, but it now stands high in the ‘hit parade’, ranking fourth in the 2002 BBC Songs of Praise poll. It has much in common with our other hymn, How Great Thou Art, which was the most popular and probably still is, thanks to recent recordings. Both hail from the early part of the twentieth century and both display a strong emphasis on creation and nature, which have become dominating discourses by the early part of the twenty-first century.
Great is Thy Faithfulness is the work of Thomas Chisholm (1866-1960), a devout Methodist from Kentucky who worked successively as a journalist, a school teacher and a life-insurance agent before becoming ordained. He wrote the verses in 1923 and later reflected that there were no special circumstances surrounding their writing and that he was simply expressing his impressions of God’s faithfulness as recounted in the Bible. Yet, as Tom White has written recently in his book on Paul, our ‘justification’ as Christians is not the result of our own ‘little faith’ so much as the great faithfulness of God as revealed in his son, Jesus Christ. Chisholm sent his poem, along with several other poems, to his friend and collaborator William Runyan (1870-1957), a fellow Methodist who achieved considerable fame in the USA as a composer of sacred music and gospel songs.
 Its early popularity in the USA was partly the result of its promotion by Dr Will Houghton, president of the Moody Bible Institute in Chicago (pictured right), who used it frequently both in the services he took and on his radio broadcasts on WMBI. George Beverly Shea, first as a singer on the station’s early morning programme, Hymns from the Chapel, and then as the lead singer at Graham’s rallies, also helped to popularise the hymn across America.
Its early popularity in the USA was partly the result of its promotion by Dr Will Houghton, president of the Moody Bible Institute in Chicago (pictured right), who used it frequently both in the services he took and on his radio broadcasts on WMBI. George Beverly Shea, first as a singer on the station’s early morning programme, Hymns from the Chapel, and then as the lead singer at Graham’s rallies, also helped to popularise the hymn across America.
The opening verse is based directly on scriptural affirmations about God. Lamentations 3.22 and 33 proclaim that His compassions fail not; they are new every morning: great is thy faithfulness, and James 1.17 declares that every good gift and every perfect gift is from above, and cometh down from the Father of lights, with whom there is no variableness, neither shadow of turning:
Great is thy faithfulness, O God my Father,
there is no shadow of turning with thee;
thou changest not, thy compassions they fail not,
as thou hast been, thou for ever wilt be!
Great is thy faithfulness!
Great is thy faithfulness!
Morning by morning new mercies I see;
all I have needed thy hand hath provided –
great is thy faithfulness, Lord unto me!
Summer and winter, and spring-time and harvest,
sun, moon and stars in their courses above,
join with all nature in manifold witness
to thy great faithfulness, mercy and love.
Inspired by a Summer Evening in Sweden:
The second verse places the individual Christian in the context of the wider creation and emphasises the interdependence of the whole created order under its creator. This is the theme which is taken up in How Great Thou Art.

According to the 2002 Songs of Praise poll, this is Britain’s favourite hymn, and readers of the Catholic weekly, The Tablet, voted it third in their list of top ten hymns in 2004. Like Great is Thy Faithfulness, it owes much of its popularity to its extensive use in the Billy Graham crusades of the 1950s. But prior to that, the hymn owes its origins to a trail leading from Sweden to Britain via central-eastern Europe. The words in English are a translation of a Swedish poem, O store Gud, by Carl Boberg (1859-1940), an evangelist, journalist and for fifteen years a member of Sweden’s parliament. He was born the son of a shipyard worker on the south-east coast of Sweden. He came to faith at the age of nineteen and went to Bible School Kristinehamn. He returned to his native town of Monsteras as a preacher and it was there in 1886 that he wrote his nine-verse poem, inspired to praise God’s greatness one summer evening while looking across the calm waters of the inlet. A rainbow had formed, following a storm in the afternoon, and a church bell was tolling in the distance. Translated literally into English, the first verse of his poem reads:
O Thou great God! When I the world consider
Which Thou hast made by Thine almighty Word;
And how the web of life Thy wisdom guideth,
And all creation feedeth at Thy board:
Then doth my soul burst forth in song of praise:
O Thou great God! O Thou great God!

Boberg’s verses were set to music in 1891 and appeared in several Swedish hymnbooks around the turn of the century. An English translation was published in 1925 under the title O Mighty God, but never really caught on. Earlier, in 1912, a Russian version by Ivan Prokhanoff had appeared. This was almost certainly made from a German translation of the original Swedish hymn. The English translation was the work of British missionary and evangelist, Stuart K Hine (1899-1989), who heard it being sung in Russian in western Ukraine, where he had gone in 1923. After singing the hymn in Russian for many years, Hine translated the first three verses while continuing his missionary work in the Carpathian mountains in the 1930s. The scenery there inspired his second verse which draws little from Boberg’s original poem while remaining true to its general spirit of wonder at God’s creation:
O Lord my God, when I in awesome wonder
Consider all the works Thy hand hath made,
I see the stars, I hear the mighty thunder,
Thy power throughout the universe displayed:
Then sings my soul, my saviour God, to Thee,
How great Thou art! How great Thou art!
(x 2)
When through the woods and forest glades I wander
And hear the birds sing sweetly in the trees:
When I look down from lofty mountain grandeur,
And hear the brook, and feel the gentle breeze;

When are we Going to go Home?
Stuart Hine wrote the fourth verse of his hymn when he was back in Britain in 1948. In that year more than a hundred thousand refugees from Eastern Europe streamed into the United Kingdom. The question uppermost in their minds was When are we going home? In an essay on the history of the hymn, Hine wrote:
What better message for the homeless than that of the One who went to prepare a place for the ‘displaced’, of the God who invites into his own home those who will come to him through Christ.
Contrasting with a third verse which is about Christ’s ‘bearing’ of our individual burdens of sin on the cross, the final verse is about our places among the multitudes on the ‘last day’, just like the mass of homeless refugees finding a temporary home in Britain:
When Christ shall come with shout of acclamation
And take me home – what joy shall fill my heart!
Then shall I bow in humble adoration
And there proclaim, my God, how great Thou art!
Seventy years ago, Stuart Hine published both the Russian and the English versions of the hymn in his gospel magazine Grace and Peace in 1949. O Lord My God rapidly caught on in evangelical circles both in Britain and the UK, as well as in Eastern Europe, despite the oppression of the churches by the Soviet-style communist régimes which were taking control of the states where the hymn was first heard. The Hungarian Baptist Hymnbook contains a translation by Balázs Déri (born in 1954):

The hymn has been regularly sung in Hungarian Baptist Churches in recent decades, but it’s popularity probably stems, not so much to its sub-Carpathian origins, but to George Beverly Shea (below), the leading vocalist in Billy Graham’s evangelistic team, who was given a copy of it during the London crusade at the Haringey Arena in 1954. It became a favourite of Shea, the team’s choir director, Cliff Barrows and Graham himself, who wrote of it:
The reason I liked “How Great Thou Art!” was because it glorified God: it turned a Christian’s eyes toward God rather than upon himself, as so many songs do.

The hymn is still sung, universally, to the beautiful Swedish folk-melody to which Boberg’s original verses were set in 1891. It was the tune that I first fell in love with as a boy soprano when my Baptist minister father introduced my contralto sister and me to the hymn as our entry as a duet into the west Birmingham Baptists’ Eisteddfod (Festival of Arts), which was held during the same year as the lunar landing, my first year of secondary school (1968-69). Looking back, I’m convinced that it was my father’s involvement in the Billy Graham campaign as a young minister in Coventry which encouraged his love of the hymn. When it was sung by the congregation at his second church in Birmingham, he would always provide his own accompaniment on the piano, ensuring that the organist and the congregation did not ‘drag’ the tune and that it kept to a ‘Moody’ style, as in the days of the Graham Crusade.
Its reference to ‘the stars’ as evidence of the works thy hand hath made, inserted by Hine, anticipated the sense of awe and wonder experienced by the astronauts onboard the Apollo missions. Both the words and the music have continued to captivate soloists and congregations alike. Elvis Presley released his version of it, and more recently my favourite Welsh singers, Bryn Terfel, Katherine Jenkins and Aled Jones have also recorded their renditions. It was certainly a favourite of the Baptist congregations I regularly joined during my days as a student in Wales in the seventies, though they had many wonderful tunes of their own, including Hyfrydol, meaning just that. Most recently, the Mormon group, The Piano Guys recorded their ‘crossover’ instrumental version of it on their Wonders album, appropriately combining it with Ennio Morricone’s haunting composition for the film, The Mission, with Jon Schmidt at the piano and Steven Sharp Nelson on cello.


Alpha & Omega – In the Beginning and At the End:
For the astronauts on the Apollo 11 Mission, the landing was a profoundly spiritual event, according to their own testimony. They read from the gospel and even celebrated communion (see below). On Sunday (14th July 2019), a service from Leicester Cathedral to mark the 50th anniversary of the Moon landings was broadcast on the BBC under the title The Heavens are telling the glory of God. The service celebrated the achievement of the Apollo 11 Mission and asked whether the ‘giant leap’ has made us more, or less aware of our own human limitations and of our longing for God. It was led by the Dean of Leicester, the Very Reverend David Monteith, with contributions from staff at the National Space Centre and Christians involved in Astrophysics and Space Science. The Cathedral Choir led the congregation in hymns including Great Is Thy Faithfulness and The Servant King.

 The Servant King is one of many worship songs written by Graham Kendrick (born 1950), the son of a Baptist pastor, M. D. Kendrick. Graham Kendrick (pictured right, performing in 2019) began his songwriting career in the late 1960s when he underwent a profound religious experience at teacher-training college. This set him off on his itinerant ministry as a musician, hymn-writer and worship-leader. After working in full-time evangelism for Youth for Christ, with which I had been involved in Birmingham, in 1984 he decided to focus all his energies on congregational worship music. He has also become closely associated with the Ichthus Fellowship, one of the largest and most dynamic of the new house churches to emerge from the charismatic revival.
The Servant King is one of many worship songs written by Graham Kendrick (born 1950), the son of a Baptist pastor, M. D. Kendrick. Graham Kendrick (pictured right, performing in 2019) began his songwriting career in the late 1960s when he underwent a profound religious experience at teacher-training college. This set him off on his itinerant ministry as a musician, hymn-writer and worship-leader. After working in full-time evangelism for Youth for Christ, with which I had been involved in Birmingham, in 1984 he decided to focus all his energies on congregational worship music. He has also become closely associated with the Ichthus Fellowship, one of the largest and most dynamic of the new house churches to emerge from the charismatic revival.
His most successful musical accomplishment is his authorship of the song, Shine, Jesus, Shine, which is among the most widely heard songs in contemporary Christian worship worldwide. His other songs, like Meekness and Majesty, have been primarily used by worshippers in Britain. Although now best known as a worship leader and writer of worship songs, Graham Kendrick began his career as a member of the Christian beat group Whispers of Truth (formerly the Forerunners). Later, he began working as a solo concert performer and recording artist in the singer/songwriter tradition. He was closely associated with the organisation Musical Gospel Outreach and recorded several albums for their record labels. On the first, Footsteps on the Sea, released in 1972, he worked with the virtuoso guitarist Gordon Giltrap. In 1975 and 1976, he was one of the contributing artists at the second and third Greenbelt Arts Festival at Odell Castle in Bedfordshire. I was present at both of these, and also attended the fortieth, a much bigger event, at Cheltenham (see below) in 2013 where I watched him perform again.

Until the advent of Shine Jesus Shine, The Servant King was Graham Kendrick’s most popular song and is still one of the top 10 songs in the CCL (Church Copyright Licence). It was also voted 37th in the 2002 Songs of Praise poll. Written to reflect the theme for the 1984 Spring Harvest Bible teaching event and the Greenbelt Festival later that year, it illustrates Graham’s willingness to research a theme using concordances, commentaries and other biblical research tools. He found the theme very inspiring:
It was a challenge to explore the vision of Christ as the servant who would wash the disciples’ feet but who was also the Creator of the universe.
He wrote both the words and the tune, as with virtually all of his songs, first picking out the tune on the piano at home. It is a short and simple hymn which yet has a wonderful theological sweep and depth. The song is based on an incarnational root and is one of the few songs I know that can be used in worship at Christmas and Easter, and at any time between the two as a call to renewed commitment and discipleship. Its opening line is very reminiscent of Martin Luther’s Christmas hymn, From Heaven Above to Earth I Come, and it goes on to cover the agony of Jesus in the garden of tears and his crucifixion and calls on us to serve him as he did his disciples. I remember a Good Friday ‘service of nails’ in which it featured. It begins with the incarnation – From heaven you came, helpless babe – and progresses to one of Graham’s most poignant lines: Hands that flung stars into space to cruel nails surrendered:
From heaven you came helpless babe
Entered our world, your glory veiled
Not to be served but to serve
And give Your life that we might live
This is our God, the Servant King,
He calls us now to follow him,
To bring our lives as a daily offering
Of Worship to the Servant King.
Come see His hands and His feet
The scars that speak of sacrifice
Hands that flung stars into space
To cruel nails surrendered
It reminds us of the timeless nature of the acts of creation, incarnation and reconciliation, and of the inextricable link between them. Jesus is Alpha and Omega, his hands flinging stars into space, but then enters human time as a helpless babe, with the same hands being used to pin him to the cruel Roman gibbet in a once and for all act of atonement of the whole created order, fallen and the restored. For me, the final lines are among the most poignant and poetic of any hymn or worship song. It is also worthy to stand alongside the great classics of evangelical hymnody by Isaac Watts and Charles Wesley. It is more of a contemporary hymn in this classical tradition than a worship-song. It is addressed to Christ, and both its verses and chorus are cast in strophic, metrical form. Kendrick’s tune is also an unmistakably modern idiom and the resulting hymn does not ‘dumb down’ in terms of its theological subtlety and profundity. Neither does it suffer from the excessive individualism of so many contemporary worship songs. Like Great is Thy Faithfulness and O Lord My God, When I in Awesome Wonder, The Servant King places the paradox of greatness and sacrifice at the centre of the Christian religion as a truly universal faith and practice. Like his Meekness and Majesty, this hymn effectively points up the central paradox that Jesus is both king and servant, priest and victim: the one whose weakness is strength and who conquers through love.
Sources:
Ian Bradley (2005), The Daily Telegraph Book of Hymns. London: Continuum.
Wikipedia articles and pictures (Apollo 11).
Greenbelt memorabilia & DVD.
The Piano Guys, Wonders, album artwork, 2014. THEPIANOGUYS.COM.

Archaeological Insights:

The first missions to the Gentiles, as presented in the Acts of the Apostles offers a fruitful field for archaeological study. Different kinds of detail interlock. For example, Paul met the Christian couple Priscilla and Aquila in Corinth, after Emperor Claudius had expelled the Jews from Rome (Acts 18: 2). This expulsion is mentioned in pagan literature and dated to AD 49 by a later writer. During Paul’s long stay in Corinth, Gallio became governor (Acts 18: 12); he is known elsewhere from the writings of his more famous brother Seneca, and his governorship can be dated to AD 51-2 by an inscription found in Delphi. This evidence helps build a consistent and fairly precise outline for this part of Paul’s life and helps relate Acts to Paul’s letters.

Many details of the names of people and officials, places and customs in the book can be exactly illustrated from inscriptions. This does not prove its account to be historically accurate, but it does rule out any view which holds that the writer, probably Luke (Paul’s early travelling companion and author of the synoptic gospel which bears his name), was careless about such details. It also makes it hard to believe that the book was written long after the events it describes. A test case of the relationship between Acts, the Epistles and the archaeology is Paul’s letter to the Galatians. Sir William Ramsay used the evidence of inscriptions to clearly establish clearly the extent of Galatia and then argued that the letter was sent to the southern cities such as Pisidian Antioch, in Phrygia (above), which Paul had visited on his first journey (Acts 13-14). This, in turn, fits the very early dating of the letter. Thus the details of Paul’s life contained in the letter may be linked directly to those in Acts.
The Greek Writer and Theologian:
Paul’s surviving letters are found in the New Testament. Galatians was probably written before the Council of Jerusalem in about AD 50. The two letters to the Thessalonians date from his first journey to into Greece; Romans and I & II Corinthians come from his last spell in Greece before his arrest at Jerusalem. Philippians, Colossians, and Ephesians were probably written from Rome during Paul’s first imprisonment there, and Philemon may have been written during his earlier house arrest in Ephesus. The two letters to Timothy and the letter to Titus were probably written after Paul’s first stay in Rome. In them, Paul showed his mastery of Greek, and these two ‘pastoral’ letters can be counted among the classics of Greek literature. The letters were highly valued during Paul’s lifetime and were collected together soon after his death. By AD 95 they were accepted on an equal basis with other Scripture and were in their present form by AD 140. Paul’s theology was not well understood in the period immediately after his death. This was partly because the heretic Marcion rejected the Old Testament and much that was Jewish in the emerging canon of the New Testament. He considered that Matthew, Mark, Acts and Hebrews favoured Jewish readers exclusively. He also cut out the pastoral letters to Timothy and Titus, which left him with only a mutilated version of Luke’s Gospel and ten of Paul’s letters. He believed that Paul was the only apostle who did not corrupt the gospel of Jesus. As long as Marcion’s heresy was a threat, mainstream Christian teachers did not stress many of Paul’s more distinctive doctrines, such as that regarding the law of Christ and God’s grace. It was not until the time of Augustine that full weight was given to Paul’s theology.

The Missionary’s Achievements:

Paul’s achievements as a missionary were immense. The years between his Damascene conversion in AD 35 and his Antiochene preparations and initial discussions with the church in Jerusalem from AD 45 remain somewhat obscure, but during the next ten or twelve years, his activity was astounding. Between AD 47/48, when he set sail with Barnabas on his first missionary journey, and AD 57, when he returned to Jerusalem for the last time, he established flourishing churches in the major cities of the Roman provinces of Galatia, Asia, Macedonia and Achaia. His decisive role in the early Christian mission to the Gentiles was due principally to his championing of it to the first churches in Jerusalem and Antioch in Syria.
He then developed the theological defence of the Gentile mission which is clearly set out in Romans 1-11, while working hard to hold together and reconcile Jewish and Gentile Christians in the Diaspora. With this purpose in view, he kept in constant touch with the ‘mother church’ in Jerusalem, collecting a considerable sum of money among the Gentile converts for the needs of the Christians in Judea, and regularly underlined the importance of Christian unity in his letters. Finally, Paul’s principle of being ‘all things to all people’ helped him to move with relative ease between the synagogues, halls and house-churches of Graeco-Roman society, where ultimately the gospel received its greatest response. Moreover, his personal example as a self-supporting travelling missionary and his ‘settlements’ in significant cities provided a pattern of ministry for others to follow. His preference for the single life was based not on the kind of celibacy which Jesus advocated for some in Matthew 19, but on his initial sense that Christ’s return might come very soon. He certainly recognised the practical advantages for missionaries of remaining unmarried. However, like Jesus, he did not advocate a life of asceticism and self-denial as the norm for ministry and attacked the teaching that it was wrong to marry.
The origin and meaning of the word ‘apostle’ are hard to establish, and it obviously means very different things to different New Testament writers. For Luke, an apostle is one who accompanied us during all the time that the Lord Jesus went in and out among us (Acts 1: 21), thus excluding Paul. But for Paul himself, apostleship was something to be proud of, and he is very anxious to defend his own (I Cor. 9: 1). For him, the apostles are those who have been commissioned by an appearance of the risen Lord, as he had been on the road to Damascus. Later, in his Pastoral letters, Paul is the Apostle, the guardian of the faith. The one point of agreement is that apostleship is not something that can be passed on. A famous passage, I Cor. 12: 28, mentions in succession apostles, prophets and teachers, and Eph. 4: 11 has a similar list. It is doubtful, however, whether these can be regarded as different classes of ministry. Rather, they are different activities, more than one of which might be practised by a single individual:
-
Deacon is usually a general term, describing any form of ministry or service. In two passages, the deacon seems to be a particular minister, subordinate to the bishop (Phil. 1: 1; I Tim. 3: 8-13). If the two terms are used technically in Phil 1: 1, this is the only evidence we have of such a formal ministry from the Pauline letters so the terms may be general even there.
-
Elders are not mentioned at all by Paul but are to be found as ministers throughout Acts, appointed by Paul and Barnabas in every church (Acts 14: 23; cf. 15: 12 ff.; 16: 4; 20: 17; 21: 18). Here Jewish practice is followed. Villages and towns had their groups of Jewish elders, seven in each village, twenty-three in each town and seventy in Jerusalem. When a place fell vacant, it was filled by the laying on of hands, the pattern found in Acts.
-
Bishop is a term which occurs in a technical sense in Acts 20: 28., but as in Phil 1: 1 the word may be used generally as ‘overseer’. Bishop is a definite office in I Tim. 3: 1-7; Titus 1: 7-9. The relationship between elders and bishops is a classic problem, as at times the two terms could be synonyms. At the end of the second century, each bishop was in charge of a particular area. All bishops were elders, but not all elders were bishops.
We have even less evidence about the ministry at this time than about other important matters, and what is said in the ‘Apostolic Fathers’ does little to help. Clearly, the pattern varied from place to place, and development was by no means uniform.
How would Paul have assessed the significance of his work?
From differing angles, more can be said about the reasons for the surprising long-term success of Paul’s work. Tom Wright tells us that Paul’s particular vocation was to found and maintain Jew-plus-Gentile churches on Gentile soil. He realised early on that it was his job not just to teach people what to think and believe, but to teach them how; how to think clearly, scripturally, prayerfully. The One God had already built his new Temple, his new microcosmos; the Jew-plus-Gentile church was the place where the divine spirit already revealed his glory as a sign of what would happen one day throughout the whole world. Of course, Paul would not have expected all this to happen smoothly or easily. He was a realist and would never have assumed that the transformation of small and often confused communities into a much larger body, forming a majority in the Roman world, would come about without terrible suffering and horrible pitfalls. He would also have been saddened by the mistakes and heresies of the following centuries and the battles that would have to be fought. But he would also have pointed out that something had happened in Jesus which was of cosmic significance. The success of the ‘Jesus Movement’ wasn’t simply the accidental product of energetic work meeting historical opportunity. God was at work in the midst of his people to produce both the will and the energy for it to succeed. This divine design and Spirit-led motivation were bound to have their larger effect, sooner or later, and by whatever means they could find.
Paul was also very much alive to all the factors that the historian, as opposed to the theologian, might want to study. He would have been very much aware of the need for historians to demythologise scriptural narratives. In his own day, Greek scholars were doing the same kind of thing with the stories of Homer. Paul would not, himself, have wanted to ascribe the whole happening of Jesus to divine or angelic power operating without human agency, since he believed that when grace was at work, human agents were themselves were regularly called upon to work hard as a result, not least in prayer. He said this of himself (I Cor. 15: 10; Col. 1: 29). The Creator may work in a thousand ways, but one central way is, for Paul, through people who think freely, pray, make difficult decisions and work hard, especially in prayer. Since heaven and earth had come together in the persons of Jesus and his Spirit, we should expect different layers of explanation to reside together and reinforce each other. Paul was one of the most successful public intellectuals of all time precisely because he was able to take advantage of the human circumstances of his time – a common language, freedom of travel and citizenship of the Roman Empire – to establish an international movement not only for the course of his own lifetime but for an indeterminate historical future.

Paul’s Personal Attributes:
Tom Wright highlights a number of personal attributes which enabled Paul to develop the early Christian church throughout the Empire of the Eastern Mediterranean and in Rome itself. First of all, he points to the sheer energy of the missionary, which can be found not only in the narratives of Acts but also pulsing through his letters. He responds to violence in one city by going straight on to the next, saying and doing the same things there. He worked all hours, making tents when not preaching, teaching or dictating letters to a scribe. He was also ready every moment for the visitor with a question or local official worried about his status. He was ready to put down his tools and leave his workbench for an hour or two in order to go from house to house making pastoral visits to encourage the faithful, to comfort the bereaved, downhearted and distressed, to warn and pray. In between his house calls, he was thinking about what he would say in his afternoon address in the house of Titus Justus in Corinth or the hall of Tyrannus in Ephesus. In the evening, he would pause to say prayers with his close friends and travelling companions, before working long into the night, praying for those he had met that day, for the city officials and for the Christians in other cities, for the next day’s work and the next phase of his mission.

His second attribute was his direct, up-front habit of telling it as he saw it, no matter who was confronting him. From his early days in Damascus, getting into trouble, to his arguments with the apostles in Jerusalem and his confrontation with Peter in Antioch, he didn’t hold back from controversy or seek to avoid conflict if he thought it would advance the church’s mission by confronting and seeking to resolve it. Wright suggests that the only reason he didn’t say more at the Jerusalem Conference was that Barnabas was there to act as a moderating influence. His debating style might have proved effective, but it might also have alienated many more sensitive souls. He also confronted the magistrates at Philippi and relished speaking truth to the vast crowd in Ephesus; he is fearless in trying to explain himself to the lynching mob in Jerusalem and is not afraid to rebuke the High Priest. He was an astute politician who knew how to turn the various factions of the Sanhedrin against each other. He also lectured the Roman governor himself about justice, self-control, and the coming judgement. As a travelling companion, he must have been exhilarating and exasperating in equal measure, depending on whether things were going well or badly. He must have been a formidable an opponent since he seems to have driven some people to contemplate murder as their only means of ridding themselves of this troublesome missionary.

Yet there must have been something quite disarming about Paul’s vulnerable side, which helps to explain why people wanted to work alongside. He was the sort of person for whom there were no limitations in affection for his fellow Christians. His honesty shines through in the pages of his letters. He would do anything he could for the churches since God had done everything for him through the Messiah. Neither would he have asked anyone to face anything he himself had not faced, including terrible suffering and hardship. The Corinthians would have immediately recognised a self-portrait in his poem about divine love, and when he told the Philippians to rejoice and celebrate, they knew that, given half a chance, Paul would have been at the party in spirit, the life and soul of it. He modelled what he taught, and what he taught was the utter, exuberant, self-giving love of the Messiah and the joy that accompanied it. His associates were fiercely loyal to him, and there was mutual love between them. He was the sort of person who enabled others to change and grow so that they themselves would take forward the same missionary work with as much of the same energy as they themselves could muster.
Paul’s Writing:
But within two or three generations the memory of this personal relationship had faded so that it was his letters which kept his influence alive. The flow of words from his daily teaching, arguing, praying and pastoral work was captured for future generations in these short, challenging epistles. It isn’t just their content, strikingly original and authentic as it is. He wasn’t synthesising the worlds of Israel, Greece and Rome; his was a firmly Jewish picture, rooted in Israel’s ancient narrative, with its Messiah occupying centre stage and the nations of the world and their best ideas brought into new coherence around him. Nor was he simply teaching a ‘religion’ or ‘theology’, but drawing together wisdom learnt from many different ancient disciplines, which we would class under economics, history and philosophy. Yet within a generation people were grumbling that Paul was sometimes too difficult to understand and that some were misinterpreting him. But it is no accident that many of the great moments of church history and Christian thought, involving Augustine, Luther and Barth, have come about through fresh engagement with Paul’s work. Paul had insisted that what mattered was not just what you thought but how you thought. He modelled what he advocated, and generation after generation has since learned to think in this new way. In this way, his legacy has continued to generate fresh dividends.
Culture, Politics & Society:
Paul himself would claim that all this was the doing of the One God and his Messiah, whereas ‘sceptics’ might retort that the movement owed much to the spread of the Greek language and culture combined with the increasing ease of travel throughout the Roman Empire. This meant that conditions were ripe for the spread of new ideas and movements throughout the known world and even into South Asia. Paul would perhaps have rejoindered that if the Messiah was sent when the fullness of time arrived (Gal. 4: 4), then perhaps Greece and Rome were part of the plan and the preparation, as well as part of the problem. Tom Wright does not agree, however, with those who have claimed that people were getting tired of the old philosophies and pagan religions and were ready for something new. The problem in Ephesus, for example, was not that people had stopped worshipping Artemis, and so were ready for Paul’s message, but that Paul’s message about the One God had burst on the scene and stopped the worship of Artemis. Social and cultural conditions can help to explain the way things worked out, but they cannot explain it away. Paul emphasised, in letter after letter, the family life of believers; what he begins to call ‘the church’, the ekklesia. He continually emphasises the unity and the holiness of the church, as well as highlighting and ‘celebrating’ the suffering that he and others would and did endure as a result of their loyalty to Jesus. This was not about pagans experimenting with new ideas, but about a new kind of spiritual community and even a new kind of ‘politics’.

Politics is concerned with the polis – the city, the community – and how it works and runs. Sophisticated theories had been advanced in Paul’s day, often by theoreticians like Cicero and Seneca, who were also members of the ruling élite. The main feature of Paul’s political landscape was Rome, which had united the world, or so it claimed. But that top-down uniformity in which diversity was tolerated as long as it didn’t threaten the absolute sovereignty of Caesar, was often ugly. ‘Diversity’ was still seen in strictly hierarchical terms: men over women, free over slaves, Romans over everyone else. Rebels were ruthlessly suppressed. They make a wilderness, sighed the Briton Calgacus, and they call it ‘peace’ (Tacitus, Agricola 30.6). What Paul had been doing was undoubtedly building a different kind of community offering a different vision of unity, hosting a different kind of diversity based on churches of Gentiles and Jews. He was founding and maintaining an interrelated network of communities for which the only analogies were synagogue communities, on the one hand, and the Roman army and civil service on the other. But Paul’s communities were very different from either. They had the deepest roots and were not simply a freestanding innovation. Rome traced its story back nearly a thousand years, while the synagogue told the still longer story which went back to Abraham. Paul told that story too and regularly explained to his communities that they had been grafted into that great tradition. In Paul’s work, this was as much a social and communal strength as it was a theological one.
Morality & Marriage:
When the new communities spoke of a different kind of kyrios, one whose sovereignty was gained through humility and suffering, rather than wealth and conquest, many must have found that attractive, not simply for what we would call ‘religious’ reasons, but precisely because for what they might call ‘political’ ones. Paul did not, of course, have time to develop his picture of the differentiated unity of the body of Christ into a larger exposition of the church as a whole. He had not articulated a political authority to match that of Aristotle or his successors. But it was that kind of social experiment, of developing a new way of living together, that the churches of the second and third centuries sought to develop. Their inspiration for this went back to Paul’s theological vision and was not pure pragmatism. It had the power to generate an alternative social and cultural reality, to announce to the world that Jesus was Lord and Caesar wasn’t. What Paul had articulated in his letters, often in haste and to meet particular crises, was reused to encourage Christians to develop a refreshingly new kind of human society. In particular, the Christian message provided a much better prospect for women than the pagan religions, which routinely practised infanticide for unwanted children in general and girls in particular. The Christians followed the Jews in renouncing such behaviour. The consequent shortage of marriageable girls among pagans and the surplus among Christians led to an increase in inter-cultural marriages, with many of the offspring being brought up as Christians. The fresh evaluation of the role of women, begun by Jesus himself, was developed by Paul, who listed several women among his colleagues and fellow workers. For example, Phoebe was entrusted with the responsibility of delivering and expounding his letter to the Romans.
With sexual excesses all around them, it is likely that some Christians reacted against sexual indulgence from a fairly early period. However, this was not formally set out or made a matter of special praise. In fact, special vows by younger women to abstain from marriage were discouraged by Paul. During the period which followed, abstinence from marriage was left as a matter of personal choice, although in most ‘Gnostic’ sects marriage was actively discouraged on the grounds that it entangled the spiritual soul with the evil physical world. Some Jewish and Christian traditions blamed sexual differences on ‘the fall’ and believed that salvation included a return to a ‘unisex’ or asexual life. In the mainstream churches, leaders such as Melito of Sardis became known for their austere personal lives; abstinence from marriage was part of this. In many churches, too, Christian women had difficulty in finding suitable husbands. Those who remained unmarried had more time for prayer and devotion. In the same way, men who were free from family ties had more time to devote to church affairs and were often obvious choices as leaders. By the third century, celibacy was beginning to be valued as a mark of holiness. Even so, extremes were frowned upon, and Origen earned considerable disapproval because he made himself a eunuch, believing that this was commended in the Gospels. As martyrdom declined, asceticism began to become the measure of spirituality; the leaders regarded as more spiritual in the churches tended to be those who practised an ascetic way of life, though the clergy was not generally obliged to be celibate.
Poverty & Social Action:
Within a few generations, the early Christian communities set up hospitals, caring for all those within reach, and they were also enthusiastic about education, teaching their converts to read the scriptures of ancient Israel, and thereby giving them the literacy skills that previously only a maximum of thirty per cent of the populations had acquired, almost exclusively male. Some of the older Greek cities and islands had a tradition of elementary education for citizens, but for many people, this would have been minimal, and women and slaves were excluded. Converts to Christianity, therefore, gained basic reading skills that they had hitherto lacked. Christians were also technological pioneers in making books, abandoning scrolls with their natural limitations and developing the ‘codex’, the ancestor of the modern bound book. The earliest Christian congregations quickly appreciated the value of the letters written by the apostles. Some of them were obviously intended for public reading, perhaps in place of, or alongside, a sermon on the Old Testament, and for circulating among the churches. But they clearly wanted more and more people to be able to read the books the community was producing. This insistence on education and especially reading can be traced back directly to Paul, who told his churches to be ‘grown-up’ in their thinking, to be transformed by the renewal of their minds as well as their hearts. He wanted the early Christians not only to think the right things but also to think in the right way. Though he did not himself found what we would today call ‘schools’ when such things did come about, they had him to thank for the underlying impetus.
Paul’s collection for the poor of Jerusalem was followed up in each local Jesus community in its work among the poor around it. Paul congratulated the Thessalonians on their practical ‘loving-kindness’ or agape and urged them to work at it more and more. “Do good to everyone,” he wrote to the Galatians, “and particularly to the household of the faith.” He encouraged them to… Celebrate with those who are celebrating, mourn with the mourners… Shine like lights in the world. The gospel itself was designed to generate a new kind of people, a people who would be eager for good works; in fact, the new kind of humanity that was brought to birth through the gospel was created for the specific purpose of ‘good works’ (Gal. 2: 10; I Thess. 4: 9-10; Gal. 6: 10; Rom. 12: 15; Phil. 2: 15; Titus 2: 14; Eph. 2: 10). This phrase means more than ‘the performance of moral rules’, especially when played off against Paul’s doctrine of justification by faith alone. Morals matter, faith matters, but that isn’t the point here. Paul’s emphasis is all about communities through whose regular practice the surrounding world is made a better place. Through Christ’s faithfulness and their own loving-kindness, these communities would find the right way to live. Good morals and good works would follow. In Corinth, there was a tendency to divide into factions centred on the personalities of human leaders, rather than just over doctrines. A prominent member of the community was living in immorality and individual Christians were taking each other to the law-courts over minor disputes. There were also misunderstandings about the meaning of Christian liberty. Paul’s letters, as well as those of John, reveal controversies and power-struggles in the midst of encouragement and growth.
The Spread of Christian Communities:

But the church history of the second and third centuries is enough to confirm that all these things, taken together, offer good explanations for the spread of the Christian communities. These early Christians, strange though their views and lives might have seemed to those around, antisocial though some might have supposed them to be, were doing things that really do transform the wider society. By the end of the second century, Roman officials were not particularly aware of the nuances of Christian teaching, but they did know what the term ‘bishop’ meant – someone who agitated about the needs of the poor. This too was the result of a seed that Paul had planted, and when all of these began to sprout, a community came into being that challenged the ancient world with a fresh vision of a society in which each worked for all and all for each. This enabled that world to escape from the older paganism and its social, cultural and political practices and to find refuge in the new kind of community, the koinonia, the ‘fellowship’, the extended family of the One God. On the cross, Jesus had won the victory over all the other powers, or gods. This was the basic belief of these communities, which existed because all the old gods had been overthrown. Mammon, Mars and Aphrodite had been shown to be imposters, and Caesar was no longer the ultimate Lord. This was a theological, historical and political reality which the followers of Jesus demonstrated on the streets and in the market places, as well as in their homes.

The breaking through of Paul’s thinking in Graeco-Roman society was not because the other philosophies of the ancient world had ‘run out of steam’. The Stoics, Epicureans, and Platonists had serious, articulate and even ‘charismatic’ spokespeople. They were all, in the final analysis, ways of understanding the world and of finding a coherent path for humanity within it. When later generations of Christians wanted to articulate the gospel version of the same thing, they turned to Paul for help, though other sources remained vital. The prologue to the Gospel of John is an obvious example of these, but it was Paul’s engagement with the triple traditions of Israel, Greece and Rome and his transformation of them by the person and Spirit of Jesus that offered a platform for the great Christian thinkers of subsequent generations and centuries. Without this firm theological foundation, the church would not have survived the persecutions it was forced to endure in these centuries. Paul knew only too well what learning how to think would cost those who were ‘to follow’, but he believed that this new way was the only way for them to follow, a way that would win out over the other ways because of its genuine humanity.

The Wright Verdict:
Tom Wright completes his answer to his own question by summarising the several paths of explanation which converged on Paul himself in his mapping out of this ‘new Way’:
His was the vision of the united, holy, and outward-facing church. He pioneered the idea of a suffering apostleship through which the message of the crucified Jesus would not only be displayed, but be effective in the world. He could not have foreseen the ways in which these communities would develop. He might well not have approved of all that was done. But the historian and biographer can look back and discern, in Paul’s hasty and often contested work, the deep roots of a movement that changed the world…
… Paul’s vision of a united and holy community, prayerful, rooted in the scriptural story of ancient Israel, facing social and political hostility but insisting on doing good to all people, especially the poor, would always be central. His relentless personal energy, his clarity and vulnerability, and his way with words provided the motor to drive this vision, and each generation will need a few who can imitate him. His towering intellectual achievement, a theological vision of the One God reshaped around Jesus and the spirit and taking on the wider world of philosophy, would provide the robust, necessary framework for it all. When the church abandons the theological task… we should not be surprised if unity, holiness, and the care for the poor are sidelined as well.

Paul’s contribution to the Nature & Worship of the Early Church:
The church brought together ideas and people from many backgrounds. It had to cope with people who had become Christians in such disreputable seaports as Corinth, notorious for its immorality. It had to resolve the pressures to revert to pagan or Judaic practices, to sort out its attitudes towards contemporary customs and cultures, and to thrash out beliefs and opinions about issues on which there were no precedents to guide its thinking. Many Christians in the third century were willing to suffer as martyrs rather than betray their Lord by acknowledging false gods. Some, however, renounced their faith under torture or the pressure of imprisonment. Others got pagan neighbours to make the required sacrifice on their behalf, or obtained false certificates from sympathetic officials. At the opposite extreme, some Christians eagerly sought out martyrdom, even when it was not forced upon them, though this was strongly discouraged by Christian leaders. Following each wave of persecution, the church was faced with the problem of what to do with those who repented after lapsing under pressure. Some Christian leaders claimed that offences such as idolatry after baptism were unpardonable on earth, but others allowed one such occasion of forgiveness subsequent to baptism. Callistus, bishop of Rome (217-22), was among the more moderate and appealed to Paul’s letters and the parables of the lost sheep and the prodigal son for proof that no sin is unforgivable if the sinner truly turns from their sins. His referral back to Paul reveals the continuing influence of the apostle.

In Paul’s time, and for at least a century afterwards, Christianity was largely an urban movement; Paul tended to preach in big cities, and small Christian groups could more easily spring up in the anonymity of large towns. Deep penetration of the countryside only began in the third century, though the methods used in that ‘outreach’ are unclear. Nearly every known Christian congregation started by meeting in someone’s house. One example of this was Philemon’s house-church, perhaps at Laodicea. The home formed an important starting-point, although by the mid-third century congregations were beginning to have their own special buildings because congregations were too large to meet even in the courtyard of a large Roman house. Most Christian writers were increasingly rationalistic, and Eusebius mentions only a very few miracles in his history of the church during this period. They also tried to discredit contemporary pagan superstition, focusing on ‘good living’ rather than supernatural ‘signs’. In the late third centre came the first deliberate attempts to follow Paul’s earlier examples of absorbing features of pagan religions into Christianity. Churches took over from temples, martyrs replaced the old gods in popular devotion, and the festivals of the Christian year took the place of high-days and holy days of paganism.

When Irenaeus succeeded as a third-generation ‘bishop’ of the church in Rome, he described it as the very great, very ancient and universally known church, founded and organised at Rome by the two most glorious apostles, Peter and Paul. Because Christians from all parts were found there, it was a microcosm of the whole Christian world. His statement hints at some of the reasons why Rome acquired a leading position among the churches. All roads led to Rome, the capital of the Empire, not least the well-engineered roads on which the Christian missionaries travelled. A remarkable number of prominent Christians made their way to the Imperial City: Ignatius, Polycarp, Marcion, Valentinus, Tatian, Justin, Hegesippus, Irenaeus, Tertullian, Praxeas, and Origen, all followed Peter and Paul’s journeys in the sixties. Rome was the only Western church to receive a letter from an apostle, and Luke’s long account of Paul’s miraculous journey to the city reflects the importance attached to his reaching the capital. Nothing boosted the prestige of Christian Rome so much as the fact that the two chief apostles were martyred there under Nero. By the mid-second century, memorial shrines to Paul and Peter had been erected in Rome, on the Appian Way and the Vatican Hill respectively. Remains of the latter have been uncovered in modern excavations.

The Fall of Jerusalem in AD 70 enhanced the standing of the Roman church in the long-term since it became almost impossible to evangelise the Jewish settlements on the eastern shores of the Mediterranean. Christianity’s centre of gravity shifted west, where Rome was well-placed to play a central role. However, the letter to the Corinthian church known as I Clement did not imply any claim to superiority by the church of Rome. Second-century Christianity there appears to have been very varied. It included independent schools like Justin’s and immigrant groups such as the Asians who followed their traditional observance of the Pascha (Passover). Not until the last decade of the century did a strong bishop emerge – Victor, an African and the first Latin speaker. Meanwhile, the shrines of Peter and Paul bolstered a growing self-confidence.
The first bishop to claim a special authority derived from Peter by appealing to Matthew 16: 18-19, was Stephen, in his dispute with Cyprian. Paul’s position alongside Peter in the earliest church now began to be lost sight of. Cyprian regarded every bishop’s seat as ‘the see of Peter’, although he agreed that the Roman church had special importance because it had been founded so early. The Roman church already possessed considerable wealth, including the underground burial-chambers (catacombs) outside the city and several large houses whose upper floors were adapted for use as churches (tituli).

Centuries later, the Roman church criticised the British for their great lack of martyrs as compared with their own record. The leaders of the British church informed them that the leaders of the British church lived to preach and teach the Gospel and not die for it unnecessarily. As noted already, there were many in the Roman church who viewed martyrdom as a noble, worthwhile gesture to such an extent that some became fanatics. They sought martyrdom before they had achieved anything else worthwhile. The most popular claimant to the honour of being the first Christian martyr in Britain, identified with the church of St. Alban’s, was the Christianised Roman soldier, named Alban. During the Diocletian persecution in Britain, he aided a hunted British priest to escape by wearing his robe, drawing pursuit to himself. On being recognised, the Roman officer ordered a soldier standing nearby to execute the culprit. The soldier refused, admitting that he too was a Christian, with the result that both soldiers were immediately beheaded. Tradition claims they were buried together on the spot where they were killed and a church erected on the site was named St. Alban’s. However, the early British historian, Bishop Alford wrote of an earlier martyr who was apparently known to both Peter, Barnabas and Paul, Aristobulus, who was absent in Britain before Paul arrived in Rome. In the Martyrologies of the Greek church, we read:
Aristobulus was one of the seventy disciples and a follower of St. Paul the Apostle, along with whom he preached the Gospel to the whole world, and ministered to them. He was chosen by St. Paul to be the missionary bishop to the land of Britain. He was chosen by St. Paul to be the missionary to the land of Britain. He was there martyred after he had built churches and ordained deacons and priests on the island.

Dorotheus, Bishop of Tyre, recorded in AD 303 that Aristobulus who is mentioned by the Apostle in his Epistle to the Romans, was made Bishop in Britain. Haleca, Bishop of Augusta, confirms that he was one of many martyrs whose memory was celebrated by the Britons and the Adonis Martyrologia also contains a record which confirms his mission to Britain, where he founded a church before his martyrdom in circa AD 59 or 60, on 15 March. There is a legend suggesting that Paul himself may have paid a brief visit to Britain during his time in Rome, but though we know that he intended to travel to Spain, there is little evidence to suggest that he did so, or that he went further north. Apparently, in Merton College, Oxford, there is an ancient manuscript known as the ‘Paulian MS’ which purports to contain a series of letters between Paul and Seneca, which make allusions to the former’s residence in Siluria. Clement of Rome, who died in about AD 100 wrote of the martyrdoms of both Peter and Paul, whom he probably knew personally. He sums up the magnitude of Paul’s achievement in the following terms:
Paul, also, having seven times worn chains, and been hunted and stoned, received the prize of such endurance. For he was the herald of the Gospel in the West as well as in the East, and enjoyed the illustrious reputation of the faith in teaching the whole world to be righteous. And after he had been in the extremity of the West, he suffered martyrdom before the sovereigns of mankind; and thus delivered from this world, he went to his holy place, the most brilliant example of steadfastness that we possess.
In referring to ‘the extremity of the West’, Clement could be referring to Gaul or Britain, but he is more likely to be referring, in this context, to the western Mediterranean. I Clement is an open letter from one of the early bishops or presbyters of the Rome to the church at Corinth, probably written at the very end of the first century, shortly after the persecution of Emperor Domitian. It is probably the earliest surviving Christian writing outside of the New Testament. It was written to counter the disruption and disturbance of in the church at Corinth, where some of the older leaders had been deposed by a younger clique. It sheds interesting light on the nature and conduct of church life soon after the age of the apostles. It puts great stress on good order, and on Christian faith being accompanied by good works, claiming that Abraham was saved by faith and hospitality. The book quotes extensively from the Old Testament, Jewish books outside the canon and writings of the apostles. Like Paul’s own letter to the Corinthians, written earlier, Clement exhorts his readers to Christian humility and love, and it was probably read out in Corinth and other churches.

In I Corinthians, which gives the earliest description of worship in the Christian church, Paul constantly draws on the Old Testament. This letter, written in about AD 55 pictures the church as the new Israel, living a pattern of the Christian life that is based on the new exodus. Paul uses ideas drawn from the Jewish Passover, which celebrated God’s saving favour and strength in calling Israel to be his people, and rescuing them from tyranny in Egypt. According to Paul, the church succeeded the old Jewish community and combined both Jews and Greeks within God’s one family of converted men and women. This fellowship of believers in Jesus stood at the dawn of a new age of grace and power. Al this was possible through the gift of the Holy Spirit, which followed the resurrection and ascension of Jesus. This one fact of experience stamps New Testament worship as unique, however much the church owed to its Jewish inheritance. Paul used the framework of the Passover meal to interpret the Lord’s Supper. But other elements were intertwined, such as the fellowship meal, called the agape or love-feast which had its counterpart in Jewish table-customs. This had become an occasion for an ‘orgy’ of gluttony and drunkenness in Corinth, and Paul pointed out that this was a breakdown in the fellowship which both the Lord’s Supper and the agape were designed to promote. Paul believed that the Lord’s Supper served both to unite Christians with the Lord in his death and risen life, and to join believers in a bond of union as ‘one body’ in Christ, receiving him by faith and in love.

The setting for worship was ‘the first day of the week’, referring to the day of Christ’s resurrection, as in the Gospels, and is distinct from the Jewish Sabbath. The Christian Sunday was not made a ‘day of rest’ until Constantine decreed it in AD 321. Paul also wrote about baptism, a rite of initiation with its roots in the Jewish washings for ceremonial purposes, and especially in the service of tebilah, the ‘bath’ necessary for all converts to Judaism. The practice of baptism was also being misused at Corinth, and Paul objected to their misunderstanding or abuse. Baptism, he told them, should be in the name of Jesus, not in the name of leaders in the fellowship, as if these were apostolic cult figures. ‘In the name of Jesus’ meant that new converts passed under his authority, and confessed him as Lord. The enthusiasm of the Corinthian Christians also led them to misuse ‘ecstatic tongues’ and other gifts of the Spirit. Paul tried to curb this by insisting that worship must promote the healthy growth of the entire community of Christians. Personal indulgence in the gifts of the Spirit was to be brought firmly under control. Not all the features of early Christian worship at Corinth are clear. It is not known what ‘baptism for the dead’ implied. Paul did not attach great importance to it but used it simply to illustrate another matter. He also mentioned the ‘kiss of peace’ without explanation.

Prayers also played an important part in worship at Corinth. At public prayer, the response of amen (a Hebrew word of confirmation) was the natural way to show agreement. Problems arose over women who attempted to pray with uncovered heads. Paul resisted this practice, though he freely granted the right of women believers to act as prophets and leaders of prayer in the assembled church. Both prophesying and praying were seen as gifts of the Spirit. The freedom that the Corinthians were exercising to the full was to be held in check. Paul crisply summed up: Let all things be done decently and in order. ‘Singing’ with the mind and the Spirit indicates a musical side to the meeting, but references to musical instruments do not make it clear whether they were used in worship. Exactly what these hymns were, and whether snatches of them have survived, is unclear. Passages in Philippians 2: 6-11; Colossians 1: 15-20 and 1 Timothy 3: 16 contain what may be early hymns, offered, as later among Christians in Bithynia about AD 112, to Christ as God. Ephesians 5: 14 is the most likely example of a hymn from the churches instructed by Paul. The setting of that three-line invocation is clearly a service of baptism.
Evidence about Christian worship from writers who lived between the time of Paul and the middle of the second is scarce and difficult to piece together. In his letters, Pliny gives an outsider’s view of Christian worship from this time:
They were in the habit of meeting on a certain fixed day before it was light, when they sang an anthem to Christ as God, and bound themselves by a solemn oath (‘sacramentum’) not to commit any wicked deed, but to abstain from all fraud, theft and adultery, never to break their word, or deny a trust when called upon to honour it; after which it was their custom to separate, and then meet again to partake of food, but food of the ordinary and innocent kind.
(Pliny, Letters x. 96; AD 112).

Pliny’s correspondence with Emperor Trajan reveals that the early Christians shared ‘holy meals’ and that by this time the agape had been separated from the Lord’s Supper. In fact, continuing abuse of the ‘love-feast’ led to its gradual disappearance in its original form. The solemn meal of ‘holy communion’ was given more and more prominence as a sacrament. Ignatius describes it as a medicine of immortality, the antidote that we should not die, but live forever in Jesus Christ. Worship gradually became more standardised, formal and stereotyped in the period following Paul’s death, with the ‘Lord’s Supper’ becoming the focal point of the liturgy. Bishops and deacons possibly helped in this trend. New converts (catechumens) were given instruction in preparation for baptism. Worship forms connected with this are referred to in the letters of I Peter and I John. Short snatches of an elementary creed are found in such verses as Jesus is Lord (Romans 10: 9), lengthened and developed in I Timothy 3: 16 and I Peter 3: 18-22.
At first, when a person was baptised they affirmed a creed which was concerned mainly with statements about Christ’s person, as in the addition to the text in Acts 8: 37. Examples of more formal creeds, stating the belief in the three persons of the Godhead, the Trinity, occur in descriptions of baptismal services reported by Irenaeus and Hippolytus of Rome. The Apostles’ Creed, shown below, derives from the late second-century baptismal creed used in Rome, which in turn derives from Paul’s theology. Perhaps the most lasting and visible legacy of the self-proclaimed apostle is, therefore, to be found in the liturgy of the sacraments, which is still shared in most Christian churches, more than nineteen hundred and fifty years after his death.

Sources:
Tom Wright (2018), Paul: A Biography. London: SPCK.
Robert C Walton (ed.) (1970), A Source Book of the Bible for Teachers. London: SCM Press.
Tim Dowley (ed.) (1977), The History of Christianity. Berkhamsted: Lion Publishing.
George F Jowett (1961), The Drama of the Lost Disciples. London: Covenant Publishing.
Posted March 18, 2019 by AngloMagyarMedia in Archaeology, Asia Minor, Assimilation, baptism, Bible, Britain, British history, Britons, Celtic, Celts, Christian Faith, Christianity, Church, Civilization, Colonisation, Commemoration, Compromise, Conquest, Crucifixion, Education, eschatology, Ethnicity, Europe, Family, Fertility, Gentiles, Graeco-Roman, History, Imperialism, India, Israel, Jerusalem, Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, Jews, John's Gospel, Josephus, Literature, Marriage, Mediterranean, Memorial, Messiah, Middle East, Midlands, morality, multiculturalism, Music, Narrative, Nationality, New Testament, Old Testament, Palestine, Paul (Saint), Poverty, Reconciliation, Remembrance, Romans, Sacraments, Simon Peter, Synoptic Gospels, Syria, The Law, theology, tyranny, Women in the Bible
Tagged with 'agape' (love-feast), 'The Good Shepherd', Achaia, Acts of the Apostles, Alexandria, angelic power, Antioch, Apostles' Creed, apostleship, Appian Way, Aristobulus, Artemis, asceticism, Asia, Athens, Augustine, Barnabas, Barth, Bishop Alford, Bishops, Callistus, catacomb, celibacy, Christian views on marriage, Christianity, Claudius, Clement of Rome, Colossae, Corinth, Court of the Aeropagus, Creator, culture, Cyprian, Deacons, Delphi, Diaspora, Diocletian, Domitian, Dorotheus, Earth, Elders, Ephesus, Epistles, Eucharist, Eusebius, Faith, fellowship, Galatia, Gallio, Greek, Hebrews, History, Holy Communion, Holy Spirit, idolatry, Ignatius, Irenaeus, Josephus, Judea, justification, Justin, liberty, Lord's Supper, Luke, Luther, Macedonia, Marcion, martyrdom, Merton College, Messiah, morality, Nero, Origen, Passover, Philemon, Philippi, Phrygia, Pisidian Antioch, Pliny, Poetry, politics, Polycarp, Poverty, pragmatism, Prayer, Priscilla & Aquila, religion, Rome, Sanhedrin, Seneca, Siluria, social action, society, St Alban, Tacitus, Tertulian, The Prodigal Son, Thessalonica, Tiberius, Timothy, Titus, Trajan, Vatican Hill, William Ramsay
The Challenge – What was Paul thinking?

The Sources – The Great Pastoral ‘Epistles’:
To understand the thought of Paul, we naturally turn to his letters. Although Luke’s Acts of the Apostles gives a fair account of his life and work, and a general idea of what he stood for, it is in his letters that his mind is fully revealed. In the New Testament, there are thirteen letters that name Paul as their ‘author’. A fourteenth, the Letter to the Hebrews is often included with them it is, in fact, an anonymous work, since in the early church itself it was admitted that no one knew who wrote it. Of the thirteen, it is by no means certain that all were written by Paul’s hand or even at his dictation. This was not unusual for the period in which he was writing since it was not unusual for disciples of an outstanding teacher to compose books to propagate his teaching as they understood it, and to publish them under his name; we only have to remind ourselves how ‘loosely’ the gospels are connected with the disciples whose names they bear.

There are strong reasons for thinking that the Letters to Timothy and Titus might have originated in a similar way. On the other hand, the four great pastoral Epistles to the Galatians, Corinthians and the Romans, to which we might add the short note to Philemon, carry the style of the apostle’s style and personality on every page and in every verse. There is no question that Paul composed them and most scholars have claimed the same about Philippians and the two Letters to the Thessalonians. There is more doubt about Colossians, but the balance of probability falls in favour of Paul’s authorship, possibly with some collaboration. The inclusion of the Letter to the Ephesians is more debatable, because of the difference in style. Yet if it was written by a disciple, it must have been written by one with great insight into the mind of the apostle, and whether or not it comes from his own hand, it can be included in the canon in gaining a full picture of his thought in its fullest and most mature form.
The letters were almost all the result of some particular event, and none of them, except perhaps the Letter to the Romans, makes any attempt to present the author’s thinking in any systematic way. They were clearly written at intervals in the midst of an extremely busy life, but are also the product of a prodigious intellect responding to the challenge of practical problems of Christian living in a pagan environment, as in the correspondence with the church in Corinth, or of a subtle propaganda which seemed to be subversive of the truth, as in Galatians and Colossians. We have to interpret his teaching by gathering and combining what he wrote in different geographical contexts, to different people and at different times. His thought was formed both by his background and the environments he was writing in and for, as well as by his personal experiences. We have to take particular account of his strict Jewish upbringing and of what he owed to the primitive Christian community which he had joined at an early, formative stage in its history. What assessment can we then make of his brilliant mind and passionate heart? Tom Wright has the following answer:
For Paul, there was no question about the starting point. It was always Jesus: Jesus as the shocking fulfilment of Israel’s hopes; Jesus as the genuinely human being, the true ‘image’; Jesus the embodiment of Israel’s God – so that, without leaving Jewish monotheism, one would worship and invoke Jesus as Lord within, not alongside, the service of the ‘living and true God’. Jesus, the one for whose sake one would abandon all idols, all rival ‘lords’. Jesus, above all, who had come to his kingdom, the true lordship of the world, in the way that Paul’s friends who were starting to write the Jesus story at that time had emphasised: by dying under the weight of the world’s sin in order to break the power of the dark forces that had enslaved all humans, Israel included… Jesus was the starting point. And the goal.
Jewish Heritage, Judaism & the Nations:
God’s plan had always been to unite all things in heaven and on earth in Jesus, which meant, from the Jewish point of view, that Jesus was the ultimate Temple, the heaven-and-earth place. This, already accomplished in his person, was now being implemented through his spirit. Paul always believed that God’s new creation was coming, perhaps soon. By the time of his later letters he realised that he might himself die before it happened. But that the present corrupt and decaying world would one day be rescued from its state of slavery and death, emerging into a new life under the glorious rule of God’s people, God’s new humanity – this was something he never doubted. Insofar as there was an ‘apocalyptic’ view in Paul’s day, he shared it. He believed that Israel’s God, having abandoned the Temple at the time of the Babylonian exile, had revealed himself in Jesus, breaking in upon an unready world and an unready people. There was a certain contradiction deeply embedded in the monotheistic Judaism of the first century. The One God, it taught, was the God of the whole world, maker and ruler of all mankind. Yet in a special sense, he was the God of Israel, the nation bound to him in an ‘everlasting covenant’. The ‘charter’ of this covenant was the Law, which was held to be the perfect embodiment of the righteousness He required of men. As such it was absolute and universal, but it was also, primarily, Israel’s law. Paul himself gave eloquent expression to the pride which the Jew felt in this unique privilege:
You rely upon the Lord and are proud of your God; you know his will; instructed by the Law you know right from wrong; you are confident that … in the Law you see the very shape of knowledge and truth.
(Rom. 2: 17-20).
The possession of the Law marked Israel out as God’s chosen people, and it was to his people that God had revealed himself in ‘mighty acts’, through which his purpose was fulfilled. This was the central motive of its history and the key to its destiny. In this way, the highest moral idealism became wedded to an assertive nationalism. What then was the status and the destiny of the nations that did not know the Hebrew God? The answers to this question were various and uncertain. Some of them show a finely humane spirit which went as far as possible – without prejudice to Israel’s prior claim – in generosity to the Gentiles. Others seem to us today to approach the limits of chauvinistic nationalism. But there was in first-century Judaism a strong ‘missionary’ movement towards the pagan world. On one level, it was content to propagate the monotheistic idea and certain fundamental moral principles, but its ulterior aim was to bring Gentiles within the scope of the divine mercy by incorporation in the chosen people. The ‘proselyte’ submitted himself to the Law of God – that is, to the Jewish Law; he became a Jew.
On the other side, the question arose, what was the status and the destiny of the Jews who, knowing the Law, do not in practice observe its precepts? Here again, the answers were uncertain and various. The Law itself proclaimed a curse on all who do not persevere in doing everything that is written in the Book of Law (Gal. 3:10), and prophets and Rabbis alike use the language of the utmost integrity in castigating offenders. Yet there is a notable reluctance to admit that in the last resort any ‘son of Abraham’ could be rejected by God; for the sake of the fathers, he would come through in the end. For Paul, who looked at the matter with his broader view of the world outside Palestine, this was simply not realistic; moreover, it was inconsistent with the principle of monotheism. The One God could not be the exclusive God of the Jews; he also had to be the God of the Gentiles. The conclusion was therefore unavoidable, that…
God has no favourites; those who have sinned outside the pale of the Law of Moses will perish outside its pale, and all who have sinned under that Law will be judged by the Law.
(Rom 2: 11 f.)
Yet while this clears the ground by setting aside any notion of preferential treatment, it is a negative assessment of the human condition. There is no distinction in that all have sinned (Rom. 3: 22), so that while there may be some ‘good’ Jews who keep God’s Law (Rom. 2: 29), and some ‘good’ Gentiles who live by ‘the light of nature’ (Rom. 2: 14), Paul held that, fundamentally, human society is in breach of the Law of God and is therefore headed for ultimate disaster, subject, as he put it, to the law of sin and death (Rom. 8: 2). This universal human condition enters the experience of every individual in the desperate moral struggle which Paul has depicted with deep psychological insight in the seventh chapter of Romans: When I want to do the right, only the wrong is within my reach (Rom. 7: 21). The problem which began as a domestic concern within Judaism turned out to be a broader enquiry into the human condition. That is why Paul’s controversy with his Judaic opponents which looks, at first sights, like an antiquated, parochial dispute, turns out to have permanent significance. The only possible solution to this quandary that Paul could contemplate was a fresh divine initiative such as the one taken when he had established the covenant with Israel at Sinai. He now saw that this new initiative had actually taken place when Christ entered history:
What the law could not do because our lower nature robbed it of all potency, God has done – by sending us his Son.
(Rom. 8: 3).
The Divine Initiative – Doctrines & Metaphors:
This divine initiative is an entirely free and authentic, original act of God, conditioned only by his love for mankind while we were yet sinners (Rom. 5: 8). This is what Paul describes as the ‘grace’ of God. The response that is asked for from the people is ‘faith’, or ‘trust’ in God. In writing about this divine initiative in human experience, Paul uses a variety of expressions. The most frequently used was ‘salvation’. In common Greek usage, this word had a wide range of meanings. It could simply mean safety and security, deliverance from disaster, or good health and well-being. In effect, it conveyed the concept of a condition in which ‘all is well’, and the particular way in which that was the case depended on the context in which it was used. In Paul’s writings, as in those of the New Testament authors in general, salvation stands for a condition in which ‘all is well’ in the absolute sense; a condition in which we are secure from all evils that afflict, or menace, the human spirit, here or hereafter. Thus the expression, while strongly emotive, is hardly capable of telling us what precisely, as Paul sees it, God has done for us in Christ.
More illuminating are some of the metaphorical expressions he uses. Three of these have played a major part in the development of Christian doctrine, and need to be looked at more carefully. First, there is the legal, or forensic metaphor of ‘justification’, which we have previously encountered with Tom Wright in the context of the letter to the Galatians (Gal. 2: 15 f), but it is also a major theme in the later letter to the Romans (Rom. 3: 24, 26). Sin is conceived in this context as an offence, or offences, against the Law. The sinner stands at the bar and no-one but a judge with competent authority can condemn or acquit. Before the divine tribunal, the defendant is unquestionably guilty, but God acquits the guilty (Rom. 4: 5). Here Paul is setting out in the most challenging terms his conviction that God takes man as he is, with all his imperfections on his head, and gives him a fresh start so that he can then take on his moral task relieved of the crippling sense of guilt.
Secondly, there is the metaphor of ‘redemption’ (Rom 3: 24; 1 Cor. 1: 30; Eph. 1: 7; Col. 1: 14). The Greek word was used of the process by which a slave acquired his freedom; it means ‘release’, ’emancipation’, or ‘liberation’ (and is translated as such in the NEB). For Paul, the condition of a man caught in the moral dilemma he has described is a state of slavery, since he is unable to do what he wishes to do. But God, exercising all his supreme authority, declares the slave free, and free he is. All that Christ did – his entry into the human condition, his life of service, his suffering and death – may be regarded as the price God pays for the emancipation of the slave. The exultant note of liberation sounds all through the letters as Paul’s own experience as well as that of those he was writing to:
Christ set us free, to be free men.
(Gal. 5: 1)
Thirdly, there is the ritual metaphor of sacrifice. Sin can be regarded not only as a crime against the law, bringing a sense of guilt, or a state of slavery, bringing a sense of impotence, but also as ‘defilement’, which makes a man feel ashamed and disgusted with himself. In ancient religious defilement could be incurred in all sorts of ways, many of them having nothing to do with morals. It was assumed that the defilement could be removed by the performance of the proper ritual, most commonly, and perhaps most efficaciously, by the sacrifice of a victim. This was called ‘expiation’ or, less accurately, ‘atonement’. The metaphor of expiation, drawn from a world of thought quite alien to us, was ready to hand for anyone, like Paul, who was familiar with the elaborate ritual of sacrifice laid down in the Law of Moses, and in his time still practised in the temple at Jerusalem – or indeed for anyone acquainted with the religious rituals of the Greek states. This is the background of what he says about the work of Christ: God designed him to be the means of expiating sin by his sacrificial death (Rom. 3: 25). There is no suggestion, here or elsewhere, that Christ offered himself as a sacrifice to ‘propitiate’ an offended deity. In using the metaphor of sacrifice Paul is declaring his conviction that the self-sacrifice of Christ meant the release of moral power which penetrates to the deepest recesses of the human spirit, acting as a kind of ‘moral disinfectant’.
These are the metaphors which have most captured the imagination of Paul’s readers. His thought has sometimes been obscured through taking one of or another of them by itself, and then forgetting that it is, after all, a metaphor. What he was writing, all the time, was that in Christ God has done for us what we could never do for ourselves. The criminal could not pronounce his own acquittal, nor the slave set himself, nor could the slave set himself free, and God alone could ‘expiate’ the defilement we have brought upon ourselves. In the course of the following passage, perhaps the clearest and most succinct statement of his teaching on this theme:
From first to last this is the work of God. He has reconciled us men to himself through Christ … What I mean is that God was in Christ reconciling the world to himself, no longer holding their misdeeds against them.
The Ministry of Reconciliation:
In the idea of ‘reconciliation’, his thought passed out of mere metaphor and adopted the language of actual personal relations. Many people know something of what it means to be ‘alienated’ or ‘estranged’ – perhaps from their environment or their fellow-men, perhaps from the standards of their society, perhaps, indeed, from themselves. The deepest alienation is from the true end of our being, and that means estrangement from our Maker, out of which comes a distortion of all relationships. The great thing that God, from his side of the gulf that has opened, has put an end to the estrangement; he has reconciled us to himself. Nowhere does he suggest that God needed to be reconciled to us. His attitude towards his creatures is, and always was, one of unqualified goodwill; as Jesus himself said, he is kind to the unthankful and wicked. Out of that goodwill, he has provided the way to reconciliation.
It was entirely in harmony with the prophetic valuation of history as the field of the ‘mighty acts’ of God that Paul saw in the life, death and resurrection of Jesus Christ as one more ‘mighty act’, the ‘fulfilment’ of all that God had promised in the whole history of Israel. In common Jewish belief, the symbol of that fulfilment was the expected ‘Messiah’. After his conversion, Paul accepted what the followers of Jesus were saying, that in him the Messiah had come. But what Paul meant by ‘Messiah’ was something different from any of the various forms of Jewish messianic expectation. The messianic idea had to be re-thought in the light of a new set of facts. One invariable trait of the Messiah in Jewish expectation was that he would be the agent of God’s final victory over his enemies. On the popular level, this meant victory over the pagan empires which had oppressed the chosen people from time to time. In Paul’s thinking, the idea of the messianic victory is completely ‘sublimated’. It is the cosmic powers and authorities that Christ led as captives in his triumphal procession (Col. 2: 15). Here, Paul was drawing on mythology which belonged to the mentality of most men of his time (Rom. 8: 38; Gal. 4: 3; Eph. 6: 12; Col. 2: 8, 15, etc.) The mythology stood for something real in human experience: the sense that there are unexplained factors working behind the scenes, whether in the world or in our own ‘unconscious’, frustrating our best intentions and turning our good to evil.
As Paul saw it, Jesus was, in his lifetime, in conflict not only with his ostensible opponents but with dark forces lurking in the background. It was, Paul says, the powers that rule the world that crucified him (I Cor. 2: 8), perverting the intended good to evil ends, for neither Pilate nor the chief priests and Pharisees meant ill. But in the outcome, Jesus was not defeated, and unclouded goodness prevailed. His resurrection was the pledge of victory over all enemies of the human spirit, for it was the final victory over death, which Paul personifies as ‘the last enemy’ (I Cor. 15: 26). So, God gives us the victory through our Lord Jesus Christ (I Cor. 15: 57). It is for Paul highly significant that Jesus lived a truly human life, that he was a man and a Jew. But that does not mean that he is just one more individual thrown up by the historical process. On the contrary, his coming into the world can be seen as a fresh incursion of the Creator into his creation. God has now given the light of the revelation of the glory of God in the face of Jesus Christ (II Cor. 4: 6). In the act of creation, according to an influential school of Jewish thought, it was divine ‘wisdom’ that was at work, and Christ himself, Paul wrote, was ‘the wisdom of God’ visibly in action among men (I Cor. 1: 24). According to these Jewish thinkers, this wisdom was the flawless mirror of the active power of God and the image of his goodness (Wisdom of Solomon 7: 26). So Christ, Paul says, is the image of the invisible God (Col. 1: 19).
This was a new historical phenomenon, to be brought into relation with the history of Israel as the field within which the purpose of God was working itself out. The formative motive of that history was the calling into existence of a ‘people of God’ – a divine commonwealth – in and through which the will of God might be done on earth, an ‘Israel’ worth the name. The distinguishing mark of such an ‘Israel’, Paul wrote, was to be found in the promise made to Abraham, the founder of the Hebrew people, that in his posterity all nations shall find blessing (Gal. 3: 8). This ideal had never yet been realised, though in successive periods there had been some who had it in them to become such people, the ‘remnant’ of which prophets spoke (Rom. 9: 27; 11: 5). In the emergent church of Christ, Paul saw the divine commonwealth coming into active existence. If you belong to Christ, he writes, you are the issue of Abraham (Gal 3: 29), i.e. you are the true Israel in whom all nations shall find blessing.
Church & Sacraments:
 Here we have a pointer to one reason, at least, why Paul set such store by his mission to the Gentiles. The church was the consummation of a long, divinely directed, history. It is a theme to which he returns in the long and intricate discourse in Romans (9-11). The new, supra-national Israel was constituted solely on the basis of ‘belonging to Christ’, and no longer on racial descent or attachment to a particular legal system. Paul wrote: you are all one person in Christ Jesus (Gal. 3: 28). The expression ‘in Christ’ is one which recurs with remarkable frequency throughout Paul’s letters. The reality of the doctrine for which it stands was present in the church from the beginning in the two rites of baptism and the ‘breaking of bread’. It was through baptism that a person was incorporated into the community of Christ’s followers. In its suggestive ritual, in which the convert was ‘buried’ by immersion in water, and came out cleansed and renewed, Paul saw a symbolic re-enactment of the death and resurrection of Christ:
Here we have a pointer to one reason, at least, why Paul set such store by his mission to the Gentiles. The church was the consummation of a long, divinely directed, history. It is a theme to which he returns in the long and intricate discourse in Romans (9-11). The new, supra-national Israel was constituted solely on the basis of ‘belonging to Christ’, and no longer on racial descent or attachment to a particular legal system. Paul wrote: you are all one person in Christ Jesus (Gal. 3: 28). The expression ‘in Christ’ is one which recurs with remarkable frequency throughout Paul’s letters. The reality of the doctrine for which it stands was present in the church from the beginning in the two rites of baptism and the ‘breaking of bread’. It was through baptism that a person was incorporated into the community of Christ’s followers. In its suggestive ritual, in which the convert was ‘buried’ by immersion in water, and came out cleansed and renewed, Paul saw a symbolic re-enactment of the death and resurrection of Christ:
… by baptism we were buried with him and lay dead, in order that as Christ was raised from the dead in the splendour of the Father, so also we might set our feet on the new path of life (Rom. 6: 4).

Baptism affirmed the solidarity of all members of the church with Christ. So, even more clearly and emphatically, did the other primitive sacrament of the church. From the first, its fellowship had been centred in the solemn ‘breaking of bread’ at a communal meal. As the bread was broken, they recalled the mysterious words which Jesus had spoken when he broke bread for his disciples at his last supper: ‘This is my body’ (I Cor. 11: 23 f.). Reflecting on these words, Paul observed, first, that in sharing bread the company established a corporate unity among themselves: We, many as we are, are one body, for it is one loaf of which we all partake (I Cor. 10: 17). Also, Christ himself had said, This is my body. Consequently, when we break the bread, it is a means of sharing the body of Christ (I Cor. 10: 16). The church, therefore, is itself the body of Christ; he is the head, and on him, the whole body depends (Eph. 4: 16). It is in this way that the new people of God is constituted, ‘in Christ’.

In all forms of Jewish messianic belief, it was common ground that the Messiah was, in some sense, representative of Israel in its divine calling and destiny. Paul presses this idea of representation further by stating that those who adhere to Christ in sincere faith are identified with him in a peculiarly intimate way as if they were being included in him in his own being. He was the inclusive representative of the emergent people of God. Another way of putting it is to say that Christ is the second ‘Adam’, symbolic of the new humanity of which the church was the head. In the Jewish schools of thought where Paul had his training, there was much speculation about the ‘First Adam’ and about the way in which all men, as ‘sons of Adam’, are involved in his fortunes as depicted mythologically in Genesis. Paul takes up this idea: mankind is incorporate ‘in Adam’; emergent new humanity is incorporate ‘in Christ’: As in Adam all men die, so in Christ, all will be brought to life (I Cor. 15: 22; Rom. 5: 12-14). Once again, we see here a fresh expansion of the messianic idea.
The church, as the new ‘Israel of God’, in its essential nature was a united entity and this unity, he argued, should be reflected in the life of every local congregation; he was dismayed to see it being disrupted. In particular, there were persisting influences, both pagan and Jewish, in the minds of those so recently converted. Paul discusses, for example, divergences among Christians about the continued observance of Jewish holy days and food regulations (Rom. 14), and, on the other side, about the extent to which they might share in the social life of their pagan neighbours without sacrificing their principles (I Cor. 8: 1-13; 10: 18-33). But apart from such special discussions, Paul insisted on the idea of the church as a body, analogous to a living organism, in which the parts, while endlessly various, are interdependent and subordinate to one another, and each makes its indispensable contribution to the well-being of the whole. There is a passage in his First Letter to the Corinthians (12: 14-27) which is the classical statement of the idea of the social organism. He develops this idea in relation to his governing conception of the church as the body of Christ. In all its members, it is Christ who is at work, and God in Christ, through his Spirit:
There are varieties of gifts, but the same Spirit. There are varieties of service, but the same Lord. There are many forms of work, but all of them, in all men, are the work of the same God.
(I Cor. 12: 4-11).
We can see from the lists of ‘services’ in other letters (Rom. 12: 6-8; Eph. 4: 11 f.) just how complex and sophisticated the activities of the ‘primitive’ church had already become in Paul’s time. It is in this context that Paul develops his doctrine of the Spirit, which is another of his most original contributions to Christian thought. It was an innovation rooted in what he had taken from his own Jewish background as well as from the first Judaic Christians. In some forms of Jewish messianic expectation, it was held that in the days of the Messiah, or in the age to come, the divine Spirit, which was believed to have animated the prophets and heroes of Israel’s remoter past, would be poured out afresh, and in a larger measure (Acts 2: 16-18). The early followers of Jesus, when the realisation had broken upon them that he had risen from the dead, had experienced an almost intoxicating sense of new life and power. It was accompanied, as often happens in times of religious ‘revival’, by abnormal psychic phenomena, including visions, the hearing of voices, and ecstatic utterance or ‘speaking with tongues’. The early Christians valued these as evident signs that God was at work among them through his Spirit. These abnormal phenomena reproduced themselves in the new Christian communities which sprang from Paul’s mission to the Gentiles, and here they created an exciting atmosphere which he also saw to be full of danger.
Liberty & the Gifts of the Spirit:
The situation needed careful handling since Paul did not want to be seen as damping down the enthusiasm of which these strange powers were one expression (I Thess. 5: 19-21). Nor did he wish to deny that they could be the outcome of genuine inspiration. He knew from his own personal experience what it was to have visions and to hear voices (II Cor. 12: 1-4), and he could himself ‘speak with tongues’ (I Cor. 14: 18). But there were other ‘gifts of the Spirit’, less showy, but in the end far more important to the community, such as wisdom, insight, powers of leadership, the gifts of teaching, administration, and the meeting of needs of those in states of deprivation and/or distress (Rom. 12: 6-8; I Cor. 12: 28). These were gifts which helped ‘build up’ the community (I Cor. 14:12) and in emphasising them Paul diverted attention away from the abnormal and exceptional to such moral and intellectual endowments as any society would wish to find among its members. It was their devotion to such endowments to the common good that gave them real value.
It was this original concept of the Spirit as the mode of Christ’s own presence in his church opens up a new approach to ethics. Paul found himself obliged to meet a formidable challenge to his message that the Christian is free from the ‘bondage’ of the law since Christ annulled the law with its rules and regulations (Eph. 2: 15). This kind of language ran the risk of being misunderstood. His Jewish critics, both inside and outside the church, suspected that in sweeping away the discipline of the Mosaic Law he was leaving his Gentile converts without moral anchorage in a licentious environment. Paul scarcely realised at first how open to misconstruction his language was. He soon discovered that he was widely understood to be advocating a purely ‘permissive’ morality, which was in fact far from his intention. People were claiming, We are free to do anything (I Cor. 6: 12; 10: 23), in the belief that they were echoing his own views. He did point out that there were some obvious limits on freedom and that Christian morality was not conformity to an external code but sprang from an inward source. The transformation which this involved was made effective by the work of the Spirit within as the true source of Christian character and action:
“We are free to do anything,” you say; but does everything help to build up the community?
(I Cor. 10: 23)
You were called to be free men, only do not turn your liberty to license for your lower nature.
(Gal. 5: 13)
Let your minds be remade, and your whole nature transformed; then you will be able to discern the will of God, and to know what is good, acceptable and perfect.
(Rom. 12: 2)
The harvest of the Spirit is love, joy, peace, patience, kindness, goodness, fidelity, and self-control. There is no law dealing with such things as those.
(Gal. 5: 22 f.).
The church was under a ‘new covenant’, which was not, like the ‘old covenant’, guaranteed by a single code of commands and prohibitions engraved letter by letter upon a stone (II Cor. 3: 7), but by the Spirit animating the whole body of the church. But that Spirit was not simply an ‘inner light’, but the Holy Spirit, the Spirit in the church which is the Spirit of Christ working in the members of his body. This was the historical Christ who had lived and taught, died and rose again. Christians who had received the Gospel and teaching that went with it were in a position to know what it was like to be ‘Christlike’ in character and conduct, and this was an objective standard by which all inner promptings could be brought to the test. It might even be described as the law of Christ (Gal. 6: 2; I Cor. 9: 21), but Paul was obviously cautious of using such quasi-legal language; he did not wish to be introducing a kind of new Christian legalism. The ‘law of Christ’ and the ‘life-giving law of the Spirit’ are, for Paul, one and the same thing (Ro. 8: 2). Sometimes Paul wrote as if the ‘reshaping’ of the mind of the Christian took place almost immediately upon their becoming believers, but there are sufficient passages in his letters which reveal that he was aware that the process might be gradual, perhaps lengthy (Gal. 4: 19; Eph. 4: 13; I Cor. 9: 26) and possibly never completed in this life (Phil. 3: 12-14). But once the process was genuinely underway, a believer was ‘under the law of Christ’, and Christ himself – not the Christian’s own ideas, not even in the end, his conscience – is the judge to whom he defers in all his actions (I Cor. 4: 3 f.).
Loving-kindness – The Law of Christ & Social Ethics:
The ‘law of Christ’ is, therefore, Christ himself working through his Spirit in the church to give ethical direction. And it is all that we know of Christ that comes into it – his teaching, the example of his actions, and the impact of his death and resurrection. These acted as influences on Paul’s thought, not as from outside, but creatively from within. His ethical judgements are informed by the Spirit of Christ and yet are intimately his own. That is why the law of Christ, while it commands him absolutely, can never be thought of as a ‘bondage’, as the old law with its rules and regulations; where the Spirit of the Lord is, there is liberty (II Cor. 3: 17). Paul’s ethical teaching, therefore, is the application of what it means to be ‘Christlike’. His death is the commanding example of self-sacrifice for the sake of others (Gal. 2:20; Eph. 5: 2, 25), and it was his expression of his limitless love for mankind (Rom. 8: 34 f.; Eph. 3: 18 f.).
It is this quality of love, above all, that Paul holds up as the essence of what it means to be ‘Christlike’, and as the basic and all-inclusive principle of Christian living (Rom. 13: 8-10; Gal. 5: 14; Col. 3: 14; Eph. 1: 4). The word he uses is the almost untranslatable agape, a word first brought into common use in a Christian setting. It can be rendered by the older use of the word charity, from the Latin Caritas. ‘Agape’ includes feelings of affection (Rom. 12. 9 f.), but it evokes, more fully and fundamentally, the energy of goodwill or ‘loving kindness’ emanating unconditionally towards others, regardless of their merit, worthiness or attractiveness. The eloquent passage in I Corinthians 13, which has the feeling of a hymn to agape, contains pointers to the kind of attitude and behaviour it inspires, and in this context, it is presented as the highest of all ‘gifts of the Spirit’ (I Cor. 12: 31; 14: 1). It is in this ‘hymn’ that the ‘law of the Spirit’ and the ‘law of Christ’ become intertwined and thereby completely indistinguishable.
Agape, then, is the source of the distinctively Christian virtues and graces of character. It is also the most constructive principle in society; it is love that builds (I Cor. 8: 1). Thus the ideas of the building of the body and the centrality of love imply one another and form the effective basis for Paul’s teaching on social ethics. The whole of Christian behaviour can be summed up in the maxim, Love one another as Christ loved you (Eph. 5: 1; Gal. 5: 13 f.; I Thess. 4: 9; Col. 3: 14). This does not mean, however, that Paul is content to say, Love and do as you please. Nor, on the other hand, does he undertake to show how detailed rules of behaviour could be derived deductively from a single master-principle. Ethical behaviour is essentially an individual’s response to actual situations in which he finds himself in day-to-day living as a member of society. Paul envisages his readers not just in any society, but in the particular society in which their daily lives must be lived, namely the Graeco-Roman world, which he knew so well, with its political, legal and economic institutions, and within that world, the young Christian communities with their distinctive ethos and unique problems. He indicates, always in practical terms, how this whole network of relations may be permeated with the Christian quality of living.
How close these immature Christians stood to the corruptions of paganism, and how easily they could relapse into them can be gathered by some of the startling remarks which he lets fall about his converts (I Cor. 5: 1 f.; 6: 8-10; Col. 3: 5-7; I Thess. 4: 3-8), as well as from the passion with which he insists that there must be a complete break with the past (Col. 3: 5-10). So alarmed was he at the possibility of the infection of immorality that he sometimes writes as if the only safe way of avoiding this was for the church to withdraw from pagan society altogether (II Cor. 6: 14-18); but he had to explain that this was not his real intention: the idea that Christians should avoid dangerous contacts by getting right out of the world he dismisses as absurd (I Cor. 5: 9-13). In fact, it is clear that he envisaged Christians living on good terms and in normal social intercourse with their pagan neighbours (I Cor. 10: 27 f.). Their task was the more difficult one of living as full members of the society in which their lot was cast, while firmly renouncing its corruptions; to be in it, but not of it. But although deeply corrupted, Graeco-Roman civilisation was not without moral ideals. A certain standard of what was ‘fitting’ was widely accepted, at least in public. The Stoics spoke of it as the general feeling of mankind (communis sensus hominum), and there was a genuine desire to see this standard observed in corporate life. Paul was well aware of this, as he shows when he enjoins his readers: Let your aims be such as all men count honourable (Rom. 12: 17). Even after his fierce castigation of pagan vices at the beginning of his Letter to the Romans he goes on to write that the good pagan may do God’s will by the light of nature; his conscience bears true witness (Rom. 2: 14 f.). There is a broad universality about what he writes to the Philippians:
All that is true, all that is noble, all that is just and pure, all that is lovable and gracious, whatever is excellent and admirable – fill all your thoughts with these things.
(Phil. 4: 8)
It is therefore not surprising that Paul was concerned to work out his sketch of Christian behaviour within the framework of Graeco-Roman society as it actually existed, rather than as Christians might have wanted it to be. The empire was, for him, part of the divinely given setting for a Christian’s life in the world, and he made it clear that he would be following the law of Christ in obeying the Roman law, respecting the magistrates, and paying his taxes. This was an obligation imposed not merely by fear of retribution but by conscience. In fact, the fulfilment of such obligations is an application of the maxim, Love your neighbour as yourself (Rom. 13: 1-10). Similarly, in dealing with family life he took over a general scheme current among Stoics and moralists at the time which assumed the existing structure of the Graeco-Roman household, with the paterfamilias as the responsible head, and the other members, including the slaves, having their respective obligations (Eph. 5: 21 – 6: 9; Col. 3: 18 – 4: 1), and indicated how within this general structure Christian principles and values could be applied.
As far as Paul is concerned, marriage is indissoluble for Christians because there is a saying of the Lord to that effect (I Cor. 7: 10 f.; Mark 10: 2-9). Beyond that, because in Christ there is no distinction between man and woman (Gal. 3: 28), although the husband is usually the head of the household, the marriage relation itself must be completely mutual as between husband and wife. Neither can claim their own body ‘as their own’ (I Cor. 7: 4). This bond is so sacred that in a mixed marriage the ‘heathen’ spouse is ‘holy’ to God, as are the children of such a marriage (I Cor. 7: 14). So the natural ties of family relationships are valid within the Christian fellowship which is ‘the body of Christ’. However, in I Cor. 7: 26-29, Paul apparently ‘entertained’ the belief that family obligations were of limited relevance since the time we live in will not last long. It was only by the time he wrote to the Colossians that he had fully accepted the principle that family life should be part of life ‘in Christ’, though even then he only gave some brief hints about what its character should be (Col. 3: 18-21).
The Graeco-Roman household also included slaves, and here again, Christian principles and values began to make inroads into this practice. It was a fundamental principle that in Christ there was neither slave nor free man (Gal. 3: 28, Col. 3: 11). Accordingly, there is a level on which their status is equal:
The man who as a slave received the call to be a Christian is the Lord’s freedman, and, equally, the free man who received the call is a slave in the service of Christ.
(I Cor. 7: 22)
In writing to the Colossians he urges slaves to give their service…
… as if you were doing it for the Lord and not for men… Christ is the Master whose slaves you must be; … Masters, be fair and just to your slaves, knowing that you too have a master in heaven.
(Col. 3: 23 f.; 4: 1)
The Christian ideal of free mutual service transcended the legal relations of master and slave. The letter to Philemon is a short ‘note’ in which Paul deals with the particular case of the recipient’s runaway slave, Onesimus, who had also helped himself to his master’s cashbox. Somehow or other Paul came across him, and converted him. Under Roman law, anyone harbouring a fugitive slave was liable to severe penalties, and a runaway recovered by his master could expect no mercy. Paul decided to send Onesimus back to his, trusting that the ‘law of Christ’ would transform their relationship from within, without disrupting the civil order, and in Philemon’s readiness to take a fully Christian view of the matter:
Perhaps this is why you lost him for a time, that you might have him back for good, no longer as a slave, but as more than a slave, as a dear brother.
(Philemon 12-16)

Paul’s Eschatology – Christ, the Church & the Future:
The permeation of the church, and ultimately of society, with the Christian quality of life gives actuality to Paul’s doctrine of the indwelling of Christ, through his Spirit, in the body of his followers, the church. It is not simply the experience of an individual, but a force working in history. But if Christ is thus present in the church, then he has to be known not only through his historical life, supremely important as that is, but also in what he is doing in and through the church in the present and in the future into which the present dissolves at every moment. His brief career on earth had ended, so far as the world, in general, could see, in failure. His disciples may have known better, but how was the world to know? For many early Christians, the very short answer to this question that, very shortly, he would ‘come again’, and then ‘every eye shall see him’ (Rev. 1: 7). Paul began by sharing this belief. At the time when he wrote his earliest surviving letters (as they probably are), to the Thessalonians, he seems to have had no doubt that he and most Christians would live to see the ‘second advent’ (II Thess. 2: 1-3; 4: 15). Even when he wrote his first letter to the Corinthians he was still assured that ‘we shall not all die’ (I Cor. 15: 51). Before he wrote the second letter there was an occasion when his life was despaired of (II Cor. 1: 9), and it may be that for the first time he faced the likelihood that he would die before the Day, and in that way ‘go to live with the Lord’ (II Cor. 5: 8). At any rate, from this time we hear little more of the expectation of earlier years.

Tom Wright suggests that when writing II Thessalonians, Paul had perhaps foreseen the fall of Jerusalem of AD 70, quite possibly through a Roman emperor doing what Caligula had so nearly done. The ultimate monster from the sea, Rome itself, would draw itself up to its full height, demolishing the heaven-and-earth structure that had (according to Jesus) come to embody Jeremiah’s “den of robbers.” Jesus would then set up his kingdom of a different sort, one that could not be shaken. But if Jerusalem were to fall to the Romans, Paul had to get busy, because he knew what reactions such a terrible event would produce. Gentile Christians would claim that God had finally cut off the Jews, leaving ‘the church’ as a non-Jewish body. Christianity would become ‘a religion’ to be contrasted (favourably, of course) with something called ‘Judaism’. Conversely, Jewish Jesus-followers would accuse their Gentile brethren – and particularly the followers of Paul – of having precipitated this disaster by imagining that one could worship the true God without getting circumcised and following the whole Torah. And Jews who had rejected the message of Jesus as Messiah would be in no doubt at all that all this had happened because of this ‘false prophet’ and the renegade Saul, who had led Israel astray. Wright’s supposition leads him to believe that Paul was therefore determined…
… to establish and maintain Jew-plus-Gentile communities, worshipping the One God in and through Jesus his son and in the power of the spirit, ahead of the catastrophe.
Only in this way, he believed, could this potential split, the destruction of the ‘new Temple’ of I Corinthians 3 and Ephesians 2, be averted. This is why Paul insisted, in letter after letter, on the unity of the church across all traditional boundaries. This was not about the establishment of a new ‘religion’ and had nothing to do with Paul being a “self-hating Jew”. This anti-Semitic slur is still found in ill-informed ‘studies’ of his work, but Paul affirmed what he took to be the central features of the Jewish hope: One God, Israel’s Messiah, and resurrection itself. For him, what mattered was messianic eschatology and the community that embodied it. The One God had fulfilled, in a way so unexpected that most of the guardians of the promises had failed to recognise it, the entire narrative of the people of God. That was what Paul had been preaching in one synagogue after another. It was because of that fulfilment that the Gentiles were now being brought into the single family. The apostle came to be less preoccupied with a supposedly imminent ‘second advent’ as he explored the range of Christ’s present activity in the church. He saw the church expanding its influence abroad, and developing internally the complexity that marks the evolution of a living organism. If all this raised some problems, it was all part of the growth of the body – of Christ’s body – and it was Christ’s own work:
It is from the Head that the whole body, with all its joints and ligaments, receives its supplies and thus knit together grows according to God’s design.
(Col. 2: 19)

This, as Paul saw it, was the way in which Christ is revealed to the whole universe (Eph. 3: 10). Nor is there any limit to this growth, until we all, at last, attain the unity inherent in our faith (Eph. 4: 13). In the church, Paul saw men actually being drawn into unity across the barriers erected by differences of ethnicity, nationality, language, culture or social status. He was powerfully impressed by the reconciliation of Jew and Gentile in the fellowship of the church (Eph. 2: 11-22). In this, as his horizons widened, he saw the promise of a larger unity, embracing all mankind (Rom. 11: 25-32). In this unity of mankind, moreover, he finds he finds the sign and pledge of God’s purpose for his whole creation. In a passage which has much of the visionary quality of poetry or prophecy, he pictures the whole universe waiting in eager expectation for the day when it shall enter upon the liberty and splendour of the children of God (Rom. 8: 19-21). In the church, therefore, can be discerned God’s ultimate design to reconcile the whole universe to himself… to reconcile all things, whether on earth or in heaven, through Christ alone (Col. 1: 20). Such was the vision of the future which Paul bequeathed to the church for its inspiration. In a sense then, he continued to believe that he was living in the last days. For him, God had, in sending the Messiah, had brought the old world of chaos, idolatry, wickedness, and death to an end. Jesus had taken its horror onto himself and had launched something else in its place. But, as Tom Wright puts it…
… that meant that, equally, Paul was conscious of living in the first days, the opening scenes of the new drama of world history, with heaven and earth now held together not by Torah and Temple, but by Jesus and the Spirit, pointing forward to the time when the divine glory would fill the whole world and transform it from top to bottom.

This vision was not to be found in the non-Jewish world of Paul’s day. It was a thoroughly Jewish eschatology, shaped around the one believed to be Israel’s Messiah. Paul believed, not least because he saw it so clearly in the scriptures, that Israel too had its own brand of idolatry. But the point of Jesus’s ‘new Passover’ was that the powerful ‘gods’ and ‘lords’ to which mankind had given away their authority, had been defeated. The resurrection proved it and had thereby launched a new world with a new people to reflect the true God into that new world. That is why Paul’s Gentile mission was not a different idea from the idea of forgiveness of sins or the cleansing of the heart. It was because of the powerful gospel announced and made effective those realities that the old barriers between Jew and Greek were abolished in the Messiah. That is why Paul’s work just as much as ‘social’ and ‘political’ as it is ‘theological’ or ‘religious’. Every time Paul expounded ‘justification’, it formed part of his argument that in the Messiah there was a single family consisting of believing Jews and Gentiles, a family that demonstrated to the world that there was a new way of being human. Paul saw himself as a working model of exactly this:
Through the law I died to the law, so that I might live to God.
Sources:
C. H. Dodd (1970), Paul and His World; The Thought of Paul, in Robert C Walton (1970), A Source Book of the Bible for Teachers. London: SCM.
N. T. Wright (2018), Paul: A Biography. London: SPCK.
Alan T. Dale (1979), Portrait of Jesus. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Part Three: The Third Missionary Journey, Jerusalem & Rome.

Chronology:
The chronology of Paul’s career cannot be fixed precisely, but fortunately, we have one precise date to start from. The proconsul before whom Paul was cited at Corinth on his first visit there was Junius Annaeus Gallio, who was known to have held the appointment from July AD 51 to June AD 52. Based on the reports of this visit in Acts, Paul was in Corinth from early in 50 to late 51. From this fixed point, we can then calculate backwards and forwards, using the indications of time supplied in Paul’s own letters or in Acts. If Paul reached Corinth early in 50, then his ‘Second Missionary Journey’ must have begun in 49, and the visit to Jerusalem which preceded it, when he came to an agreement with the leaders of the church there, would presumably have taken place in AD 48. Paul dates his earlier visit to Jerusalem fourteen years before, pointing to AD 35, three years after his conversion, which has therefore been tentatively dated to AD 33. When exactly Paul arrived at Ephesus is a matter of conjecture, but we know that he established himself there for a full three years. His stay there seems to fall between 54 and 57 AD, rather than any earlier, and it was between these years that he undertook his ‘Third Missionary Journey’.

Ephesus & Corinth:
The ‘Third Missionary Journey’, through the interior of Asia Minor, is given the most cursory treatment in Luke’s diary which constitutes much of the Acts of the Apostles. He seems to be in a hurry, as Paul himself probably was, to reach Ephesus (Acts 18: 23; 19: 1). It is evident that he had formed definitive ideas about the most effective way of conducting his mission. He decided not to cover ground by moving rapidly from place to place, but to settle, as he had done at Corinth, in a suitable centre from which he could reach a whole province. Ephesus was to prove to be such a centre as one of the principal cities of the province of Asia, with excellent communications by land and sea. Settled by Greeks in antiquity, but always with something oriental about it, it had been a meeting place of East and West long before the conquests of Alexander had inaugurated the Hellenistic age. Its world-famous temple was dedicated to the native Anatolian fertility-goddess, Artemis, or Diana to the Romans (Acts 19: 27; 34 f.), though she had little in common with the virgin huntress of the classical pantheon. From ancient times a seat of Greek philosophical thought, Ephesus was also hospitable to all manners of superstitions, and in Paul’s time it was notorious as a centre of the ‘black arts’ of magic (Acts 19: 18 f.). This was the place which for the next three years or so was to be Paul’s headquarters (Acts 20: 31). There are evident signs that this was a planned strategy on his part. Ephesus was another meeting point of trade routes and cultures, and therefore an excellent place from which to disseminate the gospel.

Paul arrived in Ephesus and began as always in the synagogue, this time for three months. Opposition grew, however, as the disturbing implications of Paul’s way of reading the familiar stories dawned upon the puzzled hearers. Resistance hardened, and this may have been one of the occasions when submitting to synagogue discipline, Paul received the official Jewish beating of forty lashes. He tells us that he had received this five times, which in itself indicates his steady commitment to working with the synagogue congregations as long as he could since he could easily have avoided the punishment by simply not turning up. Some of the Jewish community in Ephesus had begun to spread rumours about what this “Messiah cult” was doing. From later writings, we can guess at the sneering comments about what these ‘Jesus-worshippers’ were up to behind closed doors, with men and women meeting together and talking about a new kind of “love,” not to mention the disturbing gossip about eating someone’s body and drinking their blood. So Paul realised, as he had done in Corinth, that he could no longer treat the synagogue as his base. It was time to move elsewhere. He formally ‘withdrew his converts’ and established himself on neutral territory in a lecture hall in the city, which he rented. For the next two years, he divided his time between his tent-making business and the public exposition of the faith. He held daily conferences at the hall, open to all comers, which attracted numbers of residents to the city (Acts 19: 8-10). People came from far and wide, spent time in the city, and then went on their way. They chatted about anything strange or new that they had come across in their travels. The group of early Christians who met in the lecture hall was one of these.
By this time, Paul had built up an efficient ‘staff’, whose names keep recurring in his letters – Timothy (Rom. 16: 21; 1 Cor. 4: 17; 16: 10; Phil. 2: 19-23 etc.), Luke, Tychicus (Eph. 6: 21; Col. 4: 7; II Tim. 4: 12; Titus 3: 12) and several others, though Silas had, by this time, faded out of the narrative. They were available either to work by his side at the headquarters or to be sent where they could be useful in keeping in touch with churches already founded, or in breaking new ground. It was in this way that Paul’s mission in the province spread. We happen to learn from his letters the names of the three up-country towns where churches were founded without any visit from the apostle himself – Colossae, Laodicea and Hierapolis (Col. 1: 7; 2: 1; 4: 13-16) – and there were certainly others. The author of Acts says, perhaps with some exaggeration, that…
…the whole population of the province of Asia, both Jews and pagans, heard the word of the Lord.
(Acts 19: 10)
Meanwhile, however, trouble was brewing. There was furious opposition from the Jews (Acts 20:19), and some from pagan quarters (Acts 19: 23-27), though we hear also of some of the dignitaries of the province who were friendly towards him (Acts 19: 31). We have some record both in Acts and in the letters (I Cor. 15: 32; II Cor 1: 8). From the letters to the Corinthians we also learn something that the author of Acts does not tell us, that Paul was, at this time, driven almost to distraction by disorder in the church in Corinth. In a climactic passage of his letter to the Galatians, he had pointed out that the Messiah’s people had ‘died’; they had left behind their old identities as Jews or Gentiles and had come into a new identity (Galatians 2: 19-21). That was, in part, why the gospel was “a scandal to Jews,” but, at the same time, only makes sense within a deeply Jewish, messianic view of the world. Charged with his specific responsibility, Paul was able, without compromising that messianic identity, to live alongside people of all sorts, sharing their customs while he was with them. When he had dinner with Jewish friends, they would have eaten ‘kosher’ food together, and when he went to dinner with non-Jewish friends, he would have eaten whatever they put in front of him (I Cor. 10: 27). What would then have made the difference was ‘conscience’, not Paul’s, but that of anyone else who might have been offended or who might be led back into idolatry.

This must have been a much harder path to tread than that sketched in the apostolic letter issued after the Jerusalem Conference in which simple abstinence from all relevant foods was enjoined. Paul not only thought that this was unnecessary, but that it violated the fundamental principles of Jewish belief itself. His own pragmatic solution must have seemed not just paradoxical, but also perverse to some. For instance, a Jewish family who had shared a meal with Paul and watched him keep all the Jewish customs must have found it strange that the same week he had dined with a Gentile family and eaten what they were eating, though a Gentile family would have seen little harm in it. But, once again, Paul is teaching in his letter to the Corinthians that they should think like the people of the Messiah, building on the foundation of Israel’s scriptures, interpreting them afresh in the light of the crucified and risen Messiah himself. So in Chapter eleven of his epistle, he deals with the problems of the family meal, the Lord’s Supper or ‘Eucharist’. Then in Chapter twelve, he addresses the question of unity in the fellowship and the way in which the Spirit gives to each member of ‘the Messiah’s body’ different gifts to be used for the benefit of all. In Chapter fourteen, Paul applies this to the corporate worship of the church, following his exquisite poem about divine love, agape, in chapter thirteen. In this, Paul is not just teaching them ‘ethics’, but also to think eschatologically:
We know, you see, in part;
We prophesy in part; but, with perfection,
The partial is abolished. As a child
I spoke, and thought, and reasoned like a child;
When I grew up, I threw off childish ways.
For at the moment all that we can see
Are puzzling reflections in a mirror;
But then I’ll know completely, through and through,
Even as I’m completely known. So, now,
Faith, hope and love remain, these three; and, of them
Love is the greatest.
(I Cor. 13: 9-13).
Love is not just a duty. Paul’s point is that love is the believer’s destiny. It is the reality that belongs to God’s future, glimpsed in the present like a puzzling reflection, but waiting there in full reality for the face-to-face future. And the point is that this future has come forward to the present time in the events involving Jesus and in the power of the spirit. That is why love matters for Paul even more than faith, which many have seen as his central theme. Love is the present virtue in which believers anticipate and practice the life of the ultimate life to come. That’s why the final theological chapter, fifteen, dealing with the resurrection of the body, is the centre of the gospel. It is also the beginning of a study I have made elsewhere on this website in a series of articles examining the role of eschatology in Christian thought from Paul onwards. Paul’s main point in relation to the fulfilment of Israel’s hope is about messianic eschatology. He is not saying, “We Jesus-followers have found a better sort of religion than the old Jewish one.” But if Israel’s Messiah has come and has been raised from the dead, then those who follow him are the true people of God. This is blunt but consistent and precisely what the followers of the other first-century Jewish leaders would have said. It was not disloyalty to Israel’s God, but the contested messianic loyalty that characterised Paul’s missionary thought and journeys throughout.
Jesus had described himself at his trial by the Sanhedrin as the ‘Son of Man’, which was the Hebrew and Aramaic way of saying ‘man’ and could even be used to describe the Jewish people themselves who believed themselves to be ‘God’s People’. Jesus used the words not just to describe his own ministry, but about himself and his friends, the new ‘People of God’. The word ‘Christ, the Greek translation of ‘Messiah’, meaning ‘the one who is anointed’, was a word Jesus seemed not to like and was more wary of using, including of himself. When Peter had used the word of him, he rebuked him for doing so. It was a word with a long history. Kings had been ‘anointed’ and prophets had been spoken of as ‘anointed’. The word was even used of a foreign emperor, Cyrus. In the years before Jesus began his ministry, the word had come to represent God’s ‘Chosen Leader’ whom the Jewish people expected God to send as their deliverer. But this ‘Chosen Leader’ was thought of in many different ways – sometimes as a supernatural figure, sometimes as a soldier. Yet although he did not like the word and did not use it of himself, Pilate had had him executed as a ‘messiah’, a claimant to the leadership of the Jewish people – ‘the Jewish King’, as he had put it on the official death-notice on the cross.
It seemed to Jewish Christians that no word described him better – he was ‘God’s Chosen Leader’. They began to talk about him as ‘Jesus the Messiah’, where ‘Messiah’ is a simple descriptive name. When ‘Messiah’, however, was translated into Greek as ‘Christ’, it began to change its meaning. Greek-speaking ‘foreigners’ didn’t understand it and simply used it as Jesus’ second name. Paul, of course, knew the Jewish world from the inside and used the word ‘Christ’ in his letters to describe the whole influence of Jesus – his life in Palestine and the new experience of God which he made possible, so that he could use the words ‘Spirit’, ‘Spirit of God’ and ‘Spirit of Christ’, as we have seen, to describe this new experience. Paul was struggling with an almost impossible task, and he was aware of how difficult it was. But to talk about Jesus as though he was not just a good man who had died was to be false to what he felt in his heart the new divine experience to be. His meeting with the Messiah on the Damascus Road fulfilled everything and thereby changed everything, as the following statement made clear:
Whatever I had written in on the profit side, I calculated it instead as a loss – because of the Messiah. Yes, I know that’s weird, but there’s more: I calculate everything as a loss, because knowing King Jesus as my Lord is worth far more than everything else put together! In fact, because of the Messiah I’ve suffered the loss of everything, and I now calculate it as trash, so that my profit may be the Messiah, and that I may be discovered in him, not having my own covenant status defined by the Torah, but the status which comes through the Messiah’s faithfulness: the covenant status from God which is given to faith. This means knowing him, knowing the power of his resurrection, and knowing the partnership of his sufferings. It means sharing the form and pattern of his death, so that somehow I may arrive at the final resurrection from the dead.
(Phil. 3: 7-11).

The Messiah regarded his status, “equality with God”, not as something to exploit, but as committing him instead to the life of the ‘servant’ and the shameful death of the ‘slave’. That is why he was now exalted as Lord over all. ‘Lord’ was another word the early Christians used as a common way of identifying Jesus; he was ‘the Lord Jesus Christ’. The word ‘Lord’ had been used for God in the Old Testament; God was ‘Lord’. It was also used to describe the Roman Emperors and some of the pagan gods. As Paul once wrote, There are many gods and many lords. So it came to be used of Jesus; to say that “Jesus is Lord” became the simplest way for believers to proclaim their Christian faith. It carried a sense of his presence, his love and his forgiveness, of the power to live in his way, which He gave to all who accepted his love. This is what lay at the back of the struggle to find words that really described what Jesus meant to his followers. The passage above is focused not just on a belief or theory about the Messiah, but on personal knowledge. Paul wrote of knowing King Jesus as my Lord, of knowing him, knowing the power of his resurrection, and knowing the partnership of his sufferings. Paul knew the theory thoroughly, but it meant nothing without the awareness of the person and presence of Jesus himself. His personal ‘knowledge’ of the Messiah found intimate expression in suffering. He speaks of this as a ‘partnership’, which is a translation of the Greek word koinonia, giving us synonyms such as ‘fellowship’ or ‘sharing’. It expressed a mutual belonging for which modern English does not provide exact words.
Paul had come to the point where he was content to share the Messiah’s death in order that he might arrive with him at the ultimate hope of Israel, ‘the resurrection from the dead’. The ancient story of Israel had been fulfilled in the Messiah, and all Paul’s previous zeal for God and the Torah had to be counted as “trash” by contrast. That’s why he ‘forgot’ about his past and, like an athlete with his eye on the finishing line, aims to strain every nerve to go after what’s ahead. Then comes the point of all this for the Philippians: they must learn to imitate him, as he is imitating the Messiah (Phil. 3: 13-19). But how could the Gentile Christians do this? They had not been zealous Jews, eager for the Torah, but they all had their own status, personal and civic pride. Even if they lacked status, because they were poor, or slaves, or women (though some women, like Lydia, were independent and free), they all had the standing temptation to lapse back into pagan lifestyles. So whether they were Romans reverting to proud colonial ways or simply people who found themselves lured back into sensual indulgence, they must instead resist and find instead the way of holiness and wholeness shaped by the Messiah himself, by his choice of the way of the cross, by his status as the truly human one, the true embodiment of the One God (Tom Wright).
Colossae & Corinth (again):
Paul’s later letters to both the Ephesians and Colossians are both deeply Jewish in their orientation, only making sense within that worldview. Nineteenth-century Protestantism didn’t favour Jewish thought, and didn’t want Paul to be too Jewish and, more recently, some scholars have tended to demote the two epistles as anathema to the more ‘liberal’ agenda they find in Galatians and Corinthians. Tom Wright claims that this is a mistake, resulting from contemporary ideology and moralising which seeks to ‘pigeon-hole’ Paul. Colossians was written, it appears, to a young church. Paul had been informed of its existence by Epaphus, himself from Colossae, who seems to have been converted by Paul in Ephesus and to have returned home to spread the word. Paul’s epistle to the Colossians was written at Rome, when he was in prison in Rome, shortly before his martyrdom, in about AD 63. Colossae had been a great city, but had very much declined, and was now the smallest of the three neighbouring cities in the valley of the Lycus. Laodicea and Hierapolis were still prosperous by comparison. Its church was the most insignificant of the churches which received a letter from Paul, and it was scarcely mentioned in later times. Neither in this epistle nor in the Acts is there any evidence that the apostle ever visited the Colossians. But he had “heard of their faith” (I: 4, 9) and states that they “had not seen his face in the flesh (2: 1). Nevertheless, Paul was praying for the church to grow in faith, wisdom, and understanding and to be able to draw on the “power” of Jesus in living and working to his glory (Col. 1: 9-11). In particular, Paul longed for them to develop and enrich the practice of giving thanks. To that end he supplies them with a poem, like that written to the Philippians (chapter two, above), celebrating the universal lordship of Jesus over all the powers of the world. Part of the meaning of this poem was that it was written by someone in prison. According to Tom Wright, it invites…
… those who read it or pray it to imagine a different world from the one they see around them – a world with a different ‘Lord’ in which the One God rules and rescues, a world in which a new sort of wisdom is unveiled, a world in which there is a different way to be human.
‘Wisdom’ was the key theme of much of Colossians. As always, Paul wanted people to think, not simply to imbibe rules and principles to learn by heart, but to be able to grow up to full maturity as human beings, experiencing that “Christ is all and in all,” and coming to “the knowledge of God’s mystery.” (Col. 2: 2). All this will happen when they realise that it is Jesus himself who reveals that ‘mystery’ and the means of finding all the hidden treasures of wisdom and knowledge. Paul is here drawing deeply upon two important strands of Jewish thought. First, he knows very well the traditions of prayerful meditation through which devout Jews hoped for a vision of the heavenly realm. These traditions seemed to have been developed at a time when with pagans still ruling Palestine even after the end of the Babylonian exile had ended, there was a sense that the greatest prophetic promises, particularly those concerning the visible and powerful return of Israel’s God to the Temple of Zion had not been realised. Second, there was the belief that the whole creation was made by the One God through his wisdom (Proverbs 8). To speak of “Lady Wisdom” as God’s handmaid in creation was a poetic way of saying that when God made the world, his work was neither random nor muddled, but wise – coherent and well-ordered; it made sense. To reflect God’s image, mankind needed to be wise as well.
The “mystery” tradition and the “wisdom” tradition were both focused by some writers of the period on the Temple. That was where the One God had promised to dwell. If there was to be a display of the ultimate mystery, the writers expected that it would be in the Temple. This expectation got bound together in yet another strand of Jewish thinking: David’s son Solomon, the ultimate ‘wise man’ in the Bible, was also the king who built the Temple. When Solomon consecrated the newly built shrine, the divine glory came to fill the house in such blazing brilliance that the priests could not stand there to do their work (I Kings 8). For us, living in a radically different culture, all this feels like an odd combination of disparate ideas. In Paul’s world, and especially for a well-educated Jew, all these apparently separate notions belonged like a single well-oiled machine. Here is the secret of creation, of wisdom, of mystery, of the Temple. This is how it all fits together. N T Wright challenges us to imagine all the complex but coherent Jewish thought…
… pondered and prayed by Paul as he travels, as he works in his hot little shop, as he stays in a wayside inn, as he teaches young Timothy the vast world of scripture, which is his natural habitat. Imagine him praying all that in the Temple itself as he visits Jerusalem after watching the gospel at work in Turkey and Greece. Imagine, particularly, Paul finding here fresh insight into the way in which, as the focal point of creation, of wisdom and mystery, and of the deep meaning of humanness itself, Jesus is now enthroned as Lord over all possible powers. And now imagine Paul in his moment of crisis, of despair, feeling that the “powers” had overcome him after all, reaching down into the depths of this fathomless well of truth to find, in a fresh way, what it might mean to trust in the God who raises the dead. This is what he comes up with:
“He is the image of God, the invisible one;
The firstborn of all creation.
For in him all things were created,
In the heavens and the earth.
Things we can see and things we cannot –
Thrones and lordships and rulers and powers –
All things were created both through him and for him.
And he is ahead, prior to all else
And in him all things hold together;
And he himself is supreme, the head
Over the body, the church.
He is the start of it all,
Firstborn from realms of the dead;
So in all things he might be the chief,
For in him all the Fullness was glad to dwell
And through him to reconcile all to himself,
Making peace through the blood of his cross,
Through him – yes, things on the earth,
And also the things in the heavens.
(Col. 1: 15-20.).
If this poem were less elegant, one might suggest that Paul was shaking his fist at the powers on earth and in the dark realms beyond the earth, the powers which had put him in prison in Rome and crushed his spirit to the breaking point. But he was not doing so, but rather invoking and celebrating a world in which Jesus, the one through whom all things were made, is now the one through whom, by means of his crucifixion, all things are reconciled. This is not the world that he and his friends can see with the naked eye since that is one in which allegiance is given to Caesar and there are bullying magistrates and threatening officers, with prisons and torture in their weaponry of oppression. But they are invited to see the world with the eye of faith, the eye that has learned to look through the lens of scripture and see Jesus. The Messiah is living with the Colossians, just as Paul had written to the Galatians. The ancient Jewish hope that the glory of the One God would return and fill the world is thus starting to come true. It may not look like it in Colossae, as ten or twenty oddly assorted people crowd int Philemon’s house to pray, to invoke Jesus as they worship the One God, to break bread together, and to intercede for one another and the world; but actually, the Messiah, there in their midst, is “the hope of glory.” (Col. 1:27).
From his base in Ephesus, Paul sent different members of his staff to deal with the quarrelling Corinthians (II Cor. 12: 17 f.), but he then found it necessary to interrupt his work and cross the Aegean himself (II Cor. 12: 14). There are two letters to the Corinthians in the New Testament, but these contain clear indications that the correspondence they represent was more extensive. They illustrate vividly the problems that arose when people of widely different ethnic origins, religious backgrounds, levels of education and positions in the social hierarchy were being welded into a community by the power of a common faith, while at the same time they had come to terms with the secular society to which they also owed allegiance. These problems were threatening to split the church into fragments. It may have been about the same time that the very serious trouble broke out which provoked Paul to write his fiercely controversial letter to the Galatians. If the Second Letter to the Corinthians was written at about this time, this would explain Paul’s cri de cour in it: There is the responsibility that weighs on me every day, my anxious concern for all our congregations (II Cor. 11: 28). The difficulties at Corinth were eventually resolved, and Paul, having wound up his work at Ephesus, was able to visit a church now fully reconciled.
Rome & Jerusalem:
It was at this point that he wrote his the longest and most weighty of all his surviving letters, that addressed to the Romans. In this letter, he looked back briefly on the work that lay behind him and sketched a plan for the future. He had covered the eastern provinces of the empire, from Jerusalem as far round as Illyricum. He added that he had no further scope in these parts and that it was now his ambition to bring the gospel places where the very name of Christ has not been heard. Accordingly, he was planning to open up work in the west, with Spain as his objective. On the way, he would visit Rome, and hoped to find support there for his enterprise (Rom. 15: 19-29). Paul had not yet visited Rome, but from the greetings, at the end of his letter he obviously had several friends there, and he knew quite a lot about the what was going on in both the church and the wider society. His intention to round off his work in the eastern end of the Mediterranean world and to move on to the West was a more focused ambition than simply finding more people to preach to, more “souls” to “save”. He wanted to plant the flag of the messianic gospel in key points where the “gospel” of Caesar and the ‘Pax Romana’ was being flaunted. Rome itself was, therefore, the obvious target; but beyond that, Spain, the western edge of the known world, was also a major centre of Roman culture and influence. Paul’s great contemporary Seneca had come from there. Galba, soon to be emperor, had been governor there, based in the port of Tarragona, which would presumably be Paul’s initial target. It boasted a large temple to Caesar. As in Ephesus and Corinth, Paul would have longed to announce that Jesus was the true Kyrios right under Caesar’s nose.
He knew he would have to tread somewhat warily in Rome, as the church there was not of his founding, nor was it within his ‘sphere of influence’ originally laid down by the church in Antioch. He also knew that there was some prejudice against him among the Roman Christians, who had all sorts of rumours about him. Some might distrust him, either because he was too Jewish or because he was not Jewish enough and had treated elements of Jewish practice too loosely. Some kind of outline of his teaching was a basic necessity. Before presenting himself there he sent his letter, a considered and comprehensive statement of his theological position, designed to establish his standing as a Christian teacher. There was also a more pressing need. Something had happened in the recent past in Rome that had put the Roman Christians in a new and complex position. Claudius, who had become emperor in AD 41, had banished the Jews from Rome after riots in the community sometime in the late forties. Despite the decimation of the community, not all the Jews had actually left, and those that remained had ‘gone to ground’ to hide their identity. Paul’s friends Priscilla and Aquila were among those who had left, which was why they were in Corinth when Paul first arrived there, probably in AD 49. But with Claudius’ death in 54 and Nero’s accession to the throne, Claudius’ edict was revoked. Jews could once again be permitted back in the imperial city, though they were not exactly welcomed back with open arms.
At this time, there was more than a streak of anti-Jewish sentiment in Rome. The term “anti-Jewish” is more appropriate than “anti-Semitic,” because the latter implies some kind of racial theory unknown until the second half of the nineteenth century. Also, in the first century, all Jews were identified by their Judaistic religious practises. There was no such thing as a ‘secular Jew’, as is evidenced by the fact that Jews were exempted from making sacrifices to Caesar and the Roman gods. The danger posed by Paul and Silas in Philippi was that, as Jews, they were teaching non-Jews things that it was illegal for Roman citizens and subjects to practice. In the amphitheatre at Ephesus, when Alexander, a Jew, stood up to preach, there were angry whispers. The same antagonism can be sensed on the edge of remarks by poets like Juvenal or sneering historians like Tacitus. Underneath the ethnic and cultural prejudice there was always a ‘theological’ belief that since the Jews did not worship the gods, they could, therefore, be blamed for disastrous events. This blame was subsequently transferred to the Christians in subsequent decades and centuries. Even in Corinth, Gallio’s refusal to make a judgment about Paul caused the mob to beat up the synagogue president, getting away with it. Going after the Jews was a default mode for many, right across the Roman Empire. Besides their exemption from religious observances that would compromise their beliefs, the Jews were allowed freedom of worship and the right to collect taxes for the Temple in Jerusalem, but that didn’t mean that they were integrated into wider society. For the most part, they were ostracised.
Paul’s message ran completely contrary to this social reality. Among the churches he had founded in Asia Minor and Greece this had not been so clear-cut, since he had always started in the synagogue first and made it clear that the gospel was “to the Jew first, but also, equally, to the Greek.” (Rom. 1: 16). He had given no opportunity for the creation of a Gentile-only Christian community. In most of the cities where he had preached, with the possible exception of the large metropolis of Ephesus, the probability is that the followers of Jesus were never large in number, perhaps only ever a few dozen, or in Corinth, conceivably, a few hundred. It would have been difficult for significantly different theological positions to have emerged once these communities had been established, at least not in the early decades of their communal life.

But in Rome things were different. The message of Jesus had evidently arrived there sometime in the forties, perhaps with the apostle Peter, though this is only a tradition. This places Peter as having arrived in Rome in the year AD 44, whereas Paul did not arrive there until after AD 56, a date given by St. Jerome. There were followers of ‘The Way’ present in Rome perhaps even before Peter’s visit (if it took place), but the scriptural references to ‘the Church’ should not be taken too literally, as referring to a material institution. If it existed in any united form, it was a spiritual body in Christ. The more likely case is that the followers of Jesus at Rome were unorganised, treading in fear, meeting secretly in small groups at the homes of various converts in order to worship, often quite literally ‘underground’.
The imperial capital was, in any case, a city where different cultural and ethnic groups from all over the empire would cluster together for protection in their own districts. It is therefore highly likely that there were many scattered and disparate ‘house-churches’, as is shown by the greetings given in Romans 16, all worshipping Jesus but not really in direct contact with one another, and almost certainly with differing customs and practices based on their cultures of origin. The bands of converts met in grottoes, but mostly in the catacombs among the dead. The Roman law had recognised these underground cemeteries with the decree of sanctuary. However, when the persecution of the Jesus-followers was at its worst, the Roman soldiery would waylay the worshippers on entering or leaving the catacombs. To avoid capture they would make secret entrances and outlets, often through the houses of believers. The Tiberian and Claudian ban that promised to inflict death on all who openly professed the new faith was still in place when Paul was planning his sojourn in the Imperial City. When writing to the followers in Rome, he was aware that one of the ‘churches’ met at the home of Aquila and Priscilla (Rom. 16: 5) and that as well as this Jewish ‘church of circumcision’ there were also Gentile Christian meetings elsewhere in the city. Paul’s visit to Rome, however, was not pending immediately, and probably didn’t take place until AD 58 at the earliest. First, he had to go to Jerusalem, and he implored the Roman Christians to pray for him,
… that I may be served from unbelievers in Judaea and that my errand to Jerusalem may find acceptance with God’s people.
(Rom. 15: 31)

Paul not only apprehended danger from Jewish opposition but also felt some doubt how far he would be welcome to his fellow Christians at Jerusalem. To understand this we need to look at the situation which had developed as a result of his startling success in the building, all over the eastern empire, of a close-knit network of Christian communities which was supra-national, multi-racial, and ‘egalitarian’. As he was to write to the Colossians, that there was to be no distinction between…
Greek and Jew, circumcised and uncircumcised, barbarian, Scythian, slave and free man.
(Col. 3: 11).
This inevitably antagonised those who adhered to a stiff, nationally orientated type of Judaism – those, in fact, who stood where Paul himself had stood before his conversion. He had ‘ratted’ on them, and that could not be forgiven or forgotten. In his letter to the Romans, Paul argued, as he had done in Galatians, that the church could not be allowed to become a ‘purely’ Jewish institution with Gentile Christians tolerated as second-class citizens. “There is no distinction,” he repeated (Rom. 3: 22; 10: 12). If he had been finally defeated over this, the Christian church might have had as little impact on the great world as any other of the of the numerous Jewish sects. Although he was not defeated, neither could he be said to have gained a decisive victory in his lifetime. Advocates of the narrower view dogged his steps to the end and sought to win over his converts. No doubt they were honest and conscientious men, who stood obstinately by their principles, as did he. Quite simply, as far as he was concerned, they were in the wrong, and in his letter to the Galatians, he had written of these opponents in harsh terms and with passionate indignation. His tone in Romans was softer than that of Galatians, as he also set out his mission to Jerusalem as one of reconciliation. Nevertheless, the opening passages of his letter read like a ‘manifesto’ for a religious revolution, demonstrating how vital the issue was for him:
God has shown us clearly what he is like in a new way – how he stands for what is right, overthrows what is wrong and helps men to live in his Way.
This is not altogether a new Way, as we have seen – the Men of God of the Jewish people had begun to see how God puts wrongs right. But Jesus has made it quite plain. If we are to live in God’s Way, we must trust God; this means trusting in Jesus who has made God real to us.
This is true for everybody everywhere; for God … has no favourites. We have all done wrong; none of us has lived as splendidly as God intended him to live, though we were all created to live in his Way and be like him. But God treats us as if we had learned to live splendidly; his love is given to us freely. And it is Jesus who has won this freedom for us.
There is nothing in all this to make us proud of ourselves. Keeping all the rules wouldn’t have stopped us being proud of ourselves. We have simply taken him at his word, and that leaves no room for boasting.
I am sure of this: everybody can really live as God wants him to live simply by trusting him, not by trying to keep all the rules. I mean everybody. Is God only the God of the Jewish people? Isn’t he God of all people everywhere? Of course he is, for there is only one God. So he puts Jewish people right – if they trust him; and he puts the people of other countries right if they trust him.
When the original Jerusalem concordat was made, the leaders of the church had stipulated that the ‘Gentile’ churches should take some responsibility for the support of the poverty-stricken Jewish Christians of Jerusalem. But for Paul, it was an opportunity to demonstrate the true fraternal unity of Christians, bridging any divisions that arose among them. He set up a large-scale relief fund, to be raised by voluntary subscription from members of the churches he had founded; he recommended a system of regular weekly contributions (Rom. 15: 25-28; 1 Cor. 16: 1-4; II Cor. 8: 1-9, 15). The raising of the fund had gone on for some considerable time and there was now a substantial sum in hand to be conveyed to Jerusalem. He was to be accompanied by a deputation carefully composed, it appears, so as to represent the several provinces (I Cor. 16: 3 f.; Acts 20: 4). The handing over of the relief fund was to be both an act of true Christian charity and also a formal embassy from the ‘Diaspora’ churches affirming their fellowship with the Judaean Christians in the one church. However, the goodwill mission miscarried. Paul’s reception by the leaders of the church at Jerusalem, if not unfriendly, was certainly not entirely welcoming. James was genuinely frightened of the effect of Paul’s presence in the city on both Christian and non-Christian Jews, in view of his reputation as a critic of Jewish ‘legalism’. James urged Paul to prove his personal loyalty to the Torah by carrying out certain ceremonies in the Temple (Acts 21: 20-24). Paul was quite willing to accept James’ guidance. As he had already written to the Corinthians,
To Jews, I became like a Jew, to win Jews; as they are subject to the law of Moses, I put myself under that law…
(I Cor. 9:20).

Unfortunately, however, he was recognised in the Temple by some of his arch-enemies, the Jews of Asia, who raised a cry that he was introducing Gentiles into the Holy Precincts (Acts 21: 27-29). There ran across the temple court a barrier with an inscription threatening with death any ‘foreigner’ who trespassed beyond it. There was no truth in the charge against Paul, but it was enough to rouse the rabble, and Paul was in danger of being lynched. He was rescued by the Roman security forces and put under arrest. Having identified himself as a Roman citizen, he came under the protection of the imperial authorities (Acts 21: 30-39) and was ultimately transferred for safekeeping to the headquarters at Caesarea (Acts 23: 23-33). After wearisome wrangles between the Sanhedrin and two successive Roman governors, and fearing that he might be sent back into the hands of his accusers in Jerusalem, Paul decided to exercise his right of appeal to the emperor (Acts 25: 1-12). Accordingly, he was put on board a ship bound for Rome, leading to the famous ship-wreck off Malta (Acts 27: 1 – 28: 15).

Paul in Rome:

So Paul fulfilled his cherished plan of a visit to Rome in person but as a prisoner. He was placed under something like house-arrest, occupying his own private lodging, with liberty to receive visitors, but with a soldier constantly on guard (Acts 28: 16). He was awaiting trial there, a trial which was continually delayed. It is probable, though not certain, that the Letters to the Ephesians, Philippians, and Colossians, as well as to Philemon, all of which refer to their author(s) being in prison at the time of writing, belong to this period of confinement. This period of house-arrest lasted, we are informed, for two years (Acts 28: 30). Scholars presume that the case eventually came up before the imperial tribunal, but whether it resulted in acquittal and a further period of freedom to travel, or ended in condemnation and execution, we have no means of knowing. The Letters to Timothy and Titus have been thought to refer to a further period of imprisonment in Rome, but the evidence is at best ambiguous, and it is unlikely that these letters, in the form in which we have them, come from Paul’s own hand. We know that Paul’s original plan before he went to Jerusalem, was to travel on to Spain, but we have no evidence that this goal was fulfilled. He was associated with Rome for ten years in all, and some have suggested that in addition to visiting Spain, he also travelled to Gaul and Britain. However, there is little if any hard contemporary evidence to support these assertions, which are based mainly on tradition and fanciful conjecture.

That he ultimately suffered martyrdom may be taken as certain, and there is no good reason to doubt the Roman tradition that he was beheaded at a spot on the road to Ostia known as ‘the Three Fountains’, and buried on the site now occupied by the noble church of St Paul-without-the-Walls. According to the chronology given at the beginning of this article, Paul could hardly have arrived in Jerusalem before AD 59. His period in prison in Caesarea could not, therefore, have ended until AD 61, therefore. At that point the governor Antonius Felix was succeeded by Porcius Festus, based on evidence from non-Biblical sources. Accordingly, Paul would have sailed to Rome in the autumn of 61, arriving there in early 62. His period of house arrest would have continued until AD 64 and Tom Wright dates Paul’s death to this year or later. Beyond that, we cannot go, but it may be significant that it was in the winter of 64/ 65 that the emperor Nero made his savage attack on the Christians of Rome, following the Fire which was blamed on them. The Roman-Jewish War followed in AD 66-70, during which Nero died in AD 68, and the War ended with the Fall of Jerusalem…
… (to be continued).


Antioch & Jerusalem:

We know about the conflict between Antioch and Jerusalem through the detailed colourful accounts of Josephus, a younger contemporary of Paul’s. He was anything but a neutral observer, however, but a wealthy Jewish aristocrat who claimed to have tried out the various Jewish ‘schools of thought’ and who had served as a general in the army at the start of the war against Rome (AD 66-70) before switching sides and ending his days on an imperial pension in Rome. In the middle of the first century, Jerusalem was a highly complex world of different parties, groups, messianic and prophetic movements, preachers and teachers. When the Romans closed in on Jerusalem in the last months of the war, crucifying so many Jews that they ran out of timber for crosses, Josephus recorded sorrowfully that more Jews were in fact killed by other Jews than by the Romans. Matters were not helped by the sequence of inept Roman governors sent to keep the peace during the period. There were times under the two kings named Herod Agrippa, both of whom were friendly with the Roman imperial family when many hoped for a live-and-let-live settlement. That would never have been sufficient for the young Saul of Tarsus, however, who longed for the ultimate kingdom of God. The Jerusalem of the middle decades of the first century was home to an entire generation who took a hard-line view, hating the thought of compromise and looking for something more like Hezekiah’s heaven-sent victory over Sennacherib or the overthrow of the Egyptians in the ‘Red Sea’.
The scriptures were quite clear that utter loyalty to the One God meant refusing all compromise with the pagan world. The social and cultural pressure to affirm that ancient loyalty and to be seen to abide by it was intense. To be a follower of Jesus in that world would have been a very different challenge from those faced by Jesus-followers in Syria or Turkey. Although the Jerusalem church had by this time established itself as something of a counter-cultural movement to the Temple authorities, this did not mean that its members were being ‘anti-Jewish.’ If anything, they were putting themselves on a par with other groups who regarded the Temple hierarchy (the wealthy, aristocratic Sadducees, including the high-priests’ families) as a corrupt and compromised class, out for their own ends and too eager to do deals with the Romans. The early Jerusalem church seems to have lived like other groups who believed that God was ushering in the ‘last days’. In the excitement of the early stages, they had shared their property communally, an eager social experiment which may have led to their later poverty. They lived a life of prayer, fasting, community, and care for the poor and widows. So far as we can tell they conformed faithfully to the Jewish Law. They must have seemed to many like a strange messianic variation on the Pharisees’ movement, coupling a fierce loyalty to Israel’s One God with their own belief that the One God had revealed himself in the crucified and risen bringer of the kingdom, Jesus of Nazareth.
According to Acts, it was Peter who first broke the taboo of sharing table-fellowship with non-Jews; he received strong divine validation for this radical move and persuaded his sceptical colleagues in Jerusalem that this was the right thing to do. But this move seems not to have been thought through with regard to what they believed about Jesus himself. It was a pragmatic decision on their part, led by the spirit, which meant that it must be what God wanted. It remained easy, therefore, for most of the Jerusalem-based Jesus followers to see their movement as a variation on the Jewish loyalist groupings. God might bring in some non-Jews, as had always happened in Israel’s history, as the book of Ruth and various other pages had made clear. But it could hardly be imagined that the God whose scriptures warned constantly against disloyalty to the covenant would suddenly declare the Torah redundant. But that was what many in Jerusalem, including many Jesus-followers, believed that Paul had been teaching. The word got out that Paul and Barnabas, not content with belonging to a hybrid community in Syrian Antioch, had been going around the Graeco-Roman world telling Jews that they no longer needed to obey the Law of Moses! If the Torah itself could now be set aside, who could tell what results might then follow?
All this focused on the covenant sign of circumcision, and while it is true that the prophets and Moses himself had spoken of the circumcision of the heart as the deep reality to which physical circumcision was meant to point, that reality was associated with the promise of ultimate covenant renewal. Nobody in the first century imagined that, if the One God really did renew the covenant, physical circumcision might be dispensed with for the non-Jews who would be included. On the contrary, circumcision became a symbol of ‘loyalty’. Many of the Jesus-followers had dispersed following the early persecution, but there was still a tight core, focused particularly on James himself. From the time of Stephen’s stoning, they had been regarded as potentially subversive, disloyal to the Temple and its traditions. Now, this disloyalty was showing itself in a new way: they were allied with a supposedly Jesus-related movement, out in the Diaspora, teaching Jews that they didn’t have to obey the Torah! That would introduce one compromise after another until Jews would Find themselves indistinguishable from pagans. In Jerusalem, all Jews believed that pagans were the enemy that God would one day overthrow, but out there in the Diaspora this new movement was, it seemed, treating pagans as equal partners. The Temple hierarchy was concerned that this Jesus movement in the wider world, led by ‘that wild man Paul’ would not land them in any deeper trouble, guilt by association. From all that they had heard, the signs were not encouraging.

Four things happened in quick succession. First, Peter came to Antioch and shared in the life of the church there for a while. This and the following incidents, including the writing of Paul’s first letter to the Galatians, are dated around AD 48. Second, some other followers of ‘The Way’ came to Antioch from Jerusalem, claiming to have been sent by James. This precipitated a small earthquake in the Antiochene church and a controversy denounced by Paul himself in devastating terms. Third, perhaps some weeks or months later, Paul received bad news from the little communities of non-Jewish believers in southern Anatolia, recently ‘planted’ by Barnabas and himself. The fourth event was the writing of the letter to the churches in Galatia, as mentioned above. He then set off for Jerusalem in the hopes of sorting all this out with those who seemed to be causing the trouble who naturally thought that it was he who was causing all the trouble. As Tom Wright remarks,
Controversies are always like that. Generations of Christians who have read Galatians as part of holy scripture have to remind themselves that, if Galatians is part of the Bible, it is Galatians as we have it that is part of the Bible – warts and all, sharp edges and sarcastic remarks included. Perhaps, indeed, that is what “holy scripture” really is – not a calm, serene list of truths to be learned or commands to be obeyed, but a jagged book that forces you to grow up in your thinking as you grapple with it.
Paul believed that Jesus’ own spirit was at work through him as his chosen apostle to the Gentiles to establish and maintain the life-changing communities of people whose lives had themselves been changed by the power of the gospel. And now he believed that he had a responsibility to state clearly what was at stake in the controversy in Antioch, in Jerusalem, in Galatia itself. His own obvious vulnerability was part of this process too, as he later stressed in another letter. His ‘epistles’, just like the gospel itself, were part of a radical redefinition of what ‘authority’ might look like in the new world that the One God had launched through Jesus. So Peter came to Antioch, it seems, in early 48. His arrival is unexplained, like all his movements after his remarkable escape from prison in Acts 12:17; all we know is that he had initially been happy go along with the practice of the local Jesus-followers in Antioch, having Jewish and non-Jewish believers living together as “family,” sharing the same table. This was the practice that Peter himself had embraced in Acts 10-11 when he visited Cornelius, justifying his actions to critics in Jerusalem on the basis of what he had been told in a divine commandment:
What God made clean, you must not regard as common.
Peter had acted on that principle, believing that the power of the gospel had ‘cleansed’ the Gentiles of the ritual or moral defilement that they possessed in Jewish eyes, defilement that would normally be seen as a barrier to the intimacy of table fellowship. What the new experience of God had made clear to most of the friends of Jesus, but not to all of them, was that God’s love, which Jesus made real to them, was for the whole world – everybody, everywhere. But many came slowly to these great convictions, and there was much heart-searching debate among the early Christians in Antioch: did Jesus come, essentially, to reform the Jewish religion, or did he come to call everybody everywhere to become God’s family, each in his own way? Peter now hesitated to go the whole way; when he arrived in the city of Antioch Paul confronted him on this issue. He described this confrontation in his letter to the Galatians:
Barnabas and I … were back in Antioch, and Peter Joined us there. But I had to stand up to him and tell him that he was plainly in the wrong – on this same question.
When he first came there, he ate his meals with all of us; foreigner and Jew sat down together at the same table. Then some men came from Jerusalem (they said that James had sent them), and everything changed. He started to stay away from our common meals. He was frightened of these Jewish Christians who said that you couldn’t become a Christian if you hadn’t first become a proper Jew. Other friends of Jesus in Antioch started to do the same – even Barnabas was deceived.
(Galatians 2: 11-13)
Clearly, as Paul reports these events, what changed the terms of the discourse was the arrival in Antioch of the ‘envoys’ from Jerusalem who insisted that if the Gentiles wanted to be part of the true family, sharing in the great rescue operation which God had now set in motion, they would have to be circumcised. Paul, in Galatians, wrote that this was what made Peter change his mind. Up to that point, he had been content to eat with the Jesus-believing Gentiles, but now he drew back in line with the newcomers, and, given the status that Peter had within the wider movement, it is perhaps not surprising that the other Jewish Jesus believers followed him in this. Paul tells us that even Barnabas was carried along by their sham (Galatians, 2: 13). This was not simply a disagreement about theological principles, but about an original practice of the church in Antioch which reflected the belief that all believers in Jesus, whether circumcised or not, belonged at the same table. The Judaean guests were clearly saying that this was wrong and that the loyal Jews among the believers should withdraw. Barnabas had been with Paul through all the joys and trials of the mission to Galatia and together they had welcomed many non-Jews into fellowship. They had shared everything; they had prayed and worked and celebrated and suffered side by side. Now they were on opposite sides of this debate, and that hurt Paul.
Paul was careful not to claim that the visitors from Jerusalem were sent by James personally, though it is difficult to see how they could have been there except on his authority. Certainly, the focus of their concern was the maintenance of covenant loyalty. Circumcision was, as far as they were concerned, non-negotiable, since the purity of God’s chosen people was essential. If God was indeed bringing in his kingdom, then a clean break with the Gentiles’ pagan past was vital. If they were to be allowed into the covenant, the former pagans would have to demonstrate their loyalty as well, and that meant circumcision. From the point of view of the zealous kingdom-minded Jews of Jerusalem, this made perfect sense, but from Paul’s perspective, it made no sense at all. He had already thought through what it meant that God was bringing in his kingdom through the crucified Messiah, the shocking and unexpected events of Jesus’ death and resurrection, coupled with the dramatic sense of personal redemption for which the only explanation was the outpouring of the Holy Spirit, meant that everything had changed. A new world had begun and those trying to live in it while clinging to the old one had not yet realised just how radical the transformation was. They were simply “putting on a face,” or “playacting,” for which the Greek word was hypokrisis, giving us the English word ‘hypocrisy’. Paul was similarly direct in his narrative to the Galatians, as this modern paraphrase reveals:
This was cheating – and cheating about the very thing that makes the Good News really good news. It was as plain as plain could be to me.
(Galatians 2: 14, New World)
The problem was both personal and theological for Paul. As one of the recognised ‘pillars’ of the whole movement, Peter had been followed from the common table by many of the Jewish followers of Jesus. That made it even more difficult for Paul to confront Peter, but that is exactly what he did:
When I saw that they weren’t walking straight down the line of gospel truth, I said to Cephas in front of them all: “Look here: you’re a Jew, but you’ve been living like a Gentile. How can you force Gentiles to become Jews?”
(Galatians 2: 14).
Peter had already been “living like a Gentile” – not in the sense that he had been worshipping idols or indulging in sexual immorality, but in the sense that he had been in the habit of eating with people without any regard for the distinction between Jews and Gentiles. He was therefore “in the wrong.” Either his present behaviour meant that his previous stance had been wrong, or his previous stance, being right, proved that his present behaviour was wrong. Paul himself was in no doubt which of these was the correct analysis and he went on to put the Good News plainly. He himself was a Jew by ‘race’ and not a foreigner. But he knew that a man did not become a Christian by carrying out all the details of the Jewish religion, but simply by trusting Jesus himself. That was the heart of the matter:
We are Jews by birth, not “Gentile sinners.” But we know that a person is not declared “righteous” by works of the Jewish law, but through the faithfulness of Jesus the Messiah.
(Galatians 2: 15-16).
Paul knew what the secret of his own life was. True, he went on living his ordinary life in exactly the same way as before, but he didn’t feel that he was living it – Jesus had taken charge of him so that he lived by trusting God’s son, who loved him and gave his life for him. In Western theological discourse, this has been traditionally interpreted as Paul developing his doctrine of ‘justification’, of how someone who was previously a ‘sinner’ comes to be ‘righteous’ in the eyes of God. Paul clearly believed in the importance of ‘sin’ and of being rescued from it. But that was not what was at stake at the time in Jerusalem, Antioch or Galatia. What mattered then was the individual believer’s status within the covenant family. The word ‘righteous’, like the Greek and Hebrew words from which it is often translated, refers to someone being in a right relationship with God, the ‘relationship’ in question being the collective relationship of the covenant that God made with Abraham. The question that Paul was addressing was: How can you tell who are the true children of Abraham? His answer was focused firmly on Jesus. So Paul’s point to Peter was a simple one, that what mattered to Jesus was being part of the covenant family, and that is not defined by Jewish law, but through the faithfulness of Jesus the Messiah. The word for ‘faithfulness’ is pistis in Greek, also means simply ‘faith’, ‘loyalty’ or ‘reliability’. In a world where the key value for a zealous Jew was ‘loyalty’ to God and his law, Paul believed, according to Wright:
(1) that Jesus the Messiah had been utterly faithful to the divine purpose, “obedient even to the death of the cross”… ;
(2) that following Jesus, whatever it took, had to be seen as itself a central expression of loyalty to Israel’s God;
(3) that the followers of Jesus were themselves marked out by their belief in him, confessing him as ‘Lord’ and believing that he was raised from the dead; …
(4) if this Jesus-shaped loyalty was the vital thing, “then nothing that the law could say was to come between one Jesus-follower and another.”
In other words, continuing Paul’s description of what he said to Peter:
That is why we too believed in the Messiah, Jesus: so that we might be declared ‘righteous’ on the basis of the Messiah’s faithfulness, and not on the basis of works of the Jewish law. On that basis, you see, no creature will be declared ‘righteous’.
(Galatians 2: 16).
Paul urges Peter and all the others who hear his letter when it is read out loud, to think out the new position they find themselves in:
Well then: if in seeking to be declared ‘righteous’ in the Messiah, we ourselves are found to be ‘sinners’, does that make the Messiah an agent of ‘sin’? Certainly not! If I build up once more the things which I tore down, I demonstrate that I am a law-breaker.
(Galatians 2: 17-18).
Following Paul’s definition of himself and others as Jews by birth, not ‘Gentile sinners’ in which Gentiles are automatically ‘sinners’ because they do not have the law. Therefore, if Peter found himself called to live on equal terms with ‘Gentile sinners’ did that mean that the Messiah was colluding with ‘sin’? That was exactly what the Jerusalem church and the Judaeans, in general, were concerned about, seeing it, potentially, as fraternising with the enemy. They might see, in Paul’s claim to be following the Messiah, a false Messiah who was leading the people astray. Paul countered by arguing that since Peter had started by pulling down the wall between Jews and Gentiles if he now wished to re-erect it, he was admitting that he had been wrong to ‘live like a Gentile’. Paul believed that there was only one way forward, and that is to go where the Messiah had led, through death to new life, a journey which was the same for all the Messiah’s followers, Jew and Gentile alike. Paul describes this journey in individual terms by using the first person singular because, as a zealous Jew, he was making it clear that even he had to tread his own path:
Let me explain it like this. Through the law I died to the law, so that I might live to God. I have been crucified with the Messiah. I am, however, alive – but it isn’t me any longer, it’s the Messiah who lives in me. And the life I do still live in the flesh, I live within the faithfulness of the son of God, who loved me and gave himself for me.
(Galatians 2: 17-18)
In making this statement, Paul shows us that he regarded himself as a loyal Jew, loyal to God and the law but that he had come to see the law itself as pointing forward to a kind of ‘death’, something beyond itself that could only be attained by coming out of the law’s own sphere and emerging into a new world. The law itself had envisaged a moment when it would be transcended by a messianic reality. Though Paul does not mention baptism in this passage, this is exactly what, in his view, baptism is all about (as in Romans 6), which is leaving the old life behind and coming through ‘death’ into a new life entirely. The believer then finds his own identity not in his human genealogy or status, but in the Messiah’s faithfulness and loyalty, defined and demonstrated for all time in His death and resurrection. When the believer becomes part of that messianic reality, it is this, rather than his previous standing as a ‘Jew’ or ‘Gentile’, which really matters. The idea of ‘love’ coming from the God of Israel goes all the way back to the covenant with Israel and the act of rescue of Exodus. Paul’s conclusion to this summary of what he said to Peter and James’ ‘envoys’ follows on from this theme:
I don’t set aside God’s grace. If ‘righteousness’ comes through the law, then the Messiah died for nothing.
In other words, if Peter and the envoys from Jerusalem to try to reestablish a two-tier church, with Jews at one table and Gentiles at another, all they were doing was declaring that God’s sovereign love, reaching out to the utterly undeserving – ‘grace’ – was an irrelevance. God need not have bothered with sending his son. If the Torah, the Five Books of Moses, or ‘Pentateuch’ was sufficient for all time to define the people of God, then there was no need for a crucified Messiah. On the other hand, if God had declared in the resurrection that the crucified Jesus really was the Messiah, then He was also declaring that Moses could only take the people so far. He had pointed to a promised land, an ‘inheritance’ which he himself could not enter. Paul insisted that the ‘heirs’ to this ‘inheritance’ could not be defined by the Torah, but only by the Messiah himself, the ultimate ‘heir’. It has been commonplace among New Testament scholars to give the interpretation that Paul lost this disputation and so had to set off on his later missionary journeys without the support of the church in Antioch. But the distance between Syria and Galatia was not that great and people could and did travel quickly between the two regions. The fact that he referred to the dispute at such length in his letter to the Galatians, and that he later returned to Antioch without any hint of trouble, does not suggest that he lost the argument and was ‘run out of town’.
The Galatian Background:
It was out in the world beyond Palestine, and even Syria, that what Jesus meant, why he lived as he did, how he died, and how he was ‘raised to life’ became clearer. It meant nothing less than the vision of a new world, God’s world, and a call to be God’s ‘fellow-workers’ in its making. Nothing could have made this vision sharper than the sight of men and women, of different ‘races’, classes and nations becoming Christians. Their old fears vanished; a new joy marked their lives. When Paul tried to describe what a difference Jesus had made to him personally he went back to the opening words of the book of Genesis and the story of the making of the world as the only kind of language he could use:
God, who made this bright world, filled my heart with light, the light which shines when we know him as he is, the light shining from the face of Jesus.
(II Corinthians 4: 6, New World).
This is Paul’s later account of his own experience; but it was, as he was constantly repeating, a simple experience which everyone everywhere could share. However, the background to Paul’s earlier letter to the Galatians was undoubtedly complex. Around the same time that James’ envoys arrived in Syrian Antioch, it appears that similar persons from the Jerusalem church arrived in Galatia. Their message seems to have been similar, that all fraternising with Gentiles was to stop and that any Gentiles who wanted to be identified with the true people of Israel would have to be circumcised. God’s kingdom would come, rescuing His people from the wicked ways of the world, but only those circumcised would inherit that kingdom. This sharp message also involved a personal attack on Paul himself who was only, they claimed, in Tom Wright’s phrase, a second-order representative of the Jesus message. He had picked up his ‘gospel’ in Jerusalem but had failed to grasp one of the central elements, or perhaps was unwilling to pass it on. Moreover, Jerusalem was, at that time, awash with zealous speculation about the coming kingdom, in which the Gentiles were usually portrayed as the wicked villains who would, at last, receive their punishment. People disagreed about what it meant to keep the Torah, but everyone agreed that the Torah mattered. Any Jews who were willing to treat uncircumcised Gentiles as ‘family’ were compromising the integrity of God’s people and were placing the promised inheritance itself in jeopardy.
Just as Saul of Tarsus had set off a decade earlier to round up the blaspheming followers of ‘The Way’, someone else – a shadowy, unnamed figure – set off with a few friends to bring the new movement into line. At the same time, the pressure was mounting on the Jewish communities in South Galatia. As long as everyone in the thoroughly Romanised province knew who all the Jews were within a particular town or city, they would also know that they had permission to forego participation in the local cults, as well as the exciting new cults of Caesar and Rome. One of the first and most important things that happened whenever non-Jews were grasped by the gospel of Jesus was that, once they had heard that there was a true and living God and that He loved them personally, they would turn away from the idols they had previously worshipped. Suddenly, therefore, new groups of Jesus-followers were emerging, which were obviously not Jewish, but which were staying away from pagan rituals, celebrations and ceremonies. So while the nascent Christian groups in Jerusalem were suspected of disloyalty due to their attitude towards the Torah and the Temple, those in the Diaspora were suspected of disloyalty toward their own communities and towards Rome itself because of their attitude toward the local and imperial cults.
The Jewish communities in cities like Pisidian Antioch, Iconium and Lystra – all Roman colonies – would then find themselves caught in the middle. Local synagogue congregations might well be divided in their response, but the social pressure would grow on them. In turn, local Jewish leaders would put pressure on local Jewish Jesus-followers to persuade their new ‘friends’, the Gentile believers, to come into line and get themselves circumcised. Paul, therefore, had a complex and challenging task, and he was shocked that the communities he had founded had not grasped the full meaning of Jesus’ death and resurrection and the fact that through him a new world, a new creation, had already come into being. They were in serious danger of stepping back into the old world, as though the cross and the empty tomb had never happened, as though the true and living God had not revealed his covenant love once and for all not only to Israel but through the Messiah, to the world. In his letter, he interrupts his opening greeting to insist that his ‘apostleship’ was a direct divine gift, not a secondhand or second-rate appointment from “human sources.” It derives from God himself, and from Jesus the Messiah, our Kyrios,
… who gave himself for our sins, to rescue us from the present evil age, according to the will of God our father, to whom be glory to the ages of ages. Amen.
(Galatians 1: 4-5).
The gospel Paul announced may have seemed to Jews in Jerusalem or Galatia as though it was a strange, peculiar eccentricity. But, in truth, it was the harbinger of the long-awaited new creation. This would remain central to Paul’s mission, delineating “the present evil age” from the new day which had dawned. Here, Paul affirms the widespread Jewish belief that world history was divided into two ‘ages’, the “present age” of sorrow, shame, exile, and death and the “age to come,” when all things will be put right. This was a common belief for centuries before Paul, and it remained the norm all the way through the much later rabbinic period. For Paul, the living God had acted in the person of Jesus to rescue people from the ‘present age’ and to launch ‘the age to come’. The new age had burst upon the scene while the ‘present age’ was still rumbling on. This was the divine plan by which Jesus “gave himself for our sins”; the power of the ‘present age’ was thereby broken, and the new world could begin.
Paul would later characterise his vocation as a “ministry of reconciliation,” God’s reconciliation of Jews and Gentiles into a single messianic family, as he set out clearly in his writing to those who had become Christians during and after his first visit to the highlands of Anatolia:
Your trust in God your Father has made you members of his Family; Jesus has made this possible. For when you were baptised and became Christians, you began, with his help, to live in his way, as he lived in his Father’s Way.
Living in God’s Way means that you can’t talk about one another as being ‘white’ or ‘coloured’, ‘working-class’ or ‘upper-class’, ‘men’ or ‘women’, as though that was the only thing about them that matters. The most important thing is that as Christians you are one company of friends. And if you are friends of Jesus, you are members of God’s Family as God meant you to be and promised to make you.
That is why, when the time was ripe, God sent his Son to live among us as one of us, to help us live as his sons and daughters, grown-up members of his Family. Because this is what we now are, he has given us the Spirit of his Son in our hearts. When we pray to him, we pray as Jesus did; we say ‘Father!’
You aren’t God’s slaves; God has made you, as I have said, his sons and daughters. And, as sons and daughters inherit their father’s wealth, so all the wealth of God, your Father, is yours.
(Galatians 3: 26-29; 4: 4-7, New World).
When describing this new experience, it is noticeable how Paul goes back to the story of Jesus, recalling how he lived and how he died. For him, it was the way Jesus died which made real what God’s love was like; a love which, in his own words, was broad and long and high and deep; and it was the way God had raised him from the dead that showed us how great the power of God’s love is. The very word ‘cross’ sounded differently in the Graeco-Roman ‘age’. To any Roman citizen, it could only have sounded like a savage word, like our ‘gibbet’ or ‘gallows’. It was the way Romans executed foreign criminals or rebels or slaves. But now it was transformed for Paul into the symbol of God’s ‘amazing love’ – he even wrote once to some friends that he could ‘boast’ about it. What Jesus had made plain for Paul was that God was someone we could trust and to whom we could pray as ‘Father’ (here Paul used the word ‘Abba’, the very same child-like word that Jesus used in his own prayers). There is nothing we need to fear, he tells us, not even death itself, for death ‘has been totally defeated’. The whole world and whatever may lie beyond it is God our Father’s world.
But Paul must also have carried a deep sense of shame and personal failure in his mission of reconciliation, due to his falling-out with Barnabas. This was probably the long-term result of that shocking moment in Antioch when Peter had separated himself from the non-Jewish believers and “even Barnabas” had been led astray by their “hypocrisy”. Although they had, initially, reconciled, and had gone together to Jerusalem, arguing side-by-side the case for Gentile inclusion. But Paul’s trust in his colleague had received a heavy blow and he questioned how reliable might be on further missions to the Gentiles. The specific flashpoint concerned John Mark, the probable Gospel-writer who, as a young man, had been present at the Last Supper and in the Garden of Gethsemane on the night when Jesus was betrayed. It was natural that Paul would suggest revisiting the churches of southern Anatolia, eager to see how they had turned out and able to use a different tone of voice (Galatians 4: 20). It was equally natural that Barnabas would want to take Mark and predictable that Paul would refuse. But Mark had abandoned them on the earlier journey as soon as they had on the south ‘Turkish’ mainland. Added to the question over his reliability for another mission, Mark was not only related to Barnabas but also to Peter. Although Peter had supported Paul’s mission at the Jerusalem Conference, Paul was concerned that Mark might be inclined to take the same line that Peter and Barnabas had taken in Antioch in favour of a two-table meal-time.
For Barnabas, it would have been intolerable that Paul would question his judgement, having himself stood up for Paul a decade earlier when others had doubted him. Now he wanted to do the same for his nephew and give him a second chance to prove himself. The solution that emerged was that Barnabas and John Mark would go back to Cyprus, while Paul would go to Galatia and beyond, but only after a blazing row, what Luke refers to by the Greek word, a paroxysm. It left a bitter taste in everyone’s mouth, and a sorrowful memory in their souls. So Barnabas and Mark sailed away, not only to Cyprus but right out of the narrative of Acts, though Mark later re-emerges as a trusted and valued colleague of Paul’s (Col. 4: 10; Philemon 23; 2 Tim. 4: 11). Paul chose Silas (or ‘Silvanus’) as his new travel companion, like Paul a Roman citizen and a member of the church in Jerusalem who had been entrusted with the epistle that the elders had sent to the wider churches. The church in Antioch sent them on their way, commending them to God’s grace.
The Second Missionary Journey:

The ‘Second Missionary Journey’ was to be marked by a momentous new departure, but it was not premeditated as such. It began, unadventurously, as a return visit to the young churches founded on the previous tour. Following this, the missionaries pursued a curiously devious and uncertain course, without finding any opening for fresh work, until they reached the shore of the Aegean at Troas, not far south of the Dardanelles (Acts 16: 6-8). It is at this point that we come upon the first extract from the ‘travel diary’ incorporated in Acts:
We at once set about getting a passage to Macedonia, concluding that God had called us to bring them the good news.
(Acts 16: 10).
The decision to cross from Asia into Europe proved a turning point, opening a new period in Paul’s missionary career, during which he really found himself. It is also a period which is richly illuminated for us by the letters he wrote during it. A comparatively short sea passage brought the party to the nearest port on the European side, and they made their way through Macedonia towards the province of Achaia or ‘Greece’. Several churches were founded, though the tour was chequered by the usual opposition. At Philippi, it came from pagans, not without tones of anti-Semitism (Acts 16: 19-24). One of the big differences between Philippi and the earlier cities of Paul’s mission was that there was no synagogue. That became significant when the locals identified Paul as a Jew; it looks as though the city knew just enough about Jews to be prejudiced against them. Paul had grown familiar with the usual Gentile jibes and sneers against his people, and now he heard them again. There was, however, a proseuche, a ‘place of prayer’ where a small number of Jews and ‘God-fearers’ (non-Jews who wanted to join in synagogue worship) would meet regularly. This was where, after a few days settling in, Paul and the others made a start. Their first convert was a businesswoman from Thyatira, Lydia by name, described as “a seller of purple.” Her story of response to the gospel appears the most straightforward of any in Acts: The Lord opened her heart to pay attention to what Paul was saying. She was the head of her household, suggesting that she may have been widowed, and was baptised with all her household, inviting the whole Christian party; Paul, Silas, Timothy and Luke to stay at her home. The announcement of Jesus as Israel’s Messiah seems to have caused little difficulty in the small Jewish meeting place, but pagans grabbed hold of Paul and Silas, dragged them into the public square and presented them to the magistrates, declaring:
“These men are throwing our city into an uproar! They are Jews, and they are teaching customs which it is illegal for us Romans to accept or practice!”
(I Cor. 4: 3-4).

The irony cannot have been lost on Paul. The anger and violence he had faced in Galatia and the opposition to his missionary strategy in Jerusalem and Antioch had been instigated by ethnic Jewish groups furious at his ‘disloyalty’ to the ancestral traditions. Now he was accused of being a subversive Jew, in common with those who had rebelled against Rome before, teaching people to be disloyal to Rome! It all ended with a public apology and with the magistrates, clearly at a loss to know what to do next, imploring Paul and Silas to go away. They took their time in complying, visiting Lydia’s house and conversing with the group of believers there, and Timothy caught up with the two of them in Berea, but not Luke. Philippi was an important city in its own right, but Thessalonica, Paul’s next ‘port of call’ was even more so. It was on the main crossroads and its role as a port at the head of the Thermaic Gulf to the west of the Chalcidice Peninsula guaranteed its prosperity. It was the capital of the Roman province of Macedonia, and the Roman general Pompey had used it as his base in the civil war. In Paul’s day, it was not an official Roman colony, however: that was to come two centuries later, but it was already a major centre of Roman influence.
Unlike Philippi, Thessalonica had a sufficiently large Jewish population to sustain a synagogue. Luke’s summary of what Paul said on the three Sabbaths he spoke there conforms both to the earlier summaries and to Paul’s own repeated statements in his letters. The message was accepted by some of the Jews, several of the God-fearing Greeks, and quite a number of the leading women. It also appears from Paul’s letter to Thessalonica, written not long after this initial visit, that many in the young church there had been polytheistic pagans and had turned to God from idols, to serve a living and true God (I Thess. 1: 9). Clearly, this was a significant group of both Jews and Gentiles. One member in particular, Jason, gave hospitality to Paul and Silas, facing the brunt of the anger aroused for doing so. Some of the synagogue community turned against the missionaries and stirred up a mob, bent on violence, but they could not find them. What mattered, however, was the political nature of the charges that were thrown around as all this was going on:
“These are the people who are turning the world upside down!” they yelled. “Now they’ve come here! Jason has them in his house! They are all acting against the decrees of Caesar – and they’re saying that there is another king, Jesus!”
(Acts 17: 6-7).

It was true, of course, that if non-Jews were abandoning idols and worshipping the God of Israel, without formally becoming Jews, then they were indeed disobeying Caesar’s decrees. Only genuine Jews had that permission. So this meant that broadly speaking, Paul and his group were turning the world upside down. Paul and his friends were announcing and modelling in their own lives a different way of being human, a different kind of community, and all because there was a different kind of ‘king’. In any case, Jason and his friends were bound over to keep the peace, while Paul and Silas were smuggled out-of-town by night and sent on to Berea, about fifty miles to the west, but off the main route. They leave in a hurry, with a sense that the little body of believers is under threat. At Thessalonica and Beroea the old pattern reasserted itself: the Jewish opposition made mischief with the civil authorities, and Paul was obliged to move on, leaving his companions behind (Acts 17: 1-14). He arrived at Athens by boat alone (Acts 17: 15), in great disquiet (as he tells us in letters to Thessalonica written about this time) about the new converts whom he had been compelled by the local authorities to leave prematurely (I Thess. 2: 13-35; II Thess. 3: 6-16). Nevertheless, he bravely continued his ministry while waiting there for Silas and Timothy:
He wandered through the streets; everywhere there were temples and images of Greek gods. This made Paul very unhappy. He had to talk to somebody about it. He went to the Jewish Meeting House and argued there; he went to the market place and argued with anybody who happened to be there. There were many lecturers in the city, for its university was very famous; some of them met Paul, and he argued with them.
“What’s this chatterer talking about?” sneered some.
“It’s some foreign fellow talking about his gods, it seems,” said others.
The City Council was called ‘Mars Hill’, after the name of the hill where it used to meet in earlier times. This Council was specially interested in all new speakers who came to teach in Athens. The citizens of Athens and their foreign visitors always had time to talk about or listen to anything strange and new; they seemed to do nothing else.
The lecturers got hold of Paul and took him before the Council.
“Tell us, if you please, something more about this ‘news’ of yours,” they said. “What you’ve been talking about seems very strange to us. We’d like to know what it’s all about.”
Paul stood before the Council.
“Citizens of Athens,” he said, “by just wandering around your streets, I can see that religion matters very much to you. I had a good look at your temples and the images of your gods. And I noticed one altar that had these words on it: “To an Unknown God”. You do not know him; I will tell you about him.
“The God who made the world and all that’s in it by that very fact is the Master of the whole world. His home can’t be a in a street that you can build with your own hands. … We may belong to different nations now, but at the beginning God made us all one people and gave us the whole world for our home. All things are in his hands – the rise and fall of nations and the boundaries of their territories. He did all this for one purpose only – the men and women might look for him and find him.
“Yet he is very near every one of us. Your own poets have said this very thing –
‘In God we live and move and exist’,
“and…
‘We, too, belong to his family.’
“If, therefore, we belong to God, we can’t possibly think that gold and silver and stone are good enough to show us what he is like. No artist can paint God’s picture, however clever or thoughtful he may be.
“What then, has God done? He takes no notice of the past, when we didn’t know what he was like. But today, in our own time, he calls all people to change their ways. We can no longer say we do not know; Jesus has made him plain. The day is fixed when everybody everywhere will be judged by this man he has chosen – and truly judged. The proof of this he has given to all men – he has raised him from the dead.”
Some of them laughed out loud at Paul when they heard him talk like this – about God ‘raising Jesus from the dead’. But there were others.
“We will hear you again about all this,” they said.

For this, and for other reasons, he was in low spirits (as he tells us in retrospect in I Cor. 2: 3) as he left Athens for Corinth which became, as it turned out, the scene of his greatest success to date. Corinth had been one of the most important of the old Greek city-states. After its destruction by the Romans, it had been re-founded by Julius Caesar and had become capital of the province of Achaia. Situated on the isthmus which separates the Aegean from the Adriatic, and the eastern part of the empire from the western, it had become an immensely busy and prosperous centre of trade, with a multi-cultural population. It also had the unsavoury reputation which cosmopolitan seaport towns seem to attract.

It was in Corinth that Paul, reunited with his companions, spent nearly two years, maintaining himself by working at his trade of tent-making (Acts 18: 3, 11, 18). It was his longest sojourn anywhere since he had started on his journeys. His breach with the orthodox Jews set him free for independent action. He left the synagogue, taking with him one of its office-holders, and (perhaps in an act of deliberate defiance) set up his headquarters in a nearby house belonging to a Gentile believer (Acts 18: 5-8). The opposition once more tried to embroil him with the civil authorities, but the proconsul refused to enter the charges they brought, as being no more than some bickering about words and names and your Jewish law. The case was dismissed, which must have considerably strengthened Paul’s position (Acts 18: 12-17). He succeeded in building up a numerous and active if somewhat turbulent, Christian community, predominantly Gentile in membership before he left to return to Jerusalem and Antioch via Ephesus (Acts 18: 18-22), which he had already marked out as his next centre of work. It was in Ephesus that he was to meet a darker level of opposition which helps us to understand why he wrote as he did in II Corinthians of reaching the point where he was giving up on life itself.

(to be continued…)
Part One – From Tarsus to Antioch & Galatia:

Introduction:
For Christmas 2018, my eldest son gave me a copy of Tom Wright’s Biography of the Apostle Paul, ‘hot off the press’. It reminded me of the time, as a child, when I found a picture book of Paul’s life on my Coventry grandmother’s bookstand and read it in one sitting, cover to cover. It also reminded me of watching the television film shown above (from which I have included stills throughout the text). Both as Saul of Tarsus and Paul the Apostle, his was an eventful and exciting life story, as he himself recognised in his later letter to the church at Corinth:
Let me tell you what I’ve had to face. I know it’s silly for me to talk like this, but here’s the list. I know what it is to work hard and live dangerously.
I’ve been beaten up more times than I can remember, been in more than one prison, and faced death more than once. Five times I’ve been thrashed by a Jewish court to within an inch of my life; three times I’ve been beaten with (Roman) rods by city magistrates; and once I was nearly stoned to death.
I’ve been shipwrecked three times; and once, I was adrift, out of sight of land, for twenty-four hours.
I don’t know how many roads I’ve tramped. I’ve faced bandits; I’ve been attacked by fellow-countrymen and by foreigners. I’ve met danger in city streets and on lonely country roads and out in the open sea.
(II Cor. 11: 23-33, New World.)
The writings of Paul have had an incalculable influence on Western culture and beyond, and his words continue to guide the lives of two billion Christians throughout the world today. In his biography, Tom Wright traces Paul’s career from the Sanhedrin’s zealous persecutor of the fledgling Church, through his journeys as the world’s greatest missionary and theologian, to his likely death as a Christian martyr under Nero in the mid-sixties of the first century.

To understand Paul, Wright insists, we must understand the Jewish world in which the young Saul grew up, a world itself firmly earthed in the soil of wider Graeco-Roman culture. This is what I want to concentrate on here, especially in the context in which Wright is writing, a twenty-first century which seems just as filled with religious and ethnic hatred and in which anti-Jewish thought, feelings and actions are once more on the rise, despite the atrocities of the previous century. The ‘Breaking News’ as I write is that incidents of anti-Semitism in Britain have risen for the third year running: 1,652 incidents were recorded by Community Security Trust (CST) in 2018, including more than 100 Assaults. Growing up in a Baptist manse in Birmingham in the 1960s and ’70s, I became conscious of anti-Semitism at the age of eleven when I asked one of the older boys I regularly walked to school with if he was a ‘Jewboy’. I had heard my father use the term, but didn’t think, at that time, that it meant anything other than a ‘Jewish’ boy and didn’t realise that it was used as a term of abuse. After they were called to the school, my parents informed me of this, I apologised to the boy and never used the term again. Later, I understood that my father’s view of the Jews was based on ‘replacement’ theology, the idea that the Christian Church had been chosen to replace the people of Judea and Israel, who had proved themselves unworthy by their rejection of Jesus and their ‘role’ in his crucifixion. One of my seventh-generation Baptist grandmother’s books, George F Jowett’s The Drama of the Lost Disciples (1961) expressed this (then) popular view:
Jesus Himself… denounces the Sadducean Jews, telling them that the glory shall be taken away from them and given to another (Matt. 21: 43). Again, when He says He came not to the Jews, but to the lost sheep of the House of Israel (Matt. 15: 24). He knew He would not convert the Sanhedrin and its following, so it had to be others – the lost sheep. Who were they? The answer lies in his answer to Paul, the converted Saul, whom he commands to go the Gentiles.
C. H. Dodd wrote (1970) that Paul was the pioneer leader in the Christian approach to the Graeco-Roman public. The fortunate preservation of a number of his letters has put us in a position to know him better than we know most individuals of the ancient world. The information they give can be supplemented from the account of his career given in the Acts of the Apostles. Whilst there are points where it is not easy to bring the two sources of our knowledge into complete harmony, there is a good reason to believe that the author of ‘Acts’, thought to be Luke (the gospel-writer and Greek doctor), was well-informed, and may have travelled with Paul himself. This made him an eye-witness, and his account may be used as a historical frame in which to set Paul’s own accounts, contained in his letters.
Saul of Tarsus:

According to Acts 21: 39, Paul was born at Tarsus in Cilicia, an ancient Greek city, and then a strong centre of Hellenistic culture, his parents belonging to the Jewish colony there. Tarsus was ten miles inland on the river Cydnus in the south-east corner of what is Turkey today, in ‘Asia Minor’, on the major east-west routes. It was a ‘noble city’ which could trace its history back two thousand years. Generals like Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar had recognised its strategic importance; the emperor Augustus had given it extra privileges. It was a city of culture and politics, of philosophy and industry. It had a thriving textile business, producing materials from goats’ hair, used to make shelters, which may well have been the basis of the family business of tent-making, in which Saul had been apprenticed and which he continued to practice.
The cosmopolitan world of the eastern Mediterranean flowed through the city, which rivalled Athens as a centre of philosophy, not least because half the philosophers of Athens had gone there a century earlier when Athens had incurred the wrath of Rome in a struggle for power. The Jews had struck a deal with Augustus Caesar by which he accepted that they were exempted from adopting the ‘divinity’ cult of his father, Julius Caesar. In return, they agreed to pray to their One God for Rome and its emperor.
We don’t know how long his family had lived in Tarsus. Later legends suggest various options, one of which is that his father or grandfather had lived in Palestine but had moved during one of the periodic social and political upheavals which always carried ‘religious’ overtones as well. They were orthodox Jews and brought their son up in the Pharisaic tradition (23:6; 26:5). The word ‘Pharisee’ has had a bad press over the centuries since. Modern research, operating at the academic rather than the popular level, has done little to dispel that impression, partly because the research in question has made things far more complicated, as research in question in question has made things far more complicated, as research often does. Most of the sources for understanding the Pharisees of Saul’s day come from a much later period. The rabbis of the third and fourth centuries AD looked back to the Pharisees as their spiritual ancestors and so tended to project onto them their own questions and ways of seeing things. But besides Paul’s writings, the other first-century source on the Pharisees, the Jewish historian Josephus, also requires caution. Having been a general at the start of the Roman-Jewish war of AD 66-70, he had gone over to the Romans and claimed that Israel’s One God had done the same thing, an alarmingly clear case of remaking the Almighty in one’s own image.
In Tarsus, as throughout the ‘Diaspora’, there were all sorts of cultural pressures which would draw devout Jews into compromise. Families and individuals faced questions such as what to eat, whom to eat with, whom to do business with, whom to marry, what attitude to take toward local officials, taxes, customs and rituals. The decisions individuals made on all of these questions would mark them out in the eyes of some as too compromised and in the eyes of others as too strict. There was seldom if ever in the ancient world a simple divide, with Jews on one side and gentiles on the other. We should envisage, rather, a complex subculture in which Jews as a whole saw themselves as broadly different from their gentile neighbours. Within that, the entire subgroups of Jews saw themselves as different from other subgroups. The parties and sects we know from Palestinian Jewish life of the time – Sadducees, Pharisees, Essenes, and a nascent militantly ‘zealous’ faction – may not have existed exactly as we describe them, not least because the Sadducees were a small Jerusalem-based aristocracy, but intra-Jewish political and social divisions would have persisted.
We can’t be sure how many Jews lived in Tarsus in Saul’s day. There were, quite possibly, a few thousand at least in a city of roughly a hundred thousand. But we can get a clear sense of how things were for the young Saul. In the ancient world, there was no such thing as ‘private life’ for individuals and families. A tiny number of the aristocracy or the very rich were able to afford a measure of privacy but for the great majority, life was lived publicly and visibly. The streets were mostly narrow, the houses and tenements were mostly cramped, there were noises and smells everywhere, and everyone knew everybody else’s business. We can assume that this was true for the Jews of Tarsus who would have lived close to each other partly for their own safety and partly for the ease of obtaining ‘kosher’ food. The questions of where one stood on the spectrum between strict adherence to the ancestral code, the Torah, and ‘compromise’ were not theoretical. They were about what one did and what one didn’t do in full view of neighbours, and about how those neighbours might react.
The Torah loomed all the larger if one lived, as did the young Saul, outside the promised land and hence away from the Temple. The Torah, in fact, functioned as a movable Temple for the many Jews who were scattered around the wider world. Wherever they were, in Rome or in Babylon, Greece or Egypt, if they prayerfully studied it, then it might be as if they were in the Temple itself. They would be in the divine presence, not in its most dramatic form, but there nonetheless. But the Temple in Jerusalem remained central, geographically and symbolically. It was the place where heaven and earth met, thus forming the signpost to the ultimate promise, the renewal and unity of heaven and earth, the new creation in which the One God would be personally present forever. We don’t know how often Saul travelled with his parents to the homeland with his parents for the great festivals. It is quite probable that, at an early age, the young Saul acquired the sense that all roads, spiritually as well as geographically, to Jerusalem. The Temple was like a cultural and theological magnet, drawing together not only heaven and earth but also the great scriptural stories and promises. In addition, therefore, it was the focal point of Israel’s hope, The One God, so the prophets had said, abandoned his house in Jerusalem because of the people’s idolatry and sin. Tom Wright argues that we will never understand how the young Saul of Tarsus thought and prayed until we grasp…
… the strange fact that, though the Temple still held powerful memories of divine presence … there was a strong sense that the promise of ultimate divine return had not yet been fulfilled. …
… The God of Israel had said he would return, but had not yet done so.
Saul of Tarsus was brought up to believe that it would happen, perhaps very soon. Israel’s God would indeed return in glory to establish his kingdom in visible global power. He was also taught that there were things Jews could be doing to keep this promise and hope on track. It was vital for Jews to keep the Torah with rigorous attention to detail and to defend the Torah, and the Temple itself, against possible attacks and threats. … That is why Saul of Tarsus persecuted Jesus’s early followers.
The young Saul was not ‘learning religion’ in the accepted modern sense of general religious education, and the mature apostle was not a teacher of it. Today, ‘religion’ for most people in the West designates a detached area of life or even a private hobby, separated by definition from politics and public life, and especially from science and technology. In Paul’s day, ‘religion’ meant almost the exact opposite. The Latin word religio has to do with binding things together. Worship, prayer, sacrifice, and other public rituals were designed to hold the unseen inhabitants (gods and ancestors) together with the visible ones, the living humans, thus providing a vital framework for ordinary life, for business, marriage, travel, home life and work. The public nature of individual life was apparent in the workplace. We know from Paul’s later letters that he engaged in manual work, both as a young apprentice and later to support himself as a missionary. ‘Tent-making’ probably included the crafting of other goods made of leather or animal hair in addition to the core product of tents themselves. Many people migrated from place to place for work, those who worked outside needed awnings and pilgrims required ‘tabernacles’ for their sojourns.
The market for tents and similar products was widespread. We might guess those likely purchasers would include regiments of soldiers, but travel was a way of life for many others in the Roman Empire. It seems unlikely that a Jewish tent-maker would be selling only to fellow Jews. We can assume, therefore, that Saul grew up in a cheerfully and strictly observant Jewish home, on the one hand, and in a polyglot, multicultural, multi-ethnic working environment on the other. Strict adherence to the ancestral tradition did not preclude know-how of the wider world of work, and how it spoke, behaved and thought. The tent-maker was unlikely to have had a ‘sheltered’ upbringing. The place where the invisible world (‘heaven’) and the visible world (‘earth’) were joined together was the Temple in Jerusalem. If, as in his case, you couldn’t get to the Temple, you could and should study and practice the Torah, and it would have the same effect. Temple and Torah, the two great symbols of Jewish life, pointed to the story in which devout Jews like Saul and his family believed themselves to be living:
… the great story of Israel and the world, which, they hoped, was at last to set up his kingdom, to make the whole world one vast glory-filled Temple, and to enable all people – or at least his chosen people – to keep the Torah perfectly. Any who prayed or sang the Psalms regularly would find themselves thinking this, hoping this, praying this, day after day, month after month.

As an apprentice in the bustling pagan city of Tarsus, the young Saul knew perfectly well what it meant to be a loyal Jew. It meant keeping oneself pure from idolatry and immorality. There were pagan temples and shrines on every corner, and Saul would have had a fair idea of what went on there. Loyalty meant keeping the Jewish community pure from all those things as well. Saul’s family seem to have lived with a fierce, joyful strictness in obedience to the ancient traditions and did their best to urge other Jews to do the same. At the same time, his father possessed the coveted status of a Roman citizen, which meant that the family had a superior standing in the local community and his son also had Roman citizenship as his birthright (Acts 22: 25-29). He grew up bilingual (fluent in both in Aramaic and Greek) and bi-cultural: at home, he was Saul, named after the first king of Israel; outside he was Paulus, a citizen of Tarsus and of Rome. He was also literate in Hebrew, able to read the scriptures in the original. His mind had the freedom of two worlds of thought: He had more than the average educated man’s understanding of Greek literature and philosophy. His language quite often carries echoes of ‘Stoicism’.
A Zealous Student in Jerusalem:

On the other hand, Saul’s formal education seems to have been entirely within the native Jewish tradition, and he was sent to Jerusalem as a young man to study under Gamaliel (Acts 22: 3), the most distinguished rabbi of his time. Paul was not only, evidently, well versed in the Scriptures, but also in the Rabbinic methods of interpreting them, which sometimes present difficulties for modern readers.
He was therefore well-equipped for his later mission to take the message of a religion rooted in Judaism to a generally non-Jewish Hellenistic public.

At every stage of Israel’s history, the people of the One God had been tempted to compromise with the wider world and forget the covenant. Resisting this pressure for Saul meant becoming zealous. In his letter to the Galatians (1: 14), Paul wrote I was extremely zealous for my ancestral traditions. Nevertheless, Saul the Pharisee and Paul the Roman, it seems, did not live in complete harmony within the same skin. There are signs of psychological tension; in early life, the Pharisee was uppermost. He recites with pride the privileges of the chosen people:
They are Israelites; they were made God’s sons; theirs is the splendour of the divine presence, theirs the covenants, the law, the temple worship, and the promises. (Rom. 9: 4, NEB)
Not only was he proud of the Hebrew people, but he was also proud beyond measure of his own standing as a Jew:
Israelite by race, of the tribe of Benjamin, a Hebrew born and bred: in my attitude to the law a Pharisee, in pious zeal a persecutor of the church, in legal rectitude faultless (Phil. 3: 5-6).
In another retrospect on his early life he added a significant claim:
In the practice of our national religion I was outstripping many of my Jewish contemporaries in my boundless devotion to the traditions of my ancestors (Gal. 1: 14).
That tells us something powerful about the man; from a young age, he had possessed an irresistible drive to excel, to be distinguished. It was necessary to his self-respect that he should himself as the perfect Pharisee: in legal rectitude faultless. This has led to some Judaistic readers to suggest that there was something extravagant or abnormal in Paul’s account of his pre-Damascene phase. The time came when he himself was forced to confess to himself that this was fantasy, not reality. He was not faultless, and his efforts in pursuit of perfection had been self-defeating:
When I want to do the right, only the wrong is within my reach. In my inmost self I delight in the law of God, but I perceive that there is in my bodily members a different law, fighting against the law that my reason approves. (Rom. 7: 21 f.).
Yet by the time Paul was studying in Jerusalem, it was clear that the Abrahamic ‘project’, Israel’s ancestral vocation, was at the point where it needed rescuing. Some Jews had returned to Palestine from Babylon, while others were scattered all over the known world. But the cry went up from one generation to the next over the four centuries to the time of the Roman occupation: We are still in exile! Exile was not just a geographical reality; it was a state of mind and heart, of politics and practicalities, of spirit and flesh. As long as pagans were ruling over Jews, and demanding taxes from them, and profaning their Holy Place, the Jews were again in exile. Since the exile was the result of Israel’s idolatry, according to the prophets, what they needed was not just a new Passover, a new rescue from slavery to pagan tyrants: they needed forgiveness. As Tom Wright has put it, …
That was the good news the prophets had spoken of, the word of comfort at every level from the spiritual to the physical. … When the One God finally puts away the idolatry and wickedness that caused his people to be exiled in the first place, then his people will be ‘free at last’, Passover people with a difference.
That was the ancient hope which Saul of Tarsus cherished along with thousands of his fellow Jews, by no means all of whom were as ‘zealous’ as he was. Few had his intellectual gifts, but they were, like him, very well aware, through scripture and liturgy, of the tensions between those promises and their present predicament. Theirs was a religious culture suffused with hope, albeit long deferred. That was the great narrative in which they lived out their daily lives in their heads and their hearts, giving shape and energy to their aspirations and motivations. Paul sought a means of working out his inner conflict in action, and it was this that made him, at first, a persecutor. His first contact with the new sect of the ‘Nazarenes’, it appears, was one of the most radical and aggressive representatives, a Hellenistic Jew (like Paul himself) named Stephen, who was reported to be…
… forever saying things against the holy place and the law … saying that Jesus of Nazareth will destroy this place (the Temple) and alter the customs handed down to us by Moses (Acts 6: 13 f.)

This was an act which impugned the most sacred pledges of Israel’s status as God’s chosen people. And when it appeared that these sectaries hailed Jesus of Nazareth as God’s Messiah, this was sheer blasphemy. Did not the Law say, cursed is everyone who is hanged on a gibbet (Gal. 3: 13)? These people were dragging the glory of Israel into the mire: they were enemies of the Temple and the Torah, enemies of Israel, enemies of Israel’s God. Jerusalem’s Temple, like the wilderness Tabernacle before it, was designed as a small working model of the entire cosmos. This was where the One God of creation would live, dwelling in the midst of his people. When the Temple was destroyed, this vision was shattered, but the prophets had declared that God would one day return and that the people should prepare for that day. Yet the Jews of Saul’s day found themselves in the long, puzzling interval between the time when the One God had abandoned the Temple and the time when he would return in glory, bringing heaven and earth together at last. Seers, mystics and poets wrote of dreams and visions whose subject matter was the rescue of Israel and the final saving ‘revelation’ (apokalypsis in Greek) of the One God. This was the world in which Saul of Tarsus, heir to these traditions, practised his fierce and loyal devotion to Israel’s God. This was how he could keep hope alive and perhaps even to glimpse its fulfilment in advance.
Locating him within this world is not a matter of psychoanalysis, but of history. We are trying to think our way into the mind of a zealous young Jew determined to do God’s will whatever its cost, eager to purge Israel from idolatry and sin, keen to hasten the time when God would come back to rule his world with justice and righteousness. All the fear and hatred that Saul felt for that in himself which was ‘fighting against the Law’ could now be directed upon overt enemies. Stephen was stoned to death, with Saul as an accessory. This was only a beginning. With characteristic determination to outstrip everyone else in his zeal for the Law, Saul obtained from the high priest a commission to hunt the heretics down wherever they might be found (Acts 9: 1 f.).
The Followers of ‘The Way’ & The Road to Damascus:

According to Acts, the Sanhedrin’s persecution of the first followers of ‘The Way’ (not yet calling themselves Christians) collapsed when Saul had his dramatic encounter with the risen Christ on the way to Damascus, and became Paul, on a permanent basis. The incredible happened, apparently. Paul was struck blind and heard the voice of Christ speaking to him and was suddenly converted to the faith of ‘The Way’. Going into hiding with those he had planned to persecute, he had his sight restored. Wright suggests that this ‘apocalyptic’ event needs to be set in the context of Saul’s seeking, through prayer and meditation, to inhabit for himself the strange old traditions of heaven-and-earth commerce, to become in mind, soul and body, a visionary whose inner eye, and perhaps whose outer eye, might glimpse the ultimate mystery. The practice of this kind of meditation was something one might well do on the long, hot journey from Jerusalem to Damascus.

When this news got back to Jerusalem, it stunned the Sanhedrin, infuriating them beyond measure. They ordered an all-out drive to seize him and kill him on sight. In a complete reversal of circumstances, the hunter became the hunted. Paul went into hiding himself, appealing for aid from Christ’s disciples. Not unnaturally, they feared this might be a ploy by a man they knew to be clever, cruel and unscrupulous to uncover their secret network of survivors of his own terror, but they finally complied, lowering him over the wall of the city with a rope (Acts 9: 25). The effects of his conversion experience on both his career and the passage of history in which he played his part are open to observation. It is evident that it brought a resolution to his personal predicament. His attempt to resolve it by externalising his inner conflict had proved to be no solution at all. He now found real reconciliation of the contending forces in his soul through his reconciliation with the ‘enemies’ he had been pursuing with such pious hatred. He threw in his lot with them and with ‘Jesus whom he was persecuting’. But to do so meant standing with one who was under the curse of the ‘Law’: it was to become an ‘outlaw’. He wrote that he had been crucified with Christ (Gal. 2: 20).

It was the most complete break possible with his past self. It took all meaning out of the desperate struggle to see himself in legal rectitude faultless. He could now accept himself as he was, aware of his weaknesses yet willing to stand at the disposal of his new Master. He wrote of how we make it our ambition to be acceptable to him (II Cor. 5: 9). This was a different type of ‘ambition’ from that which had spurred him on to outstrip his Jewish contemporaries. It was the displacement of self from the centre, which proved to be the removal of a heavy burden. But above all it was a liberating experience: ‘Christ set us free, to be free men’ (Gal. 5: 1). It shows itself in an expansion of the range of his interests and energies, no longer restricted by Jewish nationalism and orthodoxy. For an Orthodox Jew who lived the life of a great Greek city, relations with Gentiles were always problematic. Paul was repressing his natural instincts in maintaining the degree of separation from his Gentile fellow-citizens which ‘legal rectitude’ seemed to require. Now he could give those instincts free rein. From the moment of his encounter with Jesus on the road to Damascus, he knew that the ‘dividing wall’ was broken down and that he must ‘go to the Gentiles’. Thus the main direction of his new mission was decided from the outset, though it may have been some years before the required strategy was worked out. The rest of what happened to him after this escape with the disciples, as St. Paul, the Apostle to the Gentiles, is well-known, not just from the narratives in Acts, but also from his own letters. But we are scantily informed about his early years as a Christian, and the skeleton outline of the Acts tells us little. All that we have from the man himself are his recollections and reflections on the situations into which his missionary career had brought him.
Similarly, the drama of Saul’s Damascene conversion fits too neatly with the need for an early Christian account of a new departure, schism or breakaway in what, in reality, was a gradual evolution of Christianity from Judaism. At first, Christians were regarded as a Jewish sect by both Jews and Gentiles. This led to opposition and persecution of the church by the Jewish authorities, who objected to its doctrines and the admission of Gentiles without their accepting the Law. Yet since Jews were also already scattered in communities throughout the Empire and beyond, they provided Christian missionaries with an entry into the Gentile world. It was not until three years after his conversion that Paul returned to Jerusalem (Gal. 1: 17-19). At that time he stayed for a fortnight with Peter (or ‘Cephas’, as he calls him, using the Aramaic name given to him by Jesus) and also met James, ‘the Lord’s brother’. These would be able to tell him much at first-hand about Jesus. His stay in Jerusalem seems to have been cut short. however, and he then spent a period of about a dozen years in ‘the regions of Cilicia and Syria’ (Gal. 1: 21). Perhaps some of the adventures he recalls later in life belong to that period, but Acts records only his return to Tarsus, in Cilicia (9: 30) and his removal to Antioch, in Syria (Acts 11: 25 f.). It was with his arrival in the Syrian capital, where Jesus’ followers were first given the nickname ‘Christian’, that the story of his missionary journeys really begins.

The Synagogues; The Judaeo-Palestinian Converts & The Antiochene Church:

Above: Paul regularly used the local synagogue as his starting-point when bringing the gospel to a new place. Later, the bridges between Jews and Christians were broken. This reconstructed second-century synagogue is at Sardis, in modern-day Turkey.

Since these first missionaries, such as Paul and other apostles were Jews, they used the synagogues, both inside and outside Judea and Palestine as ready-made centres for evangelism. Paul regularly used the local synagogue as the starting point for bringing the gospel to a new place. Recent archaeological evidence at Capernaum and elsewhere in Palestine supports the view that early Christians were allowed to use the synagogues for their own meetings for worship. Although most of their fellow Jews remained unconverted, many God-fearing Gentiles, who were attracted to Judaism but had not gone through the ritual of total integration into the Jewish community, became Christian converts. In fact, in spite of the growing divergence between the church and the synagogue, the Christian communities worshipped and operated essentially as Jewish synagogues for more than a generation. Apart from the period of the Jewish wars, the Roman Empire enjoyed three hundred years of peace and general prosperity. This was known as the Pax Romana, the Roman peace. It allowed both Christians and Jews great freedom to travel throughout the Mediterranean world along superbly engineered roads and under the protection of the Roman government. Paul was able to do this until the final years of his life, but he was only the first of many missionaries. Equally, pilgrims to Jerusalem were able to travel in the opposite direction. This was part of the reason why Paul emphasised the importance of good government.

The ‘Christian’ community at Antioch included a substantial proportion of non-Jewish converts from paganism. The division between Jew and Gentile, from the Jewish point of view, was greater than any other social or cultural division, more important even than the other two distinctions that run through the whole ancient world, those between slave and free, on the one hand, and male and female on the other. Different Jewish community leaders would draw the lines between Jew and non-Jew at different places. Business dealings might be fine, but business partnerships might be frowned upon. Friendships were tolerated, but not intermarriage. The lines might be blurred, broken or redrawn, but they were still there. Underneath it all, there was still a sense of difference, of “them and us.” Social and cultural indicators would provide visible markers. What you ate, and who you ate with were the most obvious of these, but there were others too. From a Gentile perspective, non-Jewish writers of the day sneered at the Jews for their ‘Sabbath’, claiming that they just wanted a “lazy day” once a week. The fact that Jews didn’t eat pork, the meat most ordinarily available, looked like a ploy to appear socially superior. Jewish males were circumcised, so if they participated in the gymnasium, which normally meant going naked, they might expect taunts.
Beneath these social indicators was the more deeply seated non-Jewish suspicion that the Jews were, in reality, atheists. They didn’t worship the gods, didn’t turn out for the great festivals, didn’t go to parties at the pagan temples and didn’t offer animal sacrifices at local shrines. They claimed that there was only one true Temple, the one in Jerusalem, but rumours abounded, going back to the time when the Roman general Pompey had marched into the Holy of Holies, that the Jews had no image, no statue of their god. Hence the charge of atheism, which was not so much one of theological belief (since the authorities tolerated a whole range of beliefs) but a practical one. The gods mattered for the life and health of the community as a whole. If bad things happened, it was because the gods were angry, probably because people hadn’t been taking them seriously and offering the required worship. People who didn’t believe in the gods were, therefore, placing the entire city, the whole culture or the whole known world at risk. The Jews had their answers for all this, and Saul would have grown up knowing these debates well. After his move to Antioch, he must have heard them repeated with wearying familiarity. “Our God,” the Jews would have said, …
“… is the One God who made the whole world. He cannot be represented by a human-made image. We will demonstrate who he is by the way we live. If we join the world around in worshipping the local divinities – let alone in worshipping the Roman emperor (as people were starting to do when Saul was growing up) – we will be making the mistake our ancestors made.”
In fact, a significant minority of Gentiles admired the Jews for their integrity in this respect, preferring their clear lines of belief and behaviour to the dark muddles of paganism. Many of them attached themselves to the synagogue communities as “God-fearers.” Some went all the way to full conversion as “proselytes.” But the Jews were clear about the fact that, if they compromised with the pagan world around them, however ‘compromise’ might have been defined in any particular city or household, they would be giving up their heritage, and with it their hope for a new world, for the One God to become king at last. So what would the diaspora Jewish communities in Tarsus or Antioch think of the suggestion that the One God had already done what he had promised by sending a Messiah to be crucified? What would this mean for Jewish identity? Was this ‘good news’ simply for the Jewish people, or might it be for everyone?

Syrian Antioch, even more than Tarsus, was exactly the kind of place where these questions would rise quickly to the surface. It boasted a busy, bustling mixture of cultures, ethnic groups and religious traditions, including a substantial Jewish population. The Roman General Pompey had made it the capital of the new province of Syria, and Julius Caesar had raised it to the level of an autonomous city. With a population of around a quarter of a million, it was widely regarded in antiquity as the third or fourth city of the East, after Alexandria, Seleucia and later Constantinople. It was a classic ‘melting-pot’ in which every kind of social and cultural group was represented.
It isn’t difficult to imagine the crowded streets, the markets selling exotic fruit as well as local produce, the traders and travellers, foreigners in strange costumes and the temples on every street corner. It wasn’t surprising that some of the early followers of Jesus had found their way there, considering that everyone else had. Nor was it surprising that they were eager to share the ‘good news’ of Jesus with non-Jews as well as Jews. If the Jewish scriptures had seen the coming king as Lord of the whole world, how could membership in this kingdom be for Jews only?
Some of the believers who had come to Antioch from Cyprus and Cyrene saw no reason for any such limitation. They went about telling the non-Jews about Jesus as well. A large number of such people believed the message, abandoned their pagan ways and switched their allegiance to the Christ as Lord. Many Jews would have naturally supposed that these Gentiles would then have to become full Jews. If they were sharing in the ancient promises, ought they not to share in its ancient customs as well? What sort of common life ought this new community to develop? The introduction of this Gentile element in Antioch had no doubt acted as a stimulant, and it is not surprising that they soon found themselves impelled to reach out to a still wider public in the Graeco-Roman world. For this task, they selected a Cypriot Jew of the tribe of Levi, Joseph, known as Barnabas (Acts 4:36 f.; 11: 22-24; 13: 2.), a nickname given to him by the church in Jerusalem which means “son of encouragement.” He was one of those early followers of Jesus who had the gift of enabling others to flourish. The Jerusalem church had sent him to Antioch to see what was going on there.
 Good-hearted Barnabas (pictured in a recent film portrayal by Franco Nero, right) was not the sort to jump instinctively to a negative response, to reach for familiar prejudices just because something was new. He could see the transformed lives and transparent faith of the Gentile believers which were the work of divine grace, reaching out in generous love to people of every background and origin.
Good-hearted Barnabas (pictured in a recent film portrayal by Franco Nero, right) was not the sort to jump instinctively to a negative response, to reach for familiar prejudices just because something was new. He could see the transformed lives and transparent faith of the Gentile believers which were the work of divine grace, reaching out in generous love to people of every background and origin.
Barnabas shared Paul’s belief that the death and resurrection of Jesus Christ had broken down the barriers to Gentile inclusion in God’s kingdom. The evidence of a new dynamic in worship and of the love which meant shared obligations of mutual support told its own story to Barnabas. Others from Jerusalem, faced with the same evidence, might have reached a different conclusion. They would have urged the believers in Antioch to restrict themselves to their own ethnic groups, at least for mealtimes and perhaps even for the Lord’s meal, the “breaking of bread.” Many Jews would have assumed that Gentiles still carried contagious pollution from their culture of idolatry and immorality. But as far as Barnabas was concerned, what mattered was the depth of their belief and allegiance to the Lord. This new community was not defined by genealogy, but by the Lord himself, and what counted as a sure sign of their belonging to Him was loyalty and ‘faithfulness’.

Paul was an obvious choice to join him as a companion since Barnabas had first introduced him to the Antiochene church (Acts 11: 25 f.). They were therefore at the centre of the controversies there and became firm friends. The vibrant and excited group of Jesus-followers in Antioch was doing something radically counter-cultural, experimenting with a whole new way of being human, and Barnabas and Paul would have to help them think through what that really meant. In this way, the friendship between the two ‘brothers in Christ’ helped to shape Paul’s mind and teaching, leading to what, with long hindsight, we might call Christian theology. It had been a decade since Saul had gone to Tarsus, after his brief time in Damascus and Jerusalem. We don’t know whether anyone in either Jerusalem had seen or heard of him during that time, but Barnabas had a strong sense that he was the right man for the job. This was the beginning of a partnership that would launch the first recorded official ‘mission’ of the new movement. He worked with Barnabas and the local leaders in Antioch for a whole year, teaching and guiding the growing community.
 The pair was then sent to Jerusalem with a gift of money for the Jerusalem believers, who were suffering from their decade-long persecution by the authorities and struggling to stay alive at a time of widespread famine in AD 46-47. Paul’s own retrospective account of the visit (Gal. 2: 1-10) ends with the Jerusalem leaders admonishing him to go on “remembering the poor.”
The pair was then sent to Jerusalem with a gift of money for the Jerusalem believers, who were suffering from their decade-long persecution by the authorities and struggling to stay alive at a time of widespread famine in AD 46-47. Paul’s own retrospective account of the visit (Gal. 2: 1-10) ends with the Jerusalem leaders admonishing him to go on “remembering the poor.”
While there, Paul argued his case for inclusion of the Gentiles in the koinonia (international fellowship). The three central ‘pillars’ of the Jerusalem church; James (brother of Jesus), Peter and John, all agreed that they would continue to restrict their mission to the Jewish people in ancient Israel, while Paul, Barnabas and their friends in Antioch could continue their work among the Gentiles of the Mediterranean world.
Into Asia Minor – The First Missionary Journey:


The junior colleague soon slipped into the leading role for which his vigour and discernment marked him out. Thus began what is commonly referred to as his ‘First Missionary Journey’ which first took the two to Cyprus (Acts 13: 4-12) and then on as far as the interior of Asia Minor, and in particular to a group of towns in the southern corner of the province of Galatia (Acts 13: 14,51; 14: 6 f.). We can date this journey roughly to AD 47-48.

Above: It was through country such as this (in modern Turkey) that Paul and his companions, Barnabas and John Mark, travelled into central Asia Minor on their first arduous mission. They founded a number of churches in Galatia.
In the first of these towns, Antioch-towards-Pisidia (Acts 13: 15-50) the apostles began with an address in the synagogue to a congregation which included both Jews and ‘Gentile worshippers’. The latter was a group of people, now fairly numerous in many Hellenistic cities, as in Antioch, who were attracted to by Judaism to attend the synagogue services, without becoming regular ‘proselytes’ and members of the ‘commonwealth of Israel’. They showed a lively interest which spread to circles without previous association with the synagogue. From his letters, we can gather that Paul suggested that these people could become full members of the people of God without submitting to the Jewish Law, by joining the Christian church. This provoked a violent reaction from stricter Jews, however, who could only see this new preaching as a threat to their way of life. They denounced Paul and Barnabas as false teachers leading Israel astray.
 Paul’s response was to quote Isaiah 49: I have set you for a light to the nations so that you can be salvation-bringers to the end of the earth. This delighted the non-Jews who had heard his message: they were free to belong to God’s ancient people. But this, in turn, strengthened Jewish reaction, producing an altogether more serious turn of events.
Paul’s response was to quote Isaiah 49: I have set you for a light to the nations so that you can be salvation-bringers to the end of the earth. This delighted the non-Jews who had heard his message: they were free to belong to God’s ancient people. But this, in turn, strengthened Jewish reaction, producing an altogether more serious turn of events.
Both the leading Jews and the leading citizens of the town saw the threat of real civic disorder. When opposition turned to violence, this was sufficient to cause the missionaries to leave the town in a hurry, symbolically shaking the dust off their feet as they did so, but also leaving behind them the beginnings of a new community filled with joy and with the Holy Spirit. After that experience, however, the missionaries put out a statement of policy, making it clear to the Jewish communities in the cities they were to visit that:
It was necessary that the word of God should be declared to you first, but since you reject it … we now turn to the Gentiles (Acts 13: 46).

 This principle, to the Jew first, and also to the Greek (Rom. 1: 16; 2: 9 f.) was the principle that guided Paul’s ministry and expressed many times in his letters. In his letter to the Romans, he provided a theological justification for it (Rom. 11: 1-27). The outcome of this tour was the foundation of several communities, largely Gentile in membership, and the unleashing of Jewish hostility to Paul’s mission which was to follow him wherever he went, and to finally bring his active career to an end. When Paul and Barnabas found themselves facing people in remote highlands of ancient Anatolia with a strange language and religion, they became overnight heroes when Paul healed a man who had been crippled since birth (depicted above). As the pagan crowd began to worship them, they remonstrated with it that this was not the purpose of their mission. At that point, Jews from the towns where they had already been who had followed them there, told the pagan crowd in the town of Lystra what they thought about the missionaries:
This principle, to the Jew first, and also to the Greek (Rom. 1: 16; 2: 9 f.) was the principle that guided Paul’s ministry and expressed many times in his letters. In his letter to the Romans, he provided a theological justification for it (Rom. 11: 1-27). The outcome of this tour was the foundation of several communities, largely Gentile in membership, and the unleashing of Jewish hostility to Paul’s mission which was to follow him wherever he went, and to finally bring his active career to an end. When Paul and Barnabas found themselves facing people in remote highlands of ancient Anatolia with a strange language and religion, they became overnight heroes when Paul healed a man who had been crippled since birth (depicted above). As the pagan crowd began to worship them, they remonstrated with it that this was not the purpose of their mission. At that point, Jews from the towns where they had already been who had followed them there, told the pagan crowd in the town of Lystra what they thought about the missionaries:
That turned the crowd against them, and they started to throw stones at Paul. They thought they had killed him, and dragged him outside the town. Paul’s friends stood round him; they, too, thought he was dead. But he got up and went back into the town. (Acts 14: 8-20)

Illustration by Trevor Stubley of the stoning of Paul at Lystra,
for Alan T Dale’s Portrait of Jesus (OUP, 1979).
Paul explained to his friends that this kind of suffering was precisely the sign of the two world’s colliding; they are on the cusp of a new world, and if this is what it costs, so be it. Despite these trials and tribulations, what they had witnessed before in Syrian Antioch – the creation of a new community in which Jews and Gentiles were able to live together because all that previously separated them had been dealt with on the cross – had come true in city after city. At the heart of Paul’s message was radical messianic eschatology. ‘Eschatology’ because God’s long-awaited new day had dawned; ‘Messianic’, since Jesus was the true son of David, announced as such in his resurrection and bringing to completion the purposes announced to Abraham and extended by the psalmists and the prophets to embrace the whole world; ‘Radical’ in the sense that nothing in the backgrounds of either Paul or Barnabas had prepared them for the new state of affairs they were facing. The fact that they believed it was what the One God had always planned did not reduce their own sense of awe and astonishment.
What they could not have foreseen, as they travelled back through the southern part of the province of Galatia and then sailed home to Syria, was that the new reality they had witnessed would become the focus of sharp controversy even among Jesus’s followers and that the two of them would find themselves on opposite sides of that controversy as it boiled over. The missionaries returned to the church which had commissioned them at Antioch-on-the-Orontes (Acts 14: 25-28). Barnabas chose to return to Cyprus (Acts 15: 39). Paul took on Silas as his new travelling companion and colleague. He was a member of the church at Jerusalem (Acts 15: 22 f.), but a Hellenistic Jew and possibly, like Paul himself, a Roman citizen.
(to be continued…)
Posted February 11, 2019 by AngloMagyarMedia in anti-Semitism, Apocalypse, Baptists, Bible, Christian Faith, Christianity, Church, Civil Rights, Civilization, clannishness, cleanliness, Colonisation, Commemoration, Commonwealth, Coventry, Crucifixion, Education, Egalitarianism, Empire, Ethnic cleansing, Galilee, Gentiles, Gospel of Luke, Gospel of Mark, History, hygeine, Immigration, Integration, Israel, Jerusalem, Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, Jews, Josephus, manufacturing, Mediterranean, Memorial, Middle East, Migration, Militancy, multiculturalism, multilingualism, Mysticism, Narrative, nationalism, New Testament, Palestine, Population, Poverty, Remembrance, Respectability, Resurrection, Romans, Security, Simon Peter, Statehood, Syria, terror, theology, Turkey, tyranny, Zionism
Tagged with 'Pax Romana', 'The Way', Abraham, Acts of the Apostles, Alexander the Great, Alexandria, Anatolia, Antioch, Asia Minor, Augustus Caesar, Babylon, Barnabas, Business, Capernaum, Cephas, Christianity, Cicilia, Citizenship, Community Security Trust, Constantinople, Converts, Corinth, culture, current-events, Cyprus, Cyrene, Damascus, David, Diaspora, Earth, Education, Emperor Nero, eschatology, Essenes, evangelism, Faith, Galatians, Gamaliel, genealogy, George F Jowett, Graeco-Roman culture, health, Hebrew, Hellenic, Hellenism, History, Holy of Holies, housing, Italy, James, Judaism, Judea, Julius Caesar, Kosher, Levi, Literature, Lystra, Magdala, martyrdom, messianic, missionaries, Moses, Nazarenes, Orontes, outlaw, paganism, Pharisees, philosophy, piety, Pisidian Antioch, Poetry, politics, Pompey, Prayer, psychology, Rabbinic, religion, revalation, Roman-Jewish War, Sabbath, Sadducees, Sanhedrin, Seleucia, Silas, society, St Luke, St Paul, Stephen, Stoicism, Synagogues, Tarsus, Temple, tent-making, The Law, Tom Wright (theologian), Torah, Trade, Turkey, Zealots
Heroes and Villains at Home and Abroad:
In the middle of all the heroic struggles for freedom in the world in 1989, the Westminster village ‘bubble’ witnessed an event which seemed anything but heroic. Thatcher had been challenged for the leadership of the Conservative Party by Sir Anthony Meyer, an elderly ‘backbencher’, pro-European, who was seen as a ‘stalking horse’ for bigger beasts to enter the fray in a challenge to the Prime Minister. He was much mocked on the Conservative benches as ‘the stalking donkey’, In the 1989 leadership election on 5 December, Meyer was defeated by 314 votes to 33, yet the vote was ominous for Thatcher when it was discovered sixty Tory MPs had either voted for ‘the donkey’ or abstained. Meyer himself said that people started to think the unthinkable, while in the shadows, prowling through Conservative associations and the corridors of Westminster was a far more dangerous, wounded creature.
Michael Heseltine, who had walked out of the Tory cabinet four years earlier, was licking his wounds, recovering and ready to pounce. He showed sympathy towards Tory MPs, in trouble in their constituencies over the poll tax, but tried neither to lick his lips nor sharpen his claws too obviously in public. On 31 March 1990, the day before the poll tax was due to take effect in England and Wales, there was a massive demonstration against it which ended with a riot in Trafalgar Square (pictured below). Scaffolding was ripped apart and used to throw at the mounted police, cars were set on fire and shop windows were smashed. More than three hundred people were arrested and four hundred policemen were hurt.

Thatcher dismissed the riots as mere wickedness, which of course they were. Yet beneath them, it was obvious that there was a growing swell of protest by the lower middle class, normally law-abiding voters who insisted that they simply could not and would not pay it. That was what shook her cabinet and her MPs, worried about their electoral prospects in 1992. One by one, the inner core of true Thatcherites peeled off from their leader. Her Environment Secretary, Nicholas Ridley, had to resign after being rude about the Germans in a magazine interview. John Major turned out to be worryingly pro-European after all. Ian Gow, one of her closest associates, was murdered by an IRA bomb at his home. As the Conservatives’ ratings slumped in the country, Tory MPs who had opposed the tax, including Michael Heseltine’s key organiser, Michael Mates, began to ask their colleagues whether it was not now time that she was removed from power.

Abroad, great world events continued to overshadow the last days of Margaret Thatcher’s premiership. A few weeks after the fall of Ceaucescu in Romania, on 11 February 1990, Nelson Mandela, the man whom Margaret Thatcher had once denounced as a terrorist, was released from gaol in South Africa to global acclaim. In April, Douglas Hurd, who had replaced Geoffrey Howe as the British Foreign Secretary, visited Mikhail Gorbachev in Moscow. The BBC’s John Simpson (pictured below) was among a group of journalists had assembled outside the Spassky Gate he Kremlin and as the bells sounded their strange falling peel on the hour they were ushered in by a side entrance.
Inside, there was little obvious security; for Simpson, the Kremlin in 1990 was a more relaxed place than the Palace of Westminster or the White House. However, a Kremlin official was watching and listening to them nervously. The doors were opened and they went into a room that was large and echoing, with Gorbachev and Hurd sitting with their translators in one corner of it, at a small table. Later, Hurd said that Gorbachev had been his usual enthusiastic and ebullient self, but to Simpson, he looked a good deal older and more tired than when he had seen him last in Belgrade, describing to the camera the problems he was having with the ‘regional problems’ in the Soviet Union. Only his eyes remained as intense and concentrated as they had then. He leaned across the table, holding Douglas Hurd’s gaze while their public compliments were translated. Simpson commented:
If the problems of coping with a collapsing empire were telling on him, they had not crushed him. The man who asked Margaret Thatcher at length in December 1984 about how Britain had divested herself of her colonies now had personal experience of the process.

At the time, Gorbachev had his problems with the demands of the Baltic States to leave the Soviet Union quickly and without face-saving negotiations. As the journalists grouped around the table where he and Douglas Hurd faced each other, Simpson caught the eye of Eduard Shevardnadze, Soviet Foreign Minister, who was sitting next to Gorbachev:
I mouthed the word ‘Question’ to him and nodded towards Gorbachev. Shevardnadze shrugged and mouthed back the English word ‘Try’. But directly my colleagues and I began asking about Lithuania, Gorbachev smiled and shook his head. “I answered several hundred questions from the ‘Komosol’ this morning. That’s enough for me,” he said. The strain in his face seemed greater than ever. We were ushered out, and the double doors closed on him.
For John Simpson, the lesson of the winter of change in Central and Eastern Europe was that, no matter how hard the Communist Party tried to reform itself, the voters would punish it for the sins and failures of the past. That was what happened at the polls in Hungary later that spring, Imre Pozsgay had made multi-party democracy a possibility; his newly-formed Hungarian Socialist Party (MSZP) of ‘reformed’ communists received a tiny percentage of the vote. I observed the spirit of national renewal which seemed to sweep the centre-right Hungarian Democratic Forum (MDF) to power under the leadership of József Antall, the first freely-elected Prime Minister for forty years. In East Germany, most people agreed that Hans Modrow, the former Communist prime minister, was the best and most respected candidate standing in the election; he and his fellow communists felt that it was a considerable achievement to have won sixteen per cent of the vote. By the first few months of 1990 the mood in the Soviet Union was such that if there had been an election there, Simpson sensed that the Communist Party would have been swept out of office. Realising this, Gorbachev insisted that his election as President of the Soviet Union should be carried out by the deputies of the People’s Congress, not by popular vote. When local elections were held in the spring, Communist candidates usually fared badly.

Above: August 1990 – The Iraqi Army invades and annexes Kuwait.
On 2 August, however, the whole world was taken by surprise by events in the Middle East. John Simpson was on holiday in the south of France (I was on a delayed honeymoon on Jersey) when Saddam Hussein invaded Kuwait, a small but oil-rich nation to the southern end of the region. Iraq was a Soviet ally, but it had also enjoyed the tacit support of both Britain and the US in its war with Iran and had secretly been provided with arms by them while it continued to torture and oppress both its Shi’ite and Kurdish minorities, as well as many dissidents. Within three hours of hearing the news on the radio, Simpson was on a plane back to London and two weeks later he was part of the first European television team to be allowed into Baghdad since the invasion. Negotiation had failed to dislodge the Iraqi forces and Thatcher had urged President George Bush to go into what became the Gulf War. An international coalition had been assembled. Simpson had decided that he wanted to report the war from the epicentre of the crisis, from Baghdad itself. He had left Iraq four months earlier, assuming that the authorities there would never have him back.
This was because he had become involved in the case of Farzad Bazoft, an Iranian journalist working for the Observer in Iraq. Between 1987 and 1989 the young Iranian had travelled to Iraq five times with nothing more substantial than British travel documents. The last time was in September 1989, and on the day he left London the news leaked out that a huge explosion had taken place at Iraqi government’s weapons manufacturing plant at Al Qa’qa sixty miles south of Baghdad. Committed to investigative journalism, Farzad Bazoft used his ‘considerable charm’ to persuade an attractive British nurse living in Baghdad, Daphne Parish, to drive him down there. He also asked an Iraqi minister and the information ministry for help to visit there and told the Observer over a heavily tapped phone line precisely what he was going to do. Farzad was picked up as he was leaving Baghdad airport at the end of his visit. In his luggage were some samples he had gathered from the roadside at Al Qa’qa; presumably, he wanted to have them analysed back in London to reveal what type of weapon had exploded there the previous month. He was tortured and eventually confessed to everything they wanted: in particular, to spying for the British and the Israelis. Daphne Parish refused to confess since she had not broken the law. When the Iraqi authorities put them together Farzad tried to persuade her to do as he had. It would, he said, mean that she would be released.
It didn’t of course; it just meant that the Iraqis had the grounds they wanted to execute Farzad Bazoft. At their trial, Farzad was sentenced to death and Parish to fifteen years. No one translated the sentence for them or told them what was going to happen. A British diplomat had to break the news to Farzad that he was to be hanged directly their meeting ended. Minutes later he was taken out and executed. Daphne Parish was released after ten difficult months in prison. Hanging Farzad Bazoft was Saddam Hussein’s first open defiance of the West. Mrs Thatcher had asked for his release, and called his action ‘an act of barbarism’. Those of us who had been campaigning on behalf of Iraqi and Kurdish dissidents who had fallen foul of such acts of imprisonment, torture and murder for the previous ten years, only to be told these were part of internecine conflict felt some vindication at last in these tragic circumstances. Had firm action, including effective sanctions, been taken against the Ba’athist régime been taken sooner, not only might Farzad and many others have been saved, but the whole sorry chapters of the wars in Iraq might have been unwritten. If the tabloid press in Britain hadn’t suddenly become hysterical about it, insulting the Iraqis, Farzad might, at least, have been spared the hangman’s noose.
All this had determined John Simpson to go to Baghdad himself to report the reality of Saddam’s reign of terror. Six weeks after Farzad’s death, he arrived there with a small team from the BBC and several other British journalists. There were daily demonstrations outside the British embassy complaining about the efforts which the British government was then belatedly making to stop weapons technology reaching Iraq. Simpson and his team were virtual prisoners in their hotel, and no one in the streets wanted to talk to them, knowing that such contacts with Western journalists were dangerous. The Ministry of Information decided to impound all of their video cassettes. Simpson had said something in a broadcast about the total surveillance under which they were working, which had upset their minders. Eamonn Matthews, the producer, decided to stay on to on for a few days to get them back and was picked up at the airport the following day exactly as Farzad had been. He was threatened, treated roughly, and kept a virtual prisoner overnight. When he walked into the Newsnight office in London his face showed signs of the stress he had been under. Simpson assumed he wouldn’t be let back into Iraq, and at that time, was not too upset about that.
When he changed his mind after the invasion of Kuwait in August, Saddam’s henchmen had already started taking British, European and American hostages. The risk seemed to be extremely high, but he couldn’t back away from it. The BBC didn’t like it, however, but he persuaded his bosses to let him see if he could get permission to return there in the first place. Since Britain had cut its diplomatic relations with Iraq after the execution of Farzad Bazoft, he had to apply for a visa in Paris. After receiving a ‘polite’ refusal from the Iraqi ambassador there, he processed through the Middle East reporting on the growing crisis and trying to find a way to get to Baghdad, with the producer and picture editor, Mike Davis. They started in Cairo, moved on to Jerusalem, and ended up in Amman, all without success in getting the visas. Just as he was about to leave for London, he heard that Tariq Aziz, the Iraqi foreign minister was coming to Amman to give a press conference. He asked a couple of questions during the course of it, then ‘doorstepped’ Aziz as he left:
“Would it be possible for the BBC to visit Baghdad?”
“Why not?” he said, as he climbed into his expensive limousine. This time, though, I had the faint sense that he meant it.
The following day the Iraqi embassy in London called. Our visas had come through.
When Simpson and his crew finally arrived in Baghdad, the streets were silent and empty. People were terrified of what might happen and mostly stayed indoors with their families. On his first afternoon there, Saddam Hussein visited some of the British hostages from Kuwait, accompanied by Iraqi television cameras, and stroked the hair of a young English boy as he talked to the parents. In an Arab context, there was nothing wrong with that, but back in Britain, the pictures set everyone’s teeth on edge. John Simpson was still meeting officials when the pictures were broadcast, and in between handshakes he tried to make out what was happening on the screen in the corner of the ministerial office. He asked if the hostages were going to be released, but the officials were vague and unwilling to commit themselves. They later discovered what Saddam had said during his meeting with the British family was that women and children taken hostage in Kuwait would be able to leave. They were brought up by coach to Baghdad and flown out from there. Many of the women behaved superbly, as Simpson reported. They smiled and kept calm while the Iraqi cameramen sweated and shoved them around. They talked in terms of quiet endearment about husbands and sons they had been forced to leave behind, and whose fate was completely uncertain. Many had no homes to go to in Britain, and no idea about where their future income would come from, or what it would be. Yet they spoke of returning to Britain’s green and pleasant lands and…
… to nice cups of tea … as if nothing had changed since the Blitz. They fought back the tears for the sake of their children, and busied themselves with their luggage so that the cameras couldn’t pry into their emotions.
Others complained. Their meals were cold, they couldn’t use the swimming pool in the luxurious hotel which the Iraqis had set aside for them in Baghdad, the journey from Kuwait had taken too long. …
Many complained that the Foreign Office or the British embassy had failed to help them enough, and seemed to feel it was all the Government’s fault, as though Saddam Hussein were an act of God like drought or flooding, and Mrs Thatcher should do something about it.
“I don’t see why we should suffer because of her and President Bush,” said one affronted woman.
Another agreed. “If she’s going to call Saddam a dictator, why didn’t she wait till we were safely out of Kuwait?”
The British tabloid press lapped all this up, of course. They weren’t allowed into Iraq, so they interviewed the women as they came through Amman. Journey Through Hell was the way one headline described the trip by air-conditioned coach from Baghdad; Burning desert, torturing thirst, fiends, evil, sobbing loved ones, anguish: the newspaper hack’s thesaurus was in constant use. When he went back to London for a short break, the first ‘poster’ he saw declared Thatcher Warns Evil Saddam. As John Simpson commented,…
When the newspapers put a compulsory ‘evil’ in front of someone’s name, you know there’s a particular need for coolness and rationality. And to prove the superiority of our civilization over Saddam’s, someone threw a brick through the window of the Iraqi Cultural Centre in Tottenham Court Road.
Simpson returned to Baghdad after a week or so, staying there from September to November 1990. There were some ‘peace tourists’ there too; well-intentioned people who hoped to prevent the war by join the Iraqi protests in Baghdad or try a bit of freelance negotiation. Others had come to plead for the release of their fellow citizens whom Saddam Hussein was holding hostage. As far as the foreign press and media were concerned, a government which had been so paranoid about them a few months earlier now invited them to Baghdad in such large numbers that the pool of English-speaking Iraqi ‘spooks’ was drained by the effort of following them around. By the autumn, there were well over a hundred journalists from the main western countries, and the main international news organisations. The man who had invited them, the chief civil servant in the Information ministry, Najji al-Haddithi, spoke fluent English and had managed to persuade his minister to approach Saddam Hussein with a plan: that Iraq should now regard Western journalists as useful in its own propaganda campaign. As a result, the régime gradually opened its doors to every major British broadsheet newspaper and every major American, Canadian, Japanese and European news organisation, which each had its own representative in Baghdad.
Simpson was allowed to stay the longest because he got on well with Najji al-Hadithi, who liked Britain and the British and had a British sense of humour. In reciprocation, and as he got to know both officials and private citizens, Simpson grew to love Iraq and to sympathise with it too. At a private dinner party in October, he asked al-Hadithi why he allowed so many foreign journalists to come to Baghdad when, only a few months before, the Iraqi government had kept the doors so firmly shut. The chief civil servant answered him,
Because we want you to see that we are human beings like yourselves. So that your readers and viewers will see it. So that if, God forbid, President Bush decides to bomb us, you will know what you are bombing. You are a form of protection for us.

In the Gulf War, US marines arrive at Khabji, Saudi Arabia, to reinforce the front line.
In all his six months in the country, however, John Simpson had not managed to meet Saddam Hussein himself. In November 1990, just as he was about to arrange the details of their meeting, he found himself suddenly unable to get in touch with the officials, including al-Hadithi. He knew that this was because of Saddam Hussein’s unwillingness to let anyone edit his words. Simpson had warned the officials that the BBC would not be able to run ninety minutes of the president uncut, that this was something that would not be allowed to any British politician, even to the Prime Minister herself. The Iraqis resolved this stand-off by offering the interview to Independent Television News instead, who said yes at once. Simpson was furious and decided to go back to London: he was also tired, after ten weeks in Baghdad without a break. More to the point, when the news came through of Margaret Thatcher’s resignation, he decided he wanted to cover the campaign for the succession.
Saint Margaret – Down and Out in Paris and London:

The final act in Margaret Thatcher’s near-eleven-year premiership had begun on the European continent earlier that autumn, which was also where it was to end at the end of that remarkable season in British politics. There was another summit in Rome and further pressure on the Delors plan. Again, Thatcher felt herself being pushed and dragged towards a federal scheme for Europe. She vented her anger in the Commons, shredding the proposals with the words, ‘No! … No! … No!’ After observing her flaming anti-Brussels tirade, Geoffrey Howe decided, that he had had enough. The former Chancellor and Foreign Secretary had already been demoted by Thatcher to being ‘Leader of the House’. Serving in the two great offices of state, and now Deputy Prime-Minister, a face-saving but significant status, he had endured a decade of her slights and snarls, her impatience and mockery. He would finally leave the government, joining Michael Heseltine and Nigel Lawson on the ‘back benches’ of the Commons but, like them, he would leave on his own terms.
Howe resigned on 1 November, but it was not until a fortnight later, on 13 November 1990, that he stood up from the back benches to make a famous resignation statement which was designed to answer Number Ten’s narrative that he had gone over nothing much at all. Howe had written a carefully worded letter of resignation in which he criticised the Prime Minister’s overall handling of UK relations with the European Community. After largely successful attempts by Number Ten to claim that there were differences only of style, rather than substance, in Howe’s disagreement with Thatcher on Europe, Howe, therefore, chose to send a powerful message of dissent. To a packed chamber, he revealed that Lawson and he had threatened to resign together the previous year at the summit in Madrid. He attacked Thatcher for running increasingly serious risks for the future of the country and criticised her for undermining the policies on EMU proposed by her own Chancellor and Governor of the Bank of England. He also accused her of sending her ministers to negotiate in Brussels without the means to do so. He used a rather strange cricketing simile about captains and broken bats, which would have meant something to most MPs, but very little to those listening on the other side of the channel concerned with British negotiations on EMU in Europe:

It is rather like sending your opening batsmen to the crease, only for them to find, as the first balls are being bowled, that their bats have been broken before the game by the team captain.
Curiously and perhaps ironically, it is this part of his statement which is best remembered and most replayed. However, his dispute with Thatcher was over matters of substance more than ones of style; this was no game, not even one of cricket. He was advocating a move back towards a more centrist position on constitutional and administrative issues, such as taxation and European integration.
Geoffrey Howe (pictured more recently, above right) represented a kind of moderate ‘Whiggery’ in the party, being educated, lawyerly, and diligent; while direct, he was conciliatory and collegiate in style. He calmly ended his speech with an appeal to his remaining cabinet colleagues:
The time has come for others to consider their own response to the tragic conflict of loyalties, with which I myself have wrestled for perhaps too long.
Television cameras had just been allowed into the Commons so that, across the country as well as across the channel, via satellite channels, people could watch Howe, with Nigel Lawson nodding beside him, Michael Heseltine’s icy-calm demeanour and the white-faced reaction of the Prime Minister herself. The next day Heseltine announced that he would stand against her for the party leadership. She told The Times that he was a socialist at heart, someone whose philosophy at its extreme end had just been defeated in the USSR. She would defeat him. But the balloting system for a leadership contest meant that she would not just have to get a majority of votes among Tory MPs, but that she had to get a clear margin of fifteen per cent in total votes cast. At a summit in Paris, she found that she had failed to clear the second hurdle by just four votes. There would be a second ballot and she announced to a surprised John Sargent of the BBC, waiting at the bottom of the steps outside the summit, that she would fight on. It was a pure pantomime moment, seen live on TV, with viewers shouting “she’s behind you” at their TV sets as she came down the steps behind him. Then she went back up the steps to rejoin the other leaders at the ballet. While she watched the dancing in front of her, Tory MPs were dancing through Westminster either in rage or delight. Her support softened as the night went on, with many key Thatcherites believing she was finished and that Heseltine would beat her in the second ballot, tearing the party in two. It would be better for her to withdraw and let someone else fight him off.
Had she been in London throughout the crisis and able to summon her cabinet together to back her, she might have survived. But by the time she got back, even Maggie couldn’t pull it off. She decided to see her ministers one-by-one in her Commons office. Douglas Hurd and John Major had already given her their reluctant agreement to nominate her for the second round, but the message from most of her ministers was surprisingly uniform. They would give her their personal backing if she was determined to fight on but felt that she would lose to Heseltine. In reality, of course, she had lost them, but none of them wanted to join Heseltine in posterity as a co-assassin. Her MPs were too scared of the electoral vengeance to be wreaked after the poll tax. Only a few on the ultra-right, mostly outside the cabinet, were sincerely urging her to continue the struggle. One of them was Alan Clark, the diarist, who told her to fight on at all costs. She later commented, …
Unfortunately, he went on to argue that… it was better to go down in a blaze of glorious defeat than to go gentle into that good night. Since I had no particular fondness for Wagnerian endings, this lifted my spirits only briefly.

She returned to Downing Street, where she announced to her cabinet secretary at 7.30 the next morning that she had decided to resign. She held an uncomfortable cabinet meeting with those she believed to have betrayed her, saw the Queen, phoned other world leaders and then finished with one final Commons performance, vigorously defending her record. When she left Downing Street for the last time, in tears, she already knew that she was replaced as Prime Minister by John Major rather than Michael Heseltine. She had rallied support by phone for him among her closest supporters, who had felt that he had not quite been supportive enough. Unlike in the first ballot, a candidate only required a simple majority of Conservative MPs to win, in this case, 186 out of 372 MPs. The ballot was held on the afternoon of 27 November; although Major fell two votes short of the required winning total, he polled far enough ahead of both Douglas Hurd and Michael Heseltine to secure immediate concessions from both of them. With no remaining challengers, Major was formally named Leader of the Conservative Party that evening and was duly appointed Prime Minister the following day. Although Thatcher herself had her private doubts about him, the public transition was complete, and the most nation-changing premiership of modern British history was at its end. Andrew Marr has conveyed something of the drama of this ‘final act’ in her political career:
She had conducted her premiership with a sense of vivid and immediate self-dramatisation, the heroine of peace and war, figthing pitched battles in coalfields and on the streets, word-punching her way through triumphal conferences, haranguing rival leaders, always with a sense that history was being freshly minted, day by day. This is why so many insults levelled at her tended to twist into unintended compliments – ‘the Iron lady’, ‘She who must be obeyed’, ‘the Blessed Margaret’ and even ‘the Great She-Elephant’… She had no sense of her own limits. The world was made anew. Her fall lived up in every way to her record. When a great leader topples, poetry requires that her personal failings bring her down. The story insists that it must be more than… weariness or age. And this story’s ending lives up to its earlier scenes.
Major (minor), Return to Baghdad & the Magic Moment in Maastricht:

John Major’s seven years in office make him the third longest-serving peacetime prime minister of modern times, behind Tony Blair and Margaret Thatcher, but he often gets overlooked, probably because he came in the middle of what is increasingly referred to as the Thatcher-Blair era in British politics. To Mrs Thatcher and others in the cabinet and Commons, he appeared to be a bland, friendly, loyal Thatcherite. He was elected because of who he was not, not a posh, old-school Tory like Douglas Hurd, nor a rich, charismatic charmer like Michael Heseltine. His father was a music-hall ‘artiste’ with a long stage career, Tom Ball: ‘Major’ was his stage name. When John Major was born, his father was already an old man, pursuing a second career as a maker of garden ornaments. He lost everything in a business deal that went wrong and the family had to move from their comfortable suburban house into a crowded flat in Brixton.
John Major-Ball was sent to grammar school, but was a poor student and left at sixteen. He worked as a clerk, made garden gnomes with his brother, looked after his mother and endured a ‘degrading’ period of unemployment before eventually pursuing a career as a banker and becoming a Conservative councillor. His politics were formed by his experiences of the inner-city and he was on the anti-Powellite, moderate wing of the party. He was selected for the Cambridgeshire seat of Huntingdon and entered Parliament in 1979, in the election which brought Thatcher to power. After the 1987 election, Thatcher promoted him to the cabinet as Chief Secretary to the Treasury, from where he became Foreign Secretary and then Chancellor. To everyone outside the Tory Party, Major was a blank canvas. At forty-seven, he was the youngest Prime Minister of the century and the least known, certainly in the post-war period. The Conservatives were content with this choice, having grown tired of amateur dramatics. He was seen by many as the bloke from next door who would lead them towards easier times. He talked of building a society of opportunity and compassion, and for privileges once available to ‘the few’ to be spread to ‘the many’. But he had little time to plan his own agenda. There were innumerable crises to be dealt with. He quickly killed off the poll tax and replaced it with a new council tax, which bore a striking resemblance to the ‘banded’ system previously proposed as an alternative.
One of the first things that John Major did as PM was to meet the elder President Bush and promise him full support through the Gulf War. When John Simpson returned to Baghdad in mid-December 1990, the atmosphere had changed as war loomed. Mr Hattem, the BBC’s driver, was much more subservient to their minders, and wouldn’t take the crew anywhere without consulting them. Once they missed an entire story as a result. Saddam Hussein had ordered the release of all the foreign hostages, a decision of considerable importance to the Coalition forces headed by the United States; public opinion at home would have been much more reluctant to support the air war if it had seemed likely that ordinary Americans, Britons and other Europeans would be killed by the bombs and missiles. The man who persuaded Saddam Hussein to give up one of his best cards in an otherwise rather empty hand was Yasser Arafat, the Palestinian leader. According to Simpson, contrary to some Western stereotypes of him, he was always instinctively a man of peace and compromise. Apparently, he told Saddam that if he let the hostages go, this would weaken the moral argument of the US. It turned out to be a tactical mistake, of course, but Arafat had assumed that Saddam had been genuine when, early on in the crisis, he had offered to withdraw from Kuwait if Israel agreed to pull out of the West Bank. He had publicly come out in support of Iraq and had settled in Baghdad for the duration of the crisis. In an interview just before Christmas, he told Simpson that he was certain there would be no war:
YA: “… I can tell you that there will be not be a war. I promise it: you will see. Something will happen: there will be an agreement. You must not think that President Bush is so foolish. You must not think that the Arab brothers are so foolish. War is a terrible thing. Nobody wants it. President Bush will compromise.
At that stage, it looked as if Arafat might well be right about a deal being made. Bush was starting to talk about going the extra mile for peace, and the Iraqi press was announcing a major diplomatic victory for Saddam Hussein. As for the threat of terrorist attacks from Palestinian extremists elsewhere in the Middle East, the PLO had far more control over them in those days, and Arafat had shown that he could be ferocious in curbing it if he chose to do so. By the third week in December, Simpson was getting discreet visits from a very senior figure in the Iraqi régime, whom he nicknamed ‘Bertie’ and who persuaded him that he should go public on Saddam Hussein’s determination not to withdraw from Kuwait before the deadline imposed by the United Nations. Like the US and UK governments, Simpson was inclined to think that Iraq would pull back at the last-minute. ‘Bertie’ was absolutely certain that this wouldn’t happen, and he was right. This was what Simpson told BBC Radio 4 over their line from London about Saddam’s intentions, on 2 January 1991:
‘People who have seen him in the past day or so have told me that he is determined to stand and fight. He told one visiter that if he pulled his forces back now, there would be an uprising against him in the army and he might not be able to cope with it. It feels it’s essential to his own survival in power to face a war: he’ll certainly do it.
Simpson continued to press the same line even when James Baker, the US Secretary of State was due to meet the Iraqi Foreign Minister, Tariq Aziz, in Geneva, and ITN reported that Aziz was bringing with him an offer of conditional withdrawal. In the event, he brought no such thing, and the meeting broke up without any possibility of a diplomatic settlement. On 13 January, ‘Bertie’ told him that Saddam had said that Iraq would only have to face two waves of air-strikes and that Baghdad would be so destroyed and loss of life would be so great that international opinion would force the US, UK and France to stop, resulting in a diplomatic victory for him. Asked by Simpson whether Saddam himself might be killed in the strikes, ‘Bertie’ said that Saddam’s ‘bunker’ was impenetrable and that he will survive, even if tens of thousands die. On 11 January, they discovered exactly where the bunker was. Saddam Hussein was due to appear at an international Islamic conference at the government centre immediately opposite the Al-Rashid Hotel, where Simpson and the BBC crew were staying, along with many other international film crews and newspaper journalists. They had stationed camera crews at every entrance to the conference centre, in the hope of getting something more than the usual official pictures of the Iraqi president. Simpson himself sat in the hotel, watching the live coverage of the event on Iraqi television:
On cue the great man appeared on stage, holding out his arm in the affected way which is his trade-mark, while the audience went wild. I looked forward to the pictures the camera crews must be getting. But when they came back, each of them said that Saddam hadn’t come past him. That convinced me. We had long heard rumours that his command complex was based under our hotel: this indicated that there were underground roads and passages from the complex to enable him to reach the various important government buildings in the area. … So there we were, living and working a hundred feet or so above Saddam Hussein’s head. We were his protection. And if he knew it, the Coalition forces did as well: the European company which had built much of the bunker had handed over all the blueprints to them. The outlook wasn’t good. The American embassy in Baghdad, before it closed down, had warned everyone who stayed that they could expect to be killed in the bombing. President Bush himself had phoned the editors of the big American organisations represented in Baghdad and begged them to pull out. … the big organisations (with the exception of CNN) obliged.
I have written elsewhere about John Simpson’s own motives for staying and his experiences and accounts of the bombing of the city which began less than a week later, on 17 January, before the BBC crew were forced to leave. Suffice it here to quote from his interview some months later (10.5.91) with Sue Lawley, the then presenter of the popular and long-running BBC Radio programme, Desert Island Discs:
SL: But these things – I mean, it’s not really enough to risk your life to write a book, is it?
(Pause)
JS: I suppose it’s just that I’m a bit of a ‘chancer’, that’s all.

The Gulf War was the first major conflict since the Second World War in which it was essential for the multi-national allied forces not to have large-scale casualties. It ended when President Bush began to get nervous about the pictures of death and destruction which were coming in from the desert. Public opinion in the United States did not want another Vietnam, Laos or Cambodia, with large-scale carpet-bombing of civilian populations, pictures of massacres and of American GIs being flown home in body bags. In Britain too, people wanted a limited war fought to expel the Iraqi forces from Kuwait, but they didn’t want a huge body-count. They didn’t get one either, though there were some significant losses among the British forces. The Gulf War achieved its limited objectives, freeing Kuwait from the Iraqi invasion and resulting in the immolation the Iraqi army’s Republican Guard. It generated nothing like the controversy of the later Iraq War. It was widely seen as a necessary act of international retribution against a particularly horrible dictator. The bigger problem for the country itself was the quarter of a million deaths which occurred after the war, caused by UN Sanctions and Saddam Hussein’s reaction to them, especially his vengeful acts of genocide against the Iraqi Kurds in the north of the country.
After the controversies and alarms of the Thatcher years, foreign affairs generated less heat, except for the great issue of European federalism. John Major had to turn straight away to confront Jacques Delors’ agenda, which was threatening to divide the Tory Party. If ever a place was well-chosen for debating the end of a Europe of independent nation-states, it was Maastricht in Holland, nestled so close to the German and Belgian borders it is almost nationless. Here the great showdown of the winter of 1991 took place. A new treaty was to be agreed and it was one which made the federal project even more explicit. There was to be fast progress to a single currency. Much of the foreign policy, defence policy and home affairs were to come under the ultimate authority of the EU. A ‘social chapter’ would oblige Britain to accept the more expensive work guarantees of the continent and surrender some of the trade union reforms brought in under Thatcher. For a country with a weak industrial base whose economy partly depended on undercutting her continental rivals, all this would be grave. For a Conservative Party which had applauded Lady Thatcher’s defiant Bruges speech, it was almost a declaration of war, in which Europe’s ‘federal’ destiny had been made more explicit.
John Major was trying to be practical. He refused to rule out the possibility of a single currency for all time, believing it would probably happen one day since it had obvious business and trading advantages. But now was too soon, partly because it would make life harder for the central European countries being freed from communism to join the EU. In his memoirs, he protests that he was accused of dithering, procrastination, lacking leadership and conviction. Yet at Maastricht, he managed, during genuinely tense negotiations, to keep Britain out of most of what was being demanded of the member states. He and his Chancellor, Norman Lamont, negotiated a special British opt-out from monetary union and managed to have the social chapter excluded from the treaty altogether. Major kept haggling late and on every detail, wearing out his fellow leaders with more politeness but as much determination as Thatcher ever had. For a man with a weak hand, under fire from his own side at home, it was quite a feat. Major returned to plaudits in the newspapers using the remark of an aide that it was ‘game, set and match’ to Britain.
Briefly, Major was a hero. He described his reception by the Tory Party in the Commons as the modern equivalent of a Roman triumph, quite something for the boy from Brixton. Soon after this, he called the election most observers thought he must lose. The most immediate worries had been economic, as the hangover caused by the Lawson boom began to throb. Inflation rose towards double figures, interest rates were at fourteen per cent and unemployment was heading towards two million again. Moreover, a serious white-collar recession was beginning to hit Britain, particularly the south, where house prices would fall by a quarter. An estimated 1.8 million people found that their homes were worth less than the money they had borrowed to buy them in the eighties when credit had been easy to obtain. Now they were in what became known as ‘negative equity’ and were often unable to sell their properties. During 1991 alone, more than seventy-five thousand families had their homes repossessed. The economy was so badly awry, the pain of the poll tax so fresh, Neil Kinnock’s Labour Party now so efficiently organised, that the Tory years seemed sure to be ending. Things turned out differently. Lamont’s pre-election had helped since it proposed to cut the bottom rate of income tax by five pence in the pound, which would help people on lower incomes, badly wrong-footing Labour.
With a party as full of anger and resentment as the Conservative Party behind him, he had little chance of succeeding as prime minister. He was a throwback to an older kind of conservatism, middle-of-the-road, not too noisy, lacking in any particular conviction except that the Conservative Party was the natural governing party of Britain. The country had indeed been governed by Conservatives like Major for most of the twentieth century, and people were slow to understand how ideological the party had become under Thatcher. John Major shared none of her deepest views. He gambled that even if the backbenchers discovered his lack of right-wing conviction, the voters of Britain who traditionally dislike extremism and ideology would give him their backing. In the eyes of the British press, Major was the council-school boy, the anorak, the ‘swot’, who had ended up in Whitehall. He seemed to fit into a recognisable niche within the dreary, peculiarly English system of snobbery and was looked down on accordingly. In addition, many in the Conservative Party resented the fact that Mrs Thatcher had been overthrown, and would have taken it out on anyone who succeeded her.
Major lacked her convictions, certainly. For the many, this was a relief. These convictions, brandished like sticks, were what made her so unpopular in the country as a whole; and if she had led the party into the 1992 election she would have lost it. No one would have blamed Major if he had led the Tories to defeat in the 1992 election, which he called for April.
(to be continued…)
“I was walking the line of Offa’s Dyke in North Wales when
the slanting late afternoon winter light raked across the landscape,
illuminating the folds in the gently rolling hillside.”

Offa’s Dyke in North Wales (foreground) with Chirk Castle in the distance.
Photo by Kevin Bleasdale, Landscape Photographer of the Year.
(www.ukgreetings.co.uk)
Bucket-lists and Border-lines:
One of the things to do on my ‘bucket list’ is the Offa’s Dyke Path, the long-distance footpath which ‘follows’ the Dark Age dyke allegedly made by the King of the Saxon Kingdom of Mercia to mark the boundary of his territory with ‘the Welsh’ territories to its west. I have done two other long-distance paths, the Pennine Way and the Pembrokeshire Coast Path, together with long sections of the South West Coast Path, between Plymouth and Teignmouth, and completed the Wessex Walk between Uphill and Wells. By comparison with these long-distance paths, only two sections of the Offa’s Dyke path, through the Black Mountains and the Clwydians, really offer the same sort of open walking country. Having completed one short section near Chirk some twenty-five years ago while staying in Llangollen, in this post, I wish to concentrate on the first of the section between Llanthony Priory and Hay-on-Wye, which I hope to tackle this summer (July 2018), fitness and weather permitting! Llwybr Clawdd Offa, as it’s known in Welsh, is Britain’s fourth long-distance path to be officially opened, runs the entire length of the border, from the Severn Estuary near the old Severn Bridge at Chepstow to the sea at Prestatyn on the north Welsh coast, a distance of 168 miles. Throughout its length, history is brought to life, not just by Offa’s frontier earthwork, but by ancient hill forts, prehistoric trackways, old drover roads, medieval castles and by the numerous small market towns and villages which are linked by the path.
As a footpath rich in scenic variety, as well as historical and literary associations, it will have attractions not just for the seasoned walker, completing the coast-to-coast walk in two or three weeks, but also the amateur historian and archaeologist, and those seeking casual recreation. The footpath was approved by the Minister of Housing and Local Government in 1955 but little progress was made for some years in opening up the many miles of new rights of way needed. Then, in 1966, the National Parks Commission decided to give greater priority to the proposal and three years later, when it became known as the Countryside Commission, came a decision to open the path during 1971. The Offa’s Dyke Association, set up to promote conservation of the Border area along the path, and to work for the path’s completion, were naturally sceptical. But with the exception of a few sections, the route had been completed with waymarks by the target date. On 10th July 1971, the path was formally opened at an open-air ceremony in Knighton, preceded by an inaugural walk along the path north of the town over the Panpunton Hill. More recently, a connecting path to Machynlleth and on to Welshpool (Y Trallwng) has been added, called Glyndwr’s Way, which provides a circuitous historical walk from the Dyke across the Cambrian mountains.
Celts, Romans, Britons and Saxons:
The History of ‘the Border Country’ goes back to Roman times when in A.D. 47 the invaders had reached westward to the Severn. On the other side of the river lay the hill country, defended by strong Celtic tribes: the warlike Silures of the south were led by their Belgic leader Caradoc (Caractacus) who had fled westward to rouse the western tribes: the Ordovices of the central border and the Deceangli of the north. Caradoc was defeated in A.D. 51, and many places along the hill margin, including ‘British Camp’ in the Malvern Hills, claim to be the site of his last battle. Strong resistance continued, however, and it was ten years before the Romans could attack the Ordovices and the Deceangli, following the establishment in A.D. 60 of the fortress and legionary headquarters of Deva (Chester). Only a year later the army had advanced to Anglesey, overrunning the hill forts. In the south, the campaign of A.D. 74 was the decisive one when Julius Frontinius fought a hard battle against the Silures, though it was four years before the Romans could move further west under Agricola.
The Border formed very much a frontier zone in the Roman expansion. Except in the south, in the Wye Valley area, and east of the hill margin, developments were essentially military in character, with no great effect on native life, which went on much as before. Roads linking the several forts that had been set up in this zone ran along the north and south coast routes, based on Deva and Isca (Caerleon), and east-west up the main valleys into the hills, the easiest into what later became Wales. A north-south road linked these roads through the hill margins. During the first century of Roman rule a number of Celtic hill forts were strengthened, for although the Celts had made use of the sharp edges of the uplands for farming, its strategic and military potential was first realised by the Romans as a base for launching their campaigns against the uplands. It was these roads and forts which first defined the border.

With the withdrawal of the Roman Legions in A.D. 410, Celtic culture saw a renaissance in craftsmanship and bardic poetry, and a growth in political and the rise and spread of Christianity by the Celtic Church. Gradually, various Romano-British kingdoms or ‘fiefdoms’ began to emerge under separate rulers or ‘chieftains’. One of these, Ambrosius Aurelius, may have been the inspiration for the Arthurian legends, having fought a series of battles against the invading Saxons which ended with Badon Hill in about A.D. 515. Along the hill margins, the kingdom of Gwynedd covered the land north of the River Dee and west of the Vale of Clwyd. The Vale itself formed a contested territory between Gwynedd and the great central kingdom of Powys, ‘the Paradise of Wales’ as it was called by the bard who wrote the ‘saga cycle’ of Llywarch Hen. On the southern margins, Brycheiniog covered Breconshire and Gwent, Monmouthshire. Powys was the great bardic centre, from where we find the reference to Taliesin singing at the court:
I sang in the meadows of the Severn
Before an illustrious lord,
Before Brochfael of Powys…
It seems to have been usual for an official bard to be attached to each court, with some lords and princes acquiring reputations as patrons of the bards. The achievement of these early poets was considerable. They created a heroic age, a new legendary past for ages to come. As long as the Welsh tradition lasted, that is to say, for at least another ten centuries, their patrons were taken as models of generosity and courage. The poems and sequences of englynion (stanzas of three or four lines) associated with Llywerch Hen (‘the Old’) were long thought to be the work of the sixth-century prince but were later shown to be about the legendary figure, rather than being by him. They belong to the ninth-century sagas, with the narrative told in prose. Llywarch was a warrior of North Britain, who bore the severed head of his lord King Urien of Rheged from the battlefield, so that it would be buried and not humiliated. He eventually found refuge to the south, in Powys, where he again found himself having to fight the Saxon invaders, and his twenty-four sons, impelled by their own ready valour and their father’s bitter tongue, fought too. One after another they perished in their father’s pride. Gwén, the last of them, arrives late for the battle, to find all his brothers dead. There is no-one left to defend the Gorlas Ford on the River Llawen. Llywerch himself, old as he is, is arming himself for the battle. Here, as Gwén too prepares for battle, father and son enter into dialogue:
Gwén:
Keen my spear, it glitters in battle.
I will indeed watch on the Ford.
If I am not back, God be with you!
Llywarch:
If you survive it, I shall see you,
If you are killed. then I’ll mourn you,
Lose not in hardship warrior’s honour!
Gwén:
I shall not shame you, giver of battles,
When the brave man arms for the border,
Though hardship beset me, I’ll stay my ground.
Llywarch:
A wave shifting over the shore,
By and by strong purpose breaks,
Boasters commonly flee in a fight.
Llywarch urges his last son to sound the horn given to him by his uncle, Urien, if he is hard-pressed in the forthcoming fight. The way that Llywarch mentions it suggests that this horn, in the saga, may have had magical properties. But Gwén replies contemptuously, Though terror press round me, and the fierce thieves of England, … I’ll not wake your maidens! It is the mutual anger between father and son, each insulting each other’s honour, that makes any genuine precautions against tragedy impossible. Magic is irrelevant in this equation. All that matters is human folly and pride. Yet there is an over-riding sense of fate or destiny, a supernatural context in which such situations are allowed, or even willed, to take place. Llywarch is not only pitted against his own pride and folly, but also against hostile destiny – tynged in Welsh – whose design is revealed to him only gradually as his downfall proceeds. And as he grows old, the bard gives him one more opportunity to reveal himself to the in-every-sense bitter end: angry, baffled, useless to man, woman or beast, a prey to pain, remorse, lacerated vanity, and a desperate loneliness. His king, his fellow-countrymen, his Patria, his sons – all are in ruins. Where has it all gone? And where is longed-for Death? As ‘folk-history’, Welsh heroic poetry was driven into the subconsciousness by the trauma of the Anglo-Saxon conquest of the sixth century, and by what Anthony Conran, in his introduction to his own translations of it, called the cultural amnesia of the times. When it re-emerged, it became intimately connected with a whole prophetic tradition, which kept up its messianic rumblings right through to the Wars of the Roses.
From the late sixth century, the mixed peoples of eastern Britain, generically labelled ‘Anglo-Saxons’ and organising themselves in kingdoms, resumed their advance into the west. It was a long, slow, piecemeal process; some of the advances may not represent straightforward conquests and there is evidence of the transient existence of people who were literally ‘mongrels’. But it was remorseless. The foundation of kingdoms in the north opened an epoch of battles with the North Britons which were to be central to later historical traditions among the Welsh. After a battle near Bath in 577, the kings of Gloucester, Bath and Cirencester were gone and Saxon power reached the Bristol Channel, from where it was able to press on into the south-west. Ceawlin, king of Wessex, drove a wedge between the Britons dwelling between the Severn Estuary and the Irish Sea and those in Devon and Cornwall. A second wedge, driven by Aethelfrith, king of Northumbria, early in the seventh century, separated the Britons in Cumbria from their compatriots, or Cymry, further south. This effectively isolated and created Walleas, the Germanic word for ‘aliens’, or ‘North Wales’, as distinct from Cornwalleas, or ‘West Wales’ including Devon, and Cumbria and Strathclyde, the kingdoms of the northern Britons.

Between 650 and 670, the Saxon advance westward had reached the borders of Powys and the River Dee, while the River Wye marked the limit of the advance in the south. In the early seventh century, Northumbria was the most powerful kingdom of the Anglo-Saxon ‘heptarchy’. The ascendancy of the midland kingdom of Mercia began during the reign of the warlike, pagan Penda (623-654). Minor kings after him rose and fell in a period of civil warfare until by 731, Bede tells us, all of ‘Aengleland’ south of the Humber was subject to Aethelbald (716-756). He, therefore, referred to himself as ‘King of the southern English’. He maintained his ascendancy for thirty years until he was murdered by his own bodyguard. From the ensuing civil war within Mercia itself, Offa emerged as the key figure in the Mercian supremacy. He reigned from 757-796 and was the first king to be styled, in imperial terms, as King of the English.

Who was Offa and why did he build a dyke?
History reveals all too little of the Mercian king whose name is forever linked to the great dyke built in the margins which had been continually disputed by the Welsh and the English. We do know that the means by which he gradually expanded his kingdom and his hegemony over the heptarchy were not always fair. In 793, Aethelbert, the Christian king of East Anglia, paid a visit to Offa to seek the hand of his daughter Aelfrida. He was murdered, either on the orders of Offa, or those of his queen. There are differing accounts of what happened, but it is most likely that Offa realised that, with Aethelbert ‘out of the way’, Mercia could take control of East Anglia, which it did. Offa was then able to deal on almost equal terms with Charlemagne who had once closed his ports to English trade for some three years.

Above: A Victorian tile from the floor of the choir in Hereford Cathedral depicting the beheading of St Aethelbert by order of King Offa.
Throughout the first half of the eighth century a protracted struggle had gone on between Mercia and Powys as the frontier was gradually driven back from the line of furthest advance marked by various short ‘dykes’ to the more settled frontiers marked by the great running earthwork constructed under Offa, probably after the last Welsh counter-attack in 784. Around this time we can picture the English as settled farmers, with greater craftsmanship and better equipment than their sixth-century predecessors, if with less military skill. The Welsh occupied the hill territory to the west, living in kinship groups (gwelau), were dependent mainly upon the cattle they summer-pastured on the hills and over-wintered in the valley meadows.

The line of the Dyke extends from Sedbury Cliffs on the Severn, through the Wye Valley and Herefordshire, across the Clun district of ‘Salop’, part of Shropshire today, and northwards via Chirk and Ruabon to the sea at Prestatyn, a distance of 149 miles. Of these, the running earthwork of the Dyke itself is traceable for eighty-one miles, consisting of an earth bank with a ditch, usually on the west-facing side, sometimes with ditches on both sides, and averaging in height some six feet above ground level, and in breadth almost sixty feet. While contemporary manuscripts throw little light on the making of the Dyke, the more recent detailed archaeological surveys have led to a much deeper understanding of the Border as it existed in Offa’s time. Its principal purpose was to provide a frontier between Mercia and the Welsh kingdoms and to control trade by directing it through defined ‘gateways’ in the earthwork. It may, at times, also have been used for defensive purposes, but by the time it was built this would have been largely incidental. Only in a time of relative peace between the Welsh and the Mercians could a work of such a scale be achieved. It must, therefore, have been an agreed frontier. Moreover, although it would have presented something of an obstacle to cattle rustlers, it would have offered little prevention to cattle straying across.

Above: The course of the path from Chepstow (bottom, left) to Prestatyn (top, right), in relation to surviving dyke sections.
The mastery of difficult terrain through which the Dyke runs suggests that the skill of its builders can only have been acquired through generations of experience. Two precedents on the ground can be found, firstly in the various short dykes that lie both to the east and west of the Great Dyke, and secondly in Wat’s Dyke which runs from Maesbury, south of Oswestry, to Holywell. A third precedent is found in the heroic poetry of the time. The short dykes found in the middle of the Border Country reinforced the most vulnerable sections of the Great Dyke where the hills of Salop are nearest to the Mercian capital of Tamworth. These dykes are similar in construction to Offa’s Dyke and are thought by archaeologists to form cross-valley screens at the head of agricultural land, while cross-ridge dykes controlled traffic along the ridge. These probably date from the time of Penda, representing the military activities of Mercia in the pre-Offan period. They are defensive in character, unlike Offa’s Dyke which represents the consolidation of the Mercian kingdom when the Saxons came to realise the limits of their ability to advance further west. Wat was a hero of Old English legend associated with an earlier Offa, a king of Schleswig and ancestor to the Mercian king. Wat’s Dyke may well have been named by Offa in commemoration of his own namesake, whose deeds were recorded in the epic poem Widsith, among them being his marking of boundaries.
As a boundary, however, Offa’s Dyke is unlikely to have been continuously manned but rather patrolled on horseback. Nevertheless, evidence reveals that it was built under the direction of men trained in military tradition. Offa himself is thought to have master-minded the work, possibly with a group of chieftains, planning both its course and its dimensions. Each landowner along its course was then consulted and subsequently made responsible for the construction of a particular section of it, depending on the extent of his lands or the labour available to him. In turn, this variation in experience and expertise, together with the willingness and size of the local workforce, inevitably resulted in differences in the quality and scale of the work. In some areas, the hostility of the local Welsh population, in particular, may have been a factor. Despite this, further evidence that it was an agreed frontier is contained in the existence of a set of laws governing the movements of both the Welsh and the English across the boundary. An early tenth-century document refers to an agreement between the English and the Welsh relating to Ergyng (Archenfield), a Welsh district between the Wye and the Monnow, now in Herefordshire, which remained Welsh-speaking into the nineteenth century and produced many Welsh ‘notables’. The same document also contains a reference to English territory north of the Wye, in Wales today, belonging to a people known as the Dunsaete. It suggests the existence of a relationship between these peoples which may well have dated from Offa’s time, deriving from Offa’s own laws for the conduct of both English and Welsh along the Border.
Offa’s laws, long thought lost, would then have provided for the setting-up of a “board” comprising both English and Welsh, the task of which was to explain the laws to their respective peoples. Included in the laws was a code for recovering livestock rustled across the Border, and another for the safe-conduct of either Welsh or Mercian ‘trespassers’ found on the “wrong” side of the Border by a specially appointed guide. However, the story that any man found ‘trespassing’ would be subjected to the punishment of losing his right hand, is an apocryphal one. Overall, the skill of the designer and eye for the detail of the landscape are remarkable. With few exceptions, even in the dissected terrain of the middle section of its length, the Dyke’s straights cleverly cling to the west-facing slopes, giving the Mercians the advantage of visual control over Welsh territories. Archaeological ‘detective work’ enabled the mapping of the Border landscape of Offa’s day. The straight alignments of the Dyke, occurring in both flat and undulating terrain, indicate a mixture of pastoral and arable farming; and in the uplands, open moorland. Small irregularities in mainly straight alignment tend to indicate the original presence of woodland. The Mercian farmers seem to have preferred sunny, south-facing slopes for growing crops, disliking the shaded north-facing hillsides which remained wooded. This is represented by alternate straight and sinuous alignments. Very irregular alignments, where the Dyke follows the contours of the landscape, occur where the terrain is especially rough, or where visibility between points was very limited.

In profile sections, the Dyke varies considerably throughout its length. It is at its most formidable on the hilltops where ridgeways passed through, and on the valley floors where skilful use was made of the east sides, in order to allow the Dyke to descend from the ridges and cross the valleys while maintaining visual contact with the west. Here, too, cultivated clearings required protection in the tradition of short, transverse dykes. In many places, there is evidence of compromise between the Mercians and the Welsh. In some sections, the broad River Severn is left to mark the boundary, whereas, in others, the Dyke follows the slopes of the eastern hills above the Severn.
This suggests that to the south of Buttington, for example, the meadow pastures on both sides of the river were conceded to Powys, for, in The Mabinogion, it was stated that the man would not prosper with a war-band in Powys who would not prosper in that cultivated land. Likewise, in the Wye Valley, both sides of the river were used by Welsh timber traders who needed to land their boats on either bank. The Dyke is therefore high up on the eastern slope, controlling a long stretch of the river upstream to the point reached by exceptionally high tides in the Severn estuary.
For much of the length of the frontier, no trace of the Dyke has been found. From the point where the Dyke reaches the Wye west of Sedbury Cliffs to the Wye west of the Tutshill look-out tower, the sheer river cliffs would have formed a sufficient natural boundary in themselves. Between Highbury and Bridge Sollers in Herefordshire, the Wye again forms the boundary. For the next thirteen miles to Rushock Hill ancient and dense oak woods on the underlying Old Red Sandstone seem to have made the building of a section of dyke unnecessary, if not impossible. In this area, the dyke is only present on what would have been cleared land. For five miles north of Buttington on the Severn, the river again forms the boundary. However, the reason why the Dyke was not completed on the last five miles to the north coast is a matter of conjecture. Certainly, the intention was that it should reach the sea at Prestatyn. We know that towards the end of Offa’s reign the Welsh seem to have made an attempt to capture the land between the Dyke and the Dee. A Welsh legend, recorded in the plaintive lament Morfa Rhuddlan, tells of a fierce battle fought in 795, ending in Welsh defeat. Offa died a year later at Rhuddlan, and it may be that with his death went the driving force behind the Dyke.

Offa was succeeded by his son, Cenwulf, who reigned until 816. His defeat at the Battle of Basingwerk marked the beginning of the decline of Mercian supremacy on the Border. Wessex was emerging as the most powerful Saxon kingdom, and Mercia was forced to turn its attention southwards. With the Dyke established, however, a degree of stability was brought to the Border Country for a time. Whereas to the east of a line from the Pennines to Salisbury Plain, there is precious little evidence of British survival into the ninth century, even in river names. West of that line, however, and into the upland watershed, there is much evidence. Place-names remain strongly Celtic, though often transmuted; Cymraeg, as well as Brythonic dialects, survived, as did Celtic farm systems and field boundaries. Early laws of the kingdom of Wessex make specific provision for a whole British hierarchy under overall Saxon rule. Further west, Cornwall survived as a British fiefdom, and in the Borderlands of the Wye and the southern Dyke, as English settlement developed, there may have been as much fusion and integration as conflict and conquest.


The concessions made to the Welsh along the Wye may also have aided this process, as Archenfield remained Welsh-speaking well into modern times, and there is also an abundance of surviving Celtic placenames to the west of the Wye in what is land on the English side of today’s border. Around Welshpool names like Buttington, Forden and Leighton also show gradual Mercian expansion in the Borderlands between 650 and 750 and strengthen the case for the concession of the Severn meadows to Powys on the building of the Dyke. In the Vale of Radnor, names like Evenjobb, Harpton and Cascob again indicate a retreat by the Welsh, but elsewhere on the whole land bordering the Dyke, there is evidence of linguistic retention on both sides. Llanymynych has obviously retained its Welsh name, despite being half in half in England, whereas Knighton is generally known by its English name, despite being wholly in Wales and having a Welsh name, Tref-y-clawdd, meaning ‘the town by the Dyke’. The area between Offa’s Dyke and Wat’s Dyke has remained Welsh-speaking in character until recent times. Despite these examples of variation, we know that the Dyke’s construction was resisted by the Welsh in numerous places along its route. Offa had driven his Dyke from coast (almost) to coast, and as Gwyn Williams (1985) wrote of the Dark Age Welsh, ‘foreigners’ in their own land …
This few and fragile people took the whole of inheritance of Britain on their shoulders. And late in the eighth century they were confronted with an imperial Offa, king of the Mercians, who had the effrontery to score his Dyke across their land and shut them out as foreigners. … The Welsh, as a people, were born disinherited.
The ‘Compatriots’ (Cymry) & their Bards:

By the ninth century, therefore, the Welsh were almost completely shut up behind Offa’s Dyke. Not unnaturally, in their ‘exile’, they turned to the stories of their old homes, in Regen, Elfed, Gododdin and the rich lands of eastern Powys – roughly Cumberland, Yorkshire, SE Scotland and Shropshire respectively, according to the later Medieval geography of Britain. This was the era in which the saga-literature was composed, in the ninth and tenth centuries, about events that took place in the sixth and early seventh centuries, during the heroic age itself. The Welsh had been cut off from their fellow countrymen in the North of Britain and in Cornwall. Only in a few pockets of rugged landscape, like ‘North Wales’ and Cumberland could the ‘Cymry’ (compatriots) be found. The sense of exile must have been further aggravated by the reappearance of Roman missionaries, in the shape of St Augustine of Canterbury, telling them that their traditional Christianity was out of step with the rest of Christendom, and demanding that they should abandon their hatred of the Anglo-Saxons and join with him in converting them. The Welsh ‘saints’ told him that they preferred the idea of the English roasting in hell forevermore!
From this point in time, the geographical centre of gravity also shifted steadily southwards and eastwards: from Mercia to Wessex and from Wessex to Normandy. With it went the Celtic influence on both Church and State as the Celts were driven more and more into the western promontories and peninsulas of Europe by the predominant Rhine-Rhone cultural axis. They were more and more in a state of siege, less and less able to move freely towards imaginative creation. The saga-literature they produced is saturated with feeling for the past. A good deal of it is lamentation of one kind or another. Sometimes it is personal, either for the death of a loved one or, as in Llywarch’s famous complaint of old age, for the speaker’s own changed state. Perhaps even more typical, however, is the lament for a ruined house that the loved one has died defending. Here the loss is by no means merely personal. Cynddylan’s Hall was the tribal centre; its overthrow represents the ruin of an entire society. In the saga of Heledd, the sister of Cynddylan, the lord of Pengwern (Shrewsbury), the English are invading the good land of Powys. They have killed Cynddylan and destroyed his home. In her Elegy on Cynddylan (the poet has composed them for the mouth of the saga’s heroine), Heledd is lamenting over the ruins.
Stand out, maids, and look on the land of Cynddylan; the court of Pengwern ia ablaze; alas for the young who long for their brothers!
Cynddylan the bright buttress of the borderland, wearing a chain, stubborn in battle, he defended Trenn, his father’s town. …
How sad it is to my heart to lay the white flesh in the black coffin, Cynddylan the leader of a hundred hosts.
Heledd has seen all her brothers killed in an unavailing defence of the townships of Powys against the English invader; she has reason to blame their destruction on herself: By my accursed tongue, they are slain! In the original Welsh, these are superb, tragic images, according to Conran, though perhaps somewhat lost even in his translation, here rendered into verse:
Stafell Gynddylan ys twywyll heno,
Heb dán, heb wely;
Wylaf wers, tawaf wedy.
(Dark is Cynddylan’s hall tonight,
With no fire, no bed;
I weep awhile, then am silent.)
Heledd’s laments are at once heart-rending and fiercely controlled, and many of the englynion on the hall of Cynddylan, the Eagle of Pengwern, the Eagle of Eli (the River Meheli in Montgomeryshire), the chapels of Bassa (Eglwysau Basa, or Basschurch) and the White Town, have the tone of great Welsh poetry. They are of a profoundly dramatic and emotional nature, but were part of a body of saga whose more direct narrative was presented in prose. Our knowledge of these sagas is unsure, for all we have are the fragments that were preserved. We must reconstruct the content of the vanished prose from the preserved verses:
The hall of Cynddylan is dark tonight, without fire, without light; longing for you comes over me.
The hall of Cynddylan, its vault is dark after the bright company; alas for him who does not do the good which falls to him!
Hall of Cynddylan, you have become shapeless, your shield is in the grave; while he lived you were not mended with hurdles.
The hall of Cynddylan is loveless tonight, after him who owned it; ah, Death, why does it spare me? …
The hall of Cynddylan, it pierces me to see it, without roof, without fire; my lord dead, myself alive …
They are enshrined in high dramatic utterance, not the merely ruminative mode of elegy. And as the elegy continues, the lamentation is raised, seemingly, not so much for one man’s death as for the ending of a way of life:
The chapels of Bassa are his resting-place tonight, his last welcome, the pillar of battle, the heart of the men of Argoed …
The chapels of Bassa have lost their rank after their destruction by the English of Cynddylan and Elfan of Powys …
The white town in the breast of the wood, this is its symbol ever – blood on the surface of its grass.
The White town in the valley, glad is the kite at the bloodshed of battle; its people have perished …
After my brothers from the lands of the Severn round the banks of the Dwyryw, woe is me, God! that I am alive …
I have looked out on a lovely land from the gravemound of Gorwynnion; long is the sun’s course – longer are my memories …
The theme, in common with the other sagas of Llywerch Hen, is that of the intertwining of both private and tribal disaster, where the facts of history are interpreted as the workings of fate and the nemesis of human pride. We leave Heledd, ‘the Proud Maiden’ and bereft Princess of Powys in her thin cloak, driving her solitary cow over the mountain pasture. In the soil that moulded her brothers, they now moulder, but she must go on living. Likewise, the Welsh went on living behind the Dyke, and the ninth to the eleventh centuries saw various attempts to create a wider unity within Wales itself, with varying degrees of success, as from time to time powerful leaders emerged: Rhodri Mawr, for instance (844-878) and Hywel Dda, his grandson, who brought together the various areas he had consolidated under the Law of Hywel Dda (the Good). But these two and a half centuries are almost without any surviving poetry. They were also punctuated by long periods of chaos, partly the result of continual Viking raids around the coasts and up the river valleys.

The early decades of the eleventh century were troubled times when usurpers like Llywelyn ap Seisyll (1018-1023) seized power. With his son Gruffudd ap Llywelyn, the whole of Wales came under a single ruling family for the first time. On the eve of the Norman conquest, Harold Godwinson defeated Gruffudd ap Llewelyn, the king of Gwynedd. With Gruffudd’s death in 1063, Wales was disunited once more, but Harold, on succeeding Edward the Confessor on the English throne, was unable to take advantage of this weakness, as he had to put all his efforts into the defence of his own crown against the claims of William of Normandy. During the last decades of the eleventh century, Welsh independence grew more and more precarious. For many years prior to the Conquest, Anglo-Saxon kings had claimed lordship over Wales and this loose relationship had been widely accepted by the Welsh princes; Earl Harold’s devastating campaign of 1063 had forcibly reminded the Welsh of the military strength of their English neighbours. As king of England, William I inherited this claim to Wales but, faced with problems in England and Normandy for some years after his victory at Hastings, he had little inclination to involve himself directly in Wales.
(to be continued…)
Posted June 29, 2018 by AngloMagyarMedia in Anglo-Saxons, Archaeology, Assimilation, Britain, British history, Britons, Celtic, Celts, Christian Faith, Christianity, Church, Civilization, clannishness, Colonisation, Commemoration, Conquest, Dark Ages, Empire, English Language, Ethnic cleansing, Footpaths, History, Humanities, Immigration, Imperialism, Integration, Leisure, Literature, Medieval, Mercia, Mythology, Narrative, Nationality, Old English, Recreation, Remembrance, Renaissance, Romans, Saxons, south Wales, Uncategorized, Wales, Warfare, Welsh language, West Midlands
Tagged with Aethelbald, Archenfield, Badon Hill, Bards, Basingwerk, Basschurch, Bath, Black Mountains, Border, Borderlands, Breconshire, Bridge Sollers, Brycheiniog, Brythonic, Buttington, Cambrian, Canterbury, Caradoc, Cascob, Celtic tribes, Cenwulf, Chepstow, Chirk, Christianity, Cirencester, Clun, Clwyd, Clwydians, Cornwall, Cumberland, Cumbria, Cymraeg, Cymry, Cynddylan, David, destiny, Deva (Chester), Dunseate, Earth, Edward the Confessor, englynion, Ergyng, Evenjobb, Faith, Forden, Gloucester, Glyndwr, Gododdin, Gruffudd ap Llywelyn, gwelau, Gwent, Harold Godwinson, Harpton, Heledd, heptarchy, Herefordshire, Highbury, hill forts, History, Holywell, Hywel Dda, Isca (Caerleon), Knighton, Leighton, Llanymynych, Llwybr Clawdd Offa, Llywarch Hen, Llywelyn ap Seisyll, Mabinogion, Machynlleth, Maesbury, Monmouthshire, Monnow, Montgomeryshire, National Parks, Normandy, Northumbria, Offa, Offa's Dyke, Oswestry, Penda, Pengwern, Poetry, Powys, Prestatyn, religion, Rheged, Rhodri Mawr, Rhuddlan, River Dee, River Llawen, River Meheli, River Wye, Ruabon, Salop, Sedbury Cliffs, Severn, Shrewsbury, society, Strathclyde, Tamworth, Trenn, Tutshill, tynged, Walleas, Wars of the Roses, Wat's Dyke, Welshpool, Wessex, William of Normandy, Wye Valley, Y Trallwng
 I was just twelve years old when the Apollo 11 lunar module landed on the moon. I remember the event very clearly, being allowed to stay up to watch on our small, black and white television. The whole event was in black and white for everyone on earth, as colour television transmissions did not begin until the following year when we went round to a friend’s house to watch the Football World Cup via satellite from Mexico.
I was just twelve years old when the Apollo 11 lunar module landed on the moon. I remember the event very clearly, being allowed to stay up to watch on our small, black and white television. The whole event was in black and white for everyone on earth, as colour television transmissions did not begin until the following year when we went round to a friend’s house to watch the Football World Cup via satellite from Mexico. Looking back over those fifty years, it’s interesting to see how much of popular culture on both sides of the Atlantic has been influenced by that event, and the subsequent two Apollo landings of the seventies. Before 1969, most classical compositions and popular song lyrics referenced the moon and the stars in the romantic terms of ‘moonlight’ and ‘Stardust’, even Sinatra’s ‘Fly me to the Moon’. These metaphors continued afterwards, but they were joined by a growing genre of songs about ‘rocketmen’ and space and time exploration which had begun in the early sixties with TV series like ‘Fireball XL-5’, ‘Dr Who’ and ‘Star Trek’.
Looking back over those fifty years, it’s interesting to see how much of popular culture on both sides of the Atlantic has been influenced by that event, and the subsequent two Apollo landings of the seventies. Before 1969, most classical compositions and popular song lyrics referenced the moon and the stars in the romantic terms of ‘moonlight’ and ‘Stardust’, even Sinatra’s ‘Fly me to the Moon’. These metaphors continued afterwards, but they were joined by a growing genre of songs about ‘rocketmen’ and space and time exploration which had begun in the early sixties with TV series like ‘Fireball XL-5’, ‘Dr Who’ and ‘Star Trek’. My Christian friends and I, having already seen the musical Lonesome Stone in Birmingham, made the trek across the country to discover more of this genre. Local fears concerning the festival in the weeks running up to it proved to be unfounded, but the festival didn’t return to the venue. We, on the other hand, were excited and enthused by what we saw and heard.
My Christian friends and I, having already seen the musical Lonesome Stone in Birmingham, made the trek across the country to discover more of this genre. Local fears concerning the festival in the weeks running up to it proved to be unfounded, but the festival didn’t return to the venue. We, on the other hand, were excited and enthused by what we saw and heard. Its early popularity in the USA was partly the result of its promotion by Dr Will Houghton, president of the Moody Bible Institute in Chicago (pictured right), who used it frequently both in the services he took and on his radio broadcasts on WMBI. George Beverly Shea, first as a singer on the station’s early morning programme, Hymns from the Chapel, and then as the lead singer at Graham’s rallies, also helped to popularise the hymn across America.
Its early popularity in the USA was partly the result of its promotion by Dr Will Houghton, president of the Moody Bible Institute in Chicago (pictured right), who used it frequently both in the services he took and on his radio broadcasts on WMBI. George Beverly Shea, first as a singer on the station’s early morning programme, Hymns from the Chapel, and then as the lead singer at Graham’s rallies, also helped to popularise the hymn across America. The Servant King is one of many worship songs written by Graham Kendrick (born 1950), the son of a Baptist pastor, M. D. Kendrick. Graham Kendrick (pictured right, performing in 2019) began his songwriting career in the late 1960s when he underwent a profound religious experience at teacher-training college. This set him off on his itinerant ministry as a musician, hymn-writer and worship-leader. After working in full-time evangelism for Youth for Christ, with which I had been involved in Birmingham, in 1984 he decided to focus all his energies on congregational worship music. He has also become closely associated with the Ichthus Fellowship, one of the largest and most dynamic of the new house churches to emerge from the charismatic revival.
The Servant King is one of many worship songs written by Graham Kendrick (born 1950), the son of a Baptist pastor, M. D. Kendrick. Graham Kendrick (pictured right, performing in 2019) began his songwriting career in the late 1960s when he underwent a profound religious experience at teacher-training college. This set him off on his itinerant ministry as a musician, hymn-writer and worship-leader. After working in full-time evangelism for Youth for Christ, with which I had been involved in Birmingham, in 1984 he decided to focus all his energies on congregational worship music. He has also become closely associated with the Ichthus Fellowship, one of the largest and most dynamic of the new house churches to emerge from the charismatic revival.


































 Here we have a pointer to one reason, at least, why Paul set such store by his mission to the Gentiles. The church was the consummation of a long, divinely directed, history. It is a theme to which he returns in the long and intricate discourse in Romans (9-11). The new, supra-national Israel was constituted solely on the basis of ‘belonging to Christ’, and no longer on racial descent or attachment to a particular legal system. Paul wrote: you are all one person in Christ Jesus (Gal. 3: 28). The expression ‘in Christ’ is one which recurs with remarkable frequency throughout Paul’s letters. The reality of the doctrine for which it stands was present in the church from the beginning in the two rites of baptism and the ‘breaking of bread’. It was through baptism that a person was incorporated into the community of Christ’s followers. In its suggestive ritual, in which the convert was ‘buried’ by immersion in water, and came out cleansed and renewed, Paul saw a symbolic re-enactment of the death and resurrection of Christ:
Here we have a pointer to one reason, at least, why Paul set such store by his mission to the Gentiles. The church was the consummation of a long, divinely directed, history. It is a theme to which he returns in the long and intricate discourse in Romans (9-11). The new, supra-national Israel was constituted solely on the basis of ‘belonging to Christ’, and no longer on racial descent or attachment to a particular legal system. Paul wrote: you are all one person in Christ Jesus (Gal. 3: 28). The expression ‘in Christ’ is one which recurs with remarkable frequency throughout Paul’s letters. The reality of the doctrine for which it stands was present in the church from the beginning in the two rites of baptism and the ‘breaking of bread’. It was through baptism that a person was incorporated into the community of Christ’s followers. In its suggestive ritual, in which the convert was ‘buried’ by immersion in water, and came out cleansed and renewed, Paul saw a symbolic re-enactment of the death and resurrection of Christ:








































 Good-hearted Barnabas (pictured in a recent film portrayal by Franco Nero, right) was not the sort to jump instinctively to a negative response, to reach for familiar prejudices just because something was new. He could see the transformed lives and transparent faith of the Gentile believers which were the work of divine grace, reaching out in generous love to people of every background and origin.
Good-hearted Barnabas (pictured in a recent film portrayal by Franco Nero, right) was not the sort to jump instinctively to a negative response, to reach for familiar prejudices just because something was new. He could see the transformed lives and transparent faith of the Gentile believers which were the work of divine grace, reaching out in generous love to people of every background and origin. The pair was then sent to Jerusalem with a gift of money for the Jerusalem believers, who were suffering from their decade-long persecution by the authorities and struggling to stay alive at a time of widespread famine in AD 46-47. Paul’s own retrospective account of the visit (Gal. 2: 1-10) ends with the Jerusalem leaders admonishing him to go on “remembering the poor.”
The pair was then sent to Jerusalem with a gift of money for the Jerusalem believers, who were suffering from their decade-long persecution by the authorities and struggling to stay alive at a time of widespread famine in AD 46-47. Paul’s own retrospective account of the visit (Gal. 2: 1-10) ends with the Jerusalem leaders admonishing him to go on “remembering the poor.”


 Paul’s response was to quote Isaiah 49: I have set you for a light to the nations so that you can be salvation-bringers to the end of the earth. This delighted the non-Jews who had heard his message: they were free to belong to God’s ancient people. But this, in turn, strengthened Jewish reaction, producing an altogether more serious turn of events.
Paul’s response was to quote Isaiah 49: I have set you for a light to the nations so that you can be salvation-bringers to the end of the earth. This delighted the non-Jews who had heard his message: they were free to belong to God’s ancient people. But this, in turn, strengthened Jewish reaction, producing an altogether more serious turn of events.
 This principle, to the Jew first, and also to the Greek (Rom. 1: 16; 2: 9 f.) was the principle that guided Paul’s ministry and expressed many times in his letters. In his letter to the Romans, he provided a theological justification for it (Rom. 11: 1-27). The outcome of this tour was the foundation of several communities, largely Gentile in membership, and the unleashing of Jewish hostility to Paul’s mission which was to follow him wherever he went, and to finally bring his active career to an end. When Paul and Barnabas found themselves facing people in remote highlands of ancient Anatolia with a strange language and religion, they became overnight heroes when Paul healed a man who had been crippled since birth (depicted above). As the pagan crowd began to worship them, they remonstrated with it that this was not the purpose of their mission. At that point, Jews from the towns where they had already been who had followed them there, told the pagan crowd in the town of Lystra what they thought about the missionaries:
This principle, to the Jew first, and also to the Greek (Rom. 1: 16; 2: 9 f.) was the principle that guided Paul’s ministry and expressed many times in his letters. In his letter to the Romans, he provided a theological justification for it (Rom. 11: 1-27). The outcome of this tour was the foundation of several communities, largely Gentile in membership, and the unleashing of Jewish hostility to Paul’s mission which was to follow him wherever he went, and to finally bring his active career to an end. When Paul and Barnabas found themselves facing people in remote highlands of ancient Anatolia with a strange language and religion, they became overnight heroes when Paul healed a man who had been crippled since birth (depicted above). As the pagan crowd began to worship them, they remonstrated with it that this was not the purpose of their mission. At that point, Jews from the towns where they had already been who had followed them there, told the pagan crowd in the town of Lystra what they thought about the missionaries:























You must be logged in to post a comment.